单链表的生成方法(C++)及单链表遍历一次中值查找
方法一:从前面插入
前面这两种方法仅供参考,主要使用后面的方法(头结点作为链表的一部分)
LinkList *s, *L;
int i;
L = new LinkList();
L->next = nullptr;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LinkList();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = L->next; //每次都在L后面插入一个节点
L->next = s;
}
对应的完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
typedef struct LNode
{
int data;
struct LNode* next;
}LinkList;
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n);
void DispList(LinkList* L);
void DestoryList(LinkList* L);
int main()
{
int n;
LinkList* head = nullptr;
std::cin >> n;
head = CreateList(head, n);
DispList(head);
DestoryList(head);
return 0;
}
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n)
{
LinkList* s;
int i;
L = new LinkList();
L->next = nullptr;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LinkList();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = L->next;
L->next = s;
}
return L;
}
void DispList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList* p = L->next;
std::cout << "The list is as following:\n";
while (p != nullptr)
{
std::cout << p->data << ' ';
p = p->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void DestoryList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList *pre = L, *p = L->next;
while (p != nullptr)
{
delete pre;
pre = p;
p = p->next;
}
delete pre;
}
/*void DestoryList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList *p = L;
while (p != nullptr)
{
L = L->next;
delete p;
p = L;
}
}*/
运行结果如下:
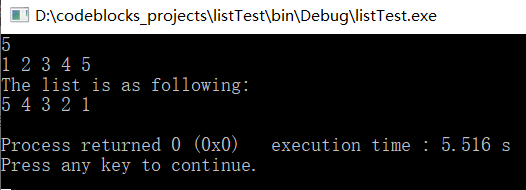
方法二:从后面插入
LinkList *head,*p,*tail;
int n,i;
head = new LinkList();
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
std::cin >> n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p = new LinkList();
std::cin >> p->data;
p->next =NULL;
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
}
对应的完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
typedef struct LNode
{
int data;
struct LNode* next;
}LinkList;
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n);
void DispList(LinkList* L);
void DestoryList(LinkList* L);
int main()
{
int n;
LinkList* head = nullptr;
std::cin >> n;
head = CreateList(head, n);
DispList(head);
DestoryList(head);
return 0;
}
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n)
{
LinkList *s, *tail;
int i;
L = new LinkList();
L->next = nullptr;
tail = L;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LinkList();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = nullptr;
tail->next = s;
tail = s;
}
return L;
}
void DispList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList* p = L->next;
std::cout << "The list is as following:\n";
while (p != nullptr)
{
std::cout << p->data << ' ';
p = p->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void DestoryList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList *pre = L, *p = L->next;
while (p != nullptr)
{
delete pre;
pre = p;
p = p->next;
}
delete pre;
}
运行结果如下:
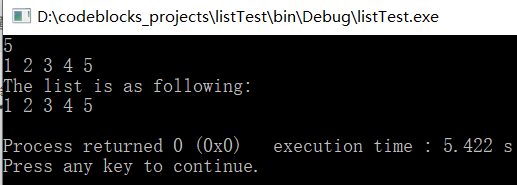
前面介绍的两种创建链表的方法是把链表头独立于链表之外创建的,接下来介绍一种将链表头作为链表一部分创建的方法
#include <iostream>
struct LNode
{
int data;
LNode* next;
};
LNode* CreateList(int n);
void DispList(LNode* L);
void DestoryList(LNode* L);
int main()
{
int n;
std::cin >> n;
LNode* head = CreateList(n);
DispList(head);
DestoryList(head);
return 0;
}
LNode* CreateList(int n)
{
LNode* s;
int i;
LNode* Lhead = new LNode();
Lhead->next = nullptr;
LNode* tail = Lhead; //从这里开始,到后面的for循环结束,是为了链表的连接
std::cin >> Lhead->data;
for (i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LNode();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = nullptr;
tail->next = s;
tail = s;
}
return Lhead;
