深入理解系统调用
一.实验要求
- 找一个系统调用,系统调用号为学号最后2位相同的系统调用
- 通过汇编指令触发该系统调用
- 通过gdb跟踪该系统调用的内核处理过程重点阅读分析系统调用入口的保存现场、恢复现场和系统调用返回,以及重点关注系统调用过程中内核堆
- 栈状态的变化
二.实验环境搭建
1.安装开发工具
sudo apt install build-essential
sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU
sudo apt install libncurses5-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
2.下载内核源码
sudo apt install axel
axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/ linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar cd linux-5.4.34
3.配置内核选项
• make defconfig # Default configuration is based on 'x86_64_defconfig' • make menuconfig • # 打开debug相关选项 • Kernel hacking ---> • Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> • [*] Compile the kernel with debug info • [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging • [*] Kernel debugging • # 关闭KASLR,否则会导致打断点失败 • Processor type and features ----> • [] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR
4.根文件系统的制作
axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2
tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2
cd busybox-1.31.1
make menuconfig
#记得要编译成静态链接,不⽤动态链接库。
Settings --->
[*] Build static binary (no shared libs)
#然后编译安装,默认会安装到源码⽬录下的 _install ⽬录中。
make -j$(nproc) && make install
5.制作根文件系统镜像
mkdir rootfs
cd rootfs
cp ../busybox-1.31.1/_install/* ./ -rf
mkdir dev proc sys home
sudo cp -a /dev/{null,console,tty,tty1,tty2,tty3,tty4} dev/
6. init脚本放到根文件系统目录下
#!/bin/sh
mount -t proc none /proc
mount -t sysfs none /sys
echo "Welcome My OS!"
echo "-------------------"
cd home
/bin/sh
7.输入代码看qemu是否正常启动
#打包成内存根⽂件系统镜像
