字典序算法
一个全排列可看做一个字符串,字符串可有前缀、后缀。
生成给定全排列的下一个排列.所谓一个的下一个就是这一个与下一个之间没有其他的。这就要求这一个与下一个有尽可能长的共同前缀,也即变化限制在尽可能短的后缀上。
[例]839647521是1--9的排列。1—9的排列最前面的是123456789,最后面的987654321,从右向左扫描若都是增的,就到了987654321,也就没有下一个了。否则找出第一次出现下降的位置。
就是找变化最小的。
例子:
【例】 如何得到346987521的下一个
1,从尾部往前找第一个P(i-1) < P(i)的位置
3 4 6 <- 9 <- 8 <- 7 <- 5 <- 2 <- 1
最终找到6是第一个变小的数字,记录下6的位置i-1
2,从i位置往后找到最后一个大于6的数
3 4 6 -> 9 -> 8 -> 7 5 2 1
最终找到7的位置,记录位置为m
3,交换位置i-1和m的值
3 4 7 9 8 6 5 2 1
4,倒序i位置后的所有数据
3 4 7 1 2 5 6 8 9
则347125689为346987521的下一个排列
代码如下:
private static void PermutationList()
{
int fromIndex, endIndex, changeIndex;
Sort(0, length - 1);
do
{
// 输出一种全排列
Output();
fromIndex = endIndex = length - 1;
// 向前查找第一个变小的元素
while (fromIndex > 0 && words[fromIndex] < words[fromIndex - 1]) --fromIndex;//有重复字符的情况改为words[fromIndex] <= words[fromIndex - 1]
changeIndex = fromIndex;
if (fromIndex == 0) break;
// 向后查找最后一个大于words[fromIndex-1]的元素
while (changeIndex + 1 < length && words[changeIndex + 1] > words[fromIndex - 1]) ++changeIndex;
Swap(fromIndex - 1, changeIndex); // 交换两个值
InvertArray(fromIndex, endIndex); // 对后面的所有值进行反向处理
} while (true);
}
递归算法:
固定第一个字符,然后依次将后面的字符串与前面的交换,那么排列的个数就是除了第一个字符以外,其他字符的排列个数+1。也就是固定一个字符串之后,之后再将问题变小,只需求出后面子串的排列个数就可以得出结果。
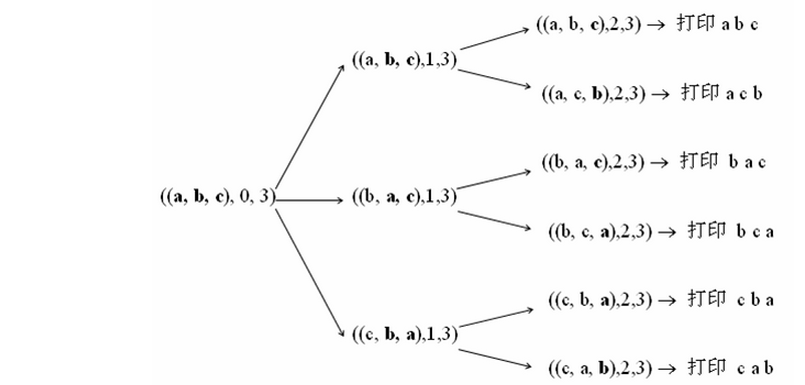
递归的出口,就是只剩一个字符的时候,递归的循环过程,就是从每个子串的第二个字符开始依次与第一个字符交换,然后继续处理子串。
代码如下:
public static void main (String[] args){ Solution p = new Solution(); System.out.println(p.Permutation("abc").toString()); } public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) { List <String> res = new ArrayList(); if (str != null&& str.length() > 0 ){ per(str.toCharArray(),0,res); Collections.sort(res); } return (ArrayList)res; } public void per(char[] ch, int i,List<String> res){ if ( i == ch.length-1){ String val =String.valueOf(ch); if (!res.contains(val))//判断是否重复,重复则不加入 res.add(val); } else{for (int j = i ;j<ch.length;j++){ swap(ch,i,j); per(ch,i+1,res); swap(ch,i,j); }}} public void swap(char[] cs, int i, int j) { char temp = cs[i]; cs[i] = cs[j]; cs[j] = temp; }
参考自:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxjchen/p/3932949.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/pmars/archive/2013/12/04/3458289.html