}
void DispList(LNode* L)
{
LNode* p = L; //和前面方法的区别在于,本代码是从链表头开始打印
std::cout << "The list is as following:\n";
while (p != nullptr)
{
std::cout << p->data << ' ';
L = L->next;//这两行代码可以改写成p = p->next;但下面的DestroyList中的却不行,因为p被释放了
p = L;//p->next就不确定了
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void DestoryList(LNode* L)
{
LNode* p = L;
while (p != nullptr)
{
L = L->next;
delete p;
p = L;
}
}
结果如下:
关于从前面插入方法的修改代码:
LNode* CreateList(int n)
{
LNode* s;
int i;
LNode* Lhead = new LNode();
Lhead->next = nullptr;
//LNode* tail = Lhead; //从这里开始,到后面的for循环结束,是为了链表的连接
std::cin >> Lhead->data;
for (i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LNode();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = Lhead;//把新的结点插入到头结点前面,作为新的头结点
Lhead = s;
//tail = s;
}
return Lhead;
}
单链表遍历一次中值查找
代码如下:(主要是考虑链表为奇数及偶数项这两种情况)
#include <iostream>
typedef struct LNode
{
int data;
struct LNode* next;
}LinkList;
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n);
int findMidNode(LinkList* L,LinkList* &q);
void DispList(LinkList* L);
void DestoryList(LinkList* L);
int main()
{
int n, res;
LinkList *head = nullptr, *t = nullptr;
std::cin >> n;
head = CreateList(head, n);
DispList(head);
res = findMidNode(head, t);
if (res)
std::cout << t->data << ' ' << t->next->data << std::endl;
else
std::cout << t->data << std::endl;
DestoryList(head);
return 0;
}
LinkList* CreateList(LinkList* L, int n)
{
LinkList *s, *tail;
int i;
L = new LinkList();
L->next = nullptr;
tail = L;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
s = new LinkList();
std::cin >> s->data;
s->next = nullptr;
tail->next = s;
tail = s;
}
return L;
}
int findMidNode(LinkList* L,LinkList* &q)
{
LinkList* p;
int iseven=0;
p=L;
q=L;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->next)//if(!p->next),p->next->next is illege
{
p=p->next->next;
q=q->next;
}
else
{
p=p->next;
iseven=1;// the length of LinkList is even
}
}
return iseven;
}
void DispList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList* p = L->next;
std::cout << "The list is as following:\n";
while (p != nullptr)
{
std::cout << p->data << ' ';
p = p->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void DestoryList(LinkList* L)
{
LinkList *pre = L, *p = L->next;
while (p != nullptr)
{
delete pre;
pre = p;
p = p->next;
}
delete pre;
}
寻找链表中值的规范代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
struct ListNode
{
int m_Value;
ListNode* p_Next;
};
ListNode* CreateListNode(int value);
void ConnectListNodes(ListNode* pCurrent, ListNode* pNext);
void PrintListNode(ListNode* pNode);
void PrintList(ListNode* pHead);
void DestroyList(ListNode* pHead);
int FindMidNode(ListNode* pHead, ListNode* &result);//指针的引用,&符号不能去掉
ListNode* CreateListNode(int value)
{
ListNode* pNode = new ListNode();
pNode->m_Value = value;
pNode->p_Next = nullptr;
return pNode;
}
void ConnectListNodes(ListNode* pCurrent, ListNode* pNext)
{
if (pCurrent == nullptr)
{
printf("Error to connect two nodes.\n");
exit(1);
}
pCurrent->p_Next = pNext;
}
void PrintListNode(ListNode* pNode)
{
if (pNode == nullptr)
{
printf("The node is nullptr\n");
}
else
{
printf("The key in node is %d.\n", pNode->m_Value);
}
}
void PrintList(ListNode* pHead)
{
printf("PrintList starts.\n");
ListNode* pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != nullptr)
{
printf("%d\t", pNode->m_Value);
pNode = pNode->p_Next;
}
printf("\nPrintList ends.\n");
}
void DestroyList(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != nullptr)
{
pHead = pHead->p_Next;
delete pNode;
pNode = pHead;
}
}
int FindMidNode(ListNode* pHead, ListNode* &result)
{
if (pHead == nullptr)
return 2;//链表为空!