find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
#测试挂载根⽂件系统,看内核启动完成后是否执⾏init脚本
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz
三、实验过程:
中断分外部中断(硬件中断)和内部中断(软件中断),内部中断⼜ 称为异常(Exception),异常⼜分为故障(fault)和陷阱(trap)。 系统调⽤就是利⽤陷阱(trap)这种软件中断⽅式主动从⽤户态进⼊ 内核态的
从⽤户态进⼊内核态是由中断触发的,可能是硬件中断, 在⽤户态进程执⾏时,硬件中断信号到来,进⼊内核态,就会执⾏这 个中断对应的中断服务例程。也可能是⽤户态程序执⾏过程中,调⽤ 了⼀个系统调⽤,陷⼊了内核态,叫作陷阱(trap)(系统调⽤是特 殊的中断)
本次实验是通过系统提供的软件中断,实现系统调用
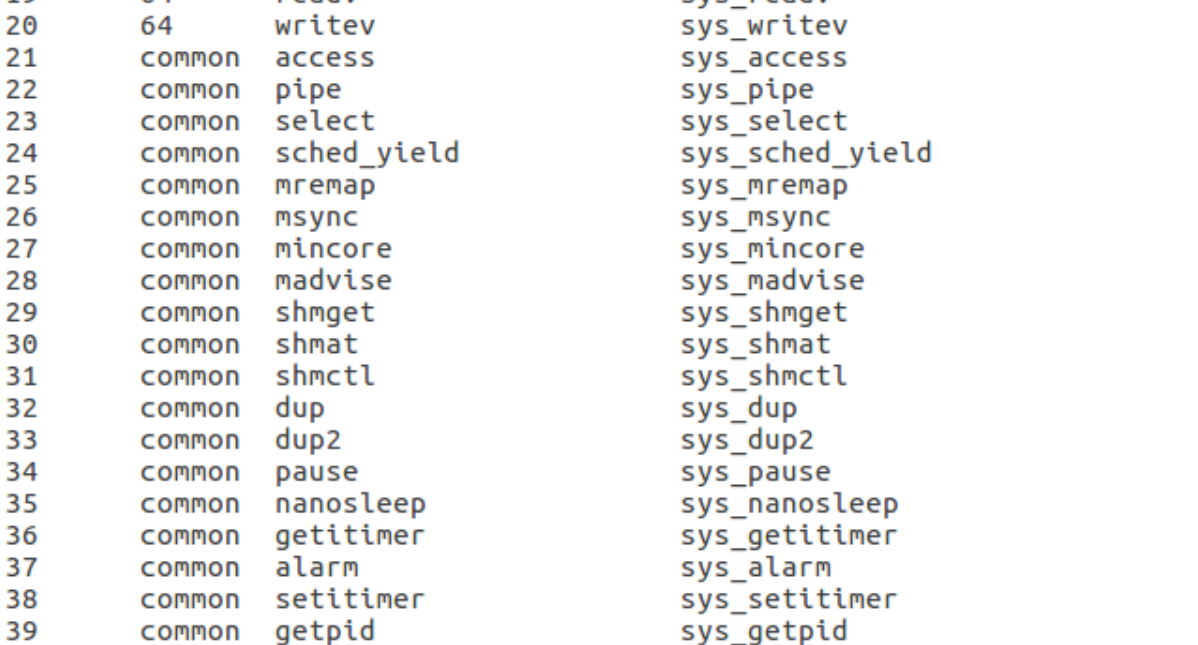
1、通过在arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl中查看linux提供的系统调用,选择以自己学号为结尾的33来实现系统调用
2、编写test_dup2.c程序,调用32号系统调用
int main()
{
asm volatile(
"movl $0x20,%eax\n\t" //使⽤EAX传递系统调⽤号33
"syscall\n\t" //触发系统调⽤
);
return 0;
}
3、使用gcc静态编译,并重新打包
gcc -o test_dup test_dup.c -static
find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
