springboot/springcloud中异步注解@Async的使用并且接收返回的结果
一、在启动类添加@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication @EnableAsync public class AccountApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(AccountApplication.class,args); } }
二、在方法上添加@Async
@Service public class UserService { @Async public synchronized String getUser() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":*用户服务被调用"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); return "这里是用户服务端!"; } }
三、Controller层
@Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping("/u") public String userInfo() { String user = userService.getUser(); return user; }
四、测试结果
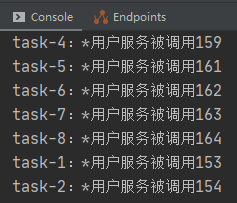
会发现异步调用没问题,但是,Controller拿不到这个异步方法返回的值,为null,浏览器页面空白,如何能异步调用又能拿到返回值呢?
五、获取结果
异步它离不开线程,得到线程有三种方法,继承Thread和实现Runnable都是没有返回值的,Callable+Future可以得到返回值,Future是干啥的呢?翻源码查看介绍如下:
* A {@code Future} represents the result of an asynchronous * computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is * complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of * the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method * {@code get} when the computation has completed, blocking if * necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the * {@code cancel} method. Additional methods are provided to * determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a * computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled. * If you would like to use a {@code Future} for the sake * of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can * declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and * return {@code null} as a result of the underlying task.
大致意思是说Future表示异步的计算结果,它提供了一些方法去检查计算是否完成,并且等待计算完成,然后接收计算的结果,并且计算完成后结果只能用get方法接收到......
看到这里我们就大致明白它怎么接收返回值的了,怎么样使用到上面异步方法中得到结果呢,直接new?但它是个接口,里面一堆方法得重写,而且并没有提供方法让我们把返回结果放进去,那怎么用呢?可以查看它的实现类(IDEA快捷键:ctrl+alt+b)发现有个ListenableFuture实现了它,但是ListenableFuture也没有提供解决的办法,继续查看ListenableFuture的实现类可以发现AsyncResult实现了它并且自带有构造器,于是乎,把异步方法的返回值放进去返回,并且用Future的get方法在Controller层接收岂不美哉,在这里又想到又是继承又是实现的绕这么大圈,何不自己写个带构造器的类并且实现Future呢,后来想想还是算了,人家都提供好了还自己写,闲得蛋疼,直接用人家提供的AsyncResult类解决,于是乎,上面Service中的异步方法就变成了这样:
@Service public class UserService { @Async //用Future<>类型返回 public Future<String> getAsycUser() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":异步用户服务被调用2"); //结果放进带构造器的Future子类AsyncResult返回 return new AsyncResult<>("这里是异步用户服务端-2!"); } }
Controller中用Future提供的get接收:
@RequestMapping("/asycu")
public String getAsycUser() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//调用异步方法返回类型为Future<>
Future<String> future = userService.getAsycUser();
//get方法得到返回的结果
return future.get();
}
测试结果:
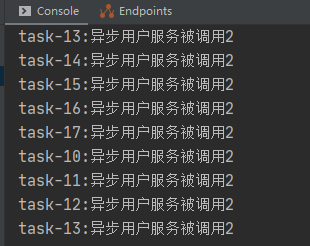
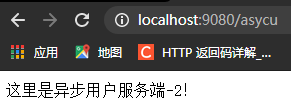
可以发现成功实现了异步并且得到了返回值,而且里面的线程数由8个增加到了了17个,此接口不光在同一个微服务中适用,在别的微服务中远程调用也同样管用。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号