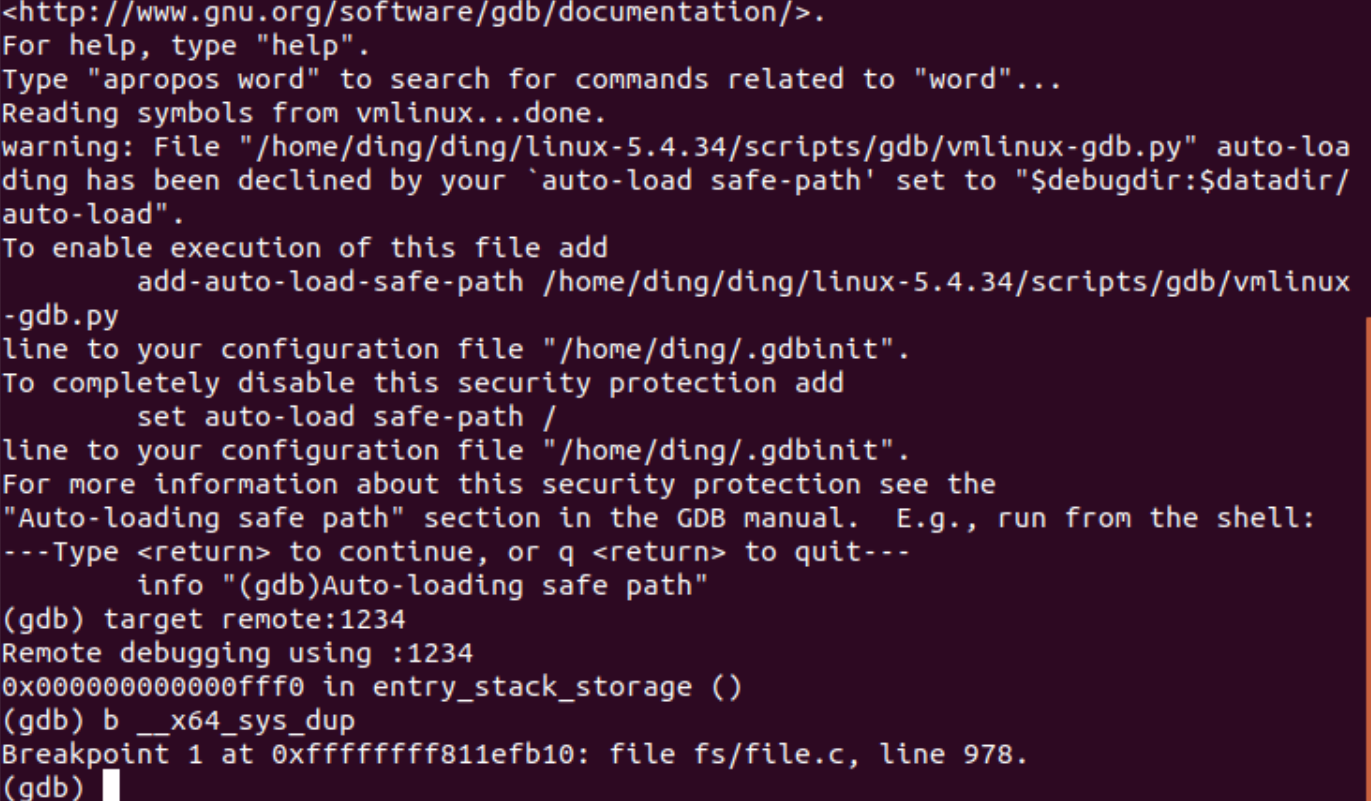
4、进行gdb调试
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s -nographic -append "console=ttyS0"
#开启新的terminal
cd linux-5.4.34
gdb vmlinux
target remote:1234
#设置断点
b __x64_sys_dup
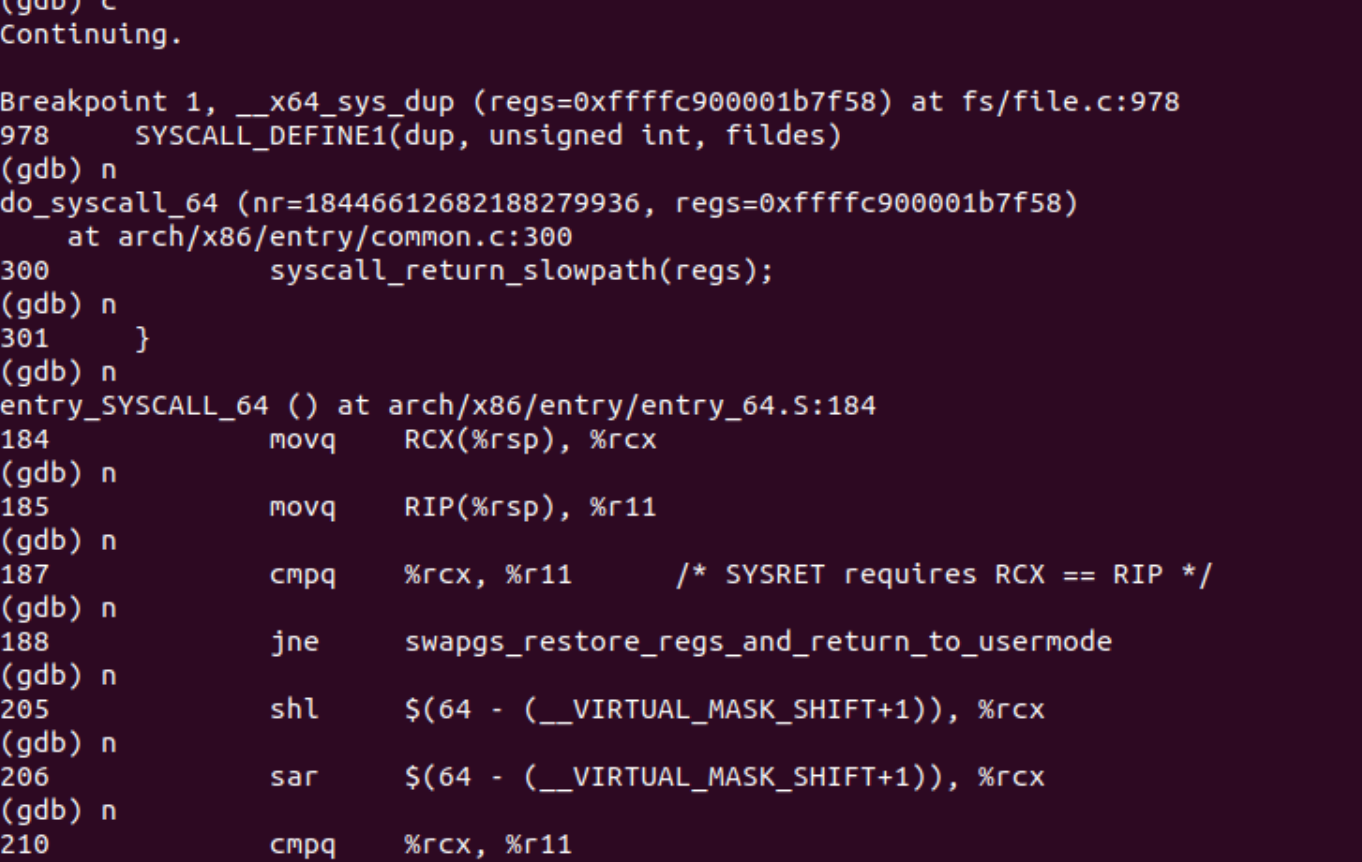
5、通过命令c来继续运行,通过n来实现gdb单步调试
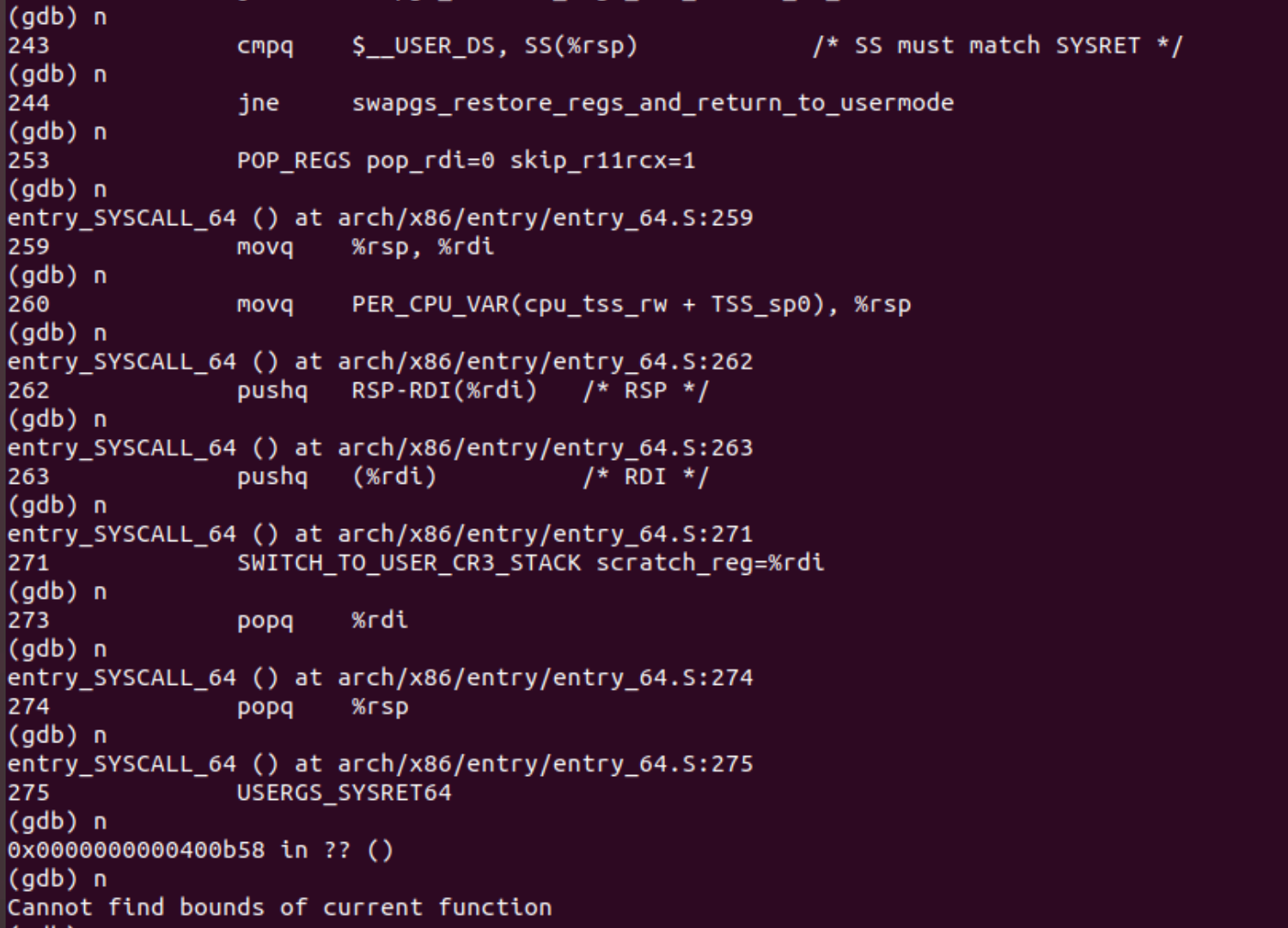
6、通过bt可观察当前堆栈信息
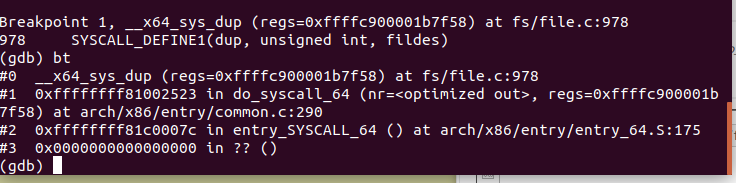
四、总结:
linux的系统调用过程:
用户程序------>C库(即API):INT 0x80 ----->system_call------->系统调用服务例程-------->内核程序
其中INT 0X80是cpu将一些关键寄存器压栈,然后内核保护现场,系统调用内核函数处理完成后恢复现场
system_call是借助CPU内部的MSR寄存器来查找系统调⽤处理⼊⼝,可以快速切换CPU的指令指针(eip/rip)到系统调⽤处理⼊⼝,但本质上还是中断处理的思路,压栈关键寄存器、保存现场、恢复现场,最后系统调⽤返回。
系统调用的作用如下:
(1) 它为用户空间提供了一种统一的硬件的抽象接口。
(2)系统调用保证了系统的稳定和安全。作为硬件设备和应用程序之间的中间人,内核能够基于权限和其它一些规则对须要进行的訪问进行裁决。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号