ListNode* temp = pHead;
int flag = 0;//是偶数
result = pHead;
while (temp != nullptr)
{
if (temp->p_Next)
{
if (temp->p_Next->p_Next != nullptr)//增加一个最后一步的判断条件
result = result->p_Next;
temp = temp->p_Next->p_Next;
}
else
{
temp = temp->p_Next;
flag = 1;//是奇数
}
}
return flag;
}
void Test(const char* testName, ListNode* pHead)
{
if (testName)
std::cout << testName << " begins :\n";
ListNode* res = nullptr;
int results = FindMidNode(pHead, res);
if (results == 0)
{
std::cout << "The middle nodes are: \n";
std::cout << res->m_Value << " and " << res->p_Next->m_Value << std::endl;
}
else if (results == 1)
{
std::cout << "The middle node is: \n";
std::cout << res->m_Value << '\n';
}
else
std::cout << "The list is empty!\n";
}
void Test1()
{
ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1);
ListNode* pNode2 = CreateListNode(2);
ListNode* pNode3 = CreateListNode(3);
ListNode* pNode4 = CreateListNode(4);
ListNode* pNode5 = CreateListNode(5);
ConnectListNodes(pNode1, pNode2);
ConnectListNodes(pNode2, pNode3);
ConnectListNodes(pNode3, pNode4);
ConnectListNodes(pNode4, pNode5);
Test("Test1", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
void Test2()
{
ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1);
ListNode* pNode2 = CreateListNode(2);
ListNode* pNode3 = CreateListNode(3);
ListNode* pNode4 = CreateListNode(4);
ListNode* pNode5 = CreateListNode(5);
ListNode* pNode6 = CreateListNode(6);
ConnectListNodes(pNode1, pNode2);
ConnectListNodes(pNode2, pNode3);
ConnectListNodes(pNode3, pNode4);
ConnectListNodes(pNode4, pNode5);
ConnectListNodes(pNode5, pNode6);
Test("Test2", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
void Test3()
{
Test("Test3", nullptr);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
return 0;
}
在上面代码的基础上修改FindMidNode函数后的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
struct ListNode
{
int m_Value;
ListNode* p_Next;
};
ListNode* CreateListNode(int value);
void ConnectListNodes(ListNode* pCurrent, ListNode* pNext);
void PrintListNode(ListNode* pNode);
void PrintList(ListNode* pHead);
void DestroyList(ListNode* pHead);
ListNode* FindMidNode(ListNode* pHead, int& flag);//引用,&符号不能去掉
ListNode* CreateListNode(int value)
{
ListNode* pNode = new ListNode();
pNode->m_Value = value;
pNode->p_Next = nullptr;
return pNode;
}
void ConnectListNodes(ListNode* pCurrent, ListNode* pNext)
{
if (pCurrent == nullptr)
{
printf("Error to connect two nodes.\n");
exit(1);
}
pCurrent->p_Next = pNext;
}
void PrintListNode(ListNode* pNode)
{
if (pNode == nullptr)
{
printf("The node is nullptr\n");
}
else
{
printf("The key in node is %d.\n", pNode->m_Value);
}
}
void PrintList(ListNode* pHead)
{
printf("PrintList starts.\n");
ListNode* pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != nullptr)
{
printf("%d\t", pNode->m_Value);
pNode = pNode->p_Next;
}
printf("\nPrintList ends.\n");
}
void DestroyList(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != nullptr)
{
pHead = pHead->p_Next;
delete pNode;
pNode = pHead;
}
}
ListNode* FindMidNode(ListNode* pHead, int& flag)
{
if (pHead == nullptr)
return nullptr;//链表为空!
ListNode* temp = pHead;
ListNode* result = pHead;
while (temp != nullptr)
{
if (temp->p_Next)
{
if (temp->p_Next->p_Next != nullptr)//增加一个最后一步的判断条件
result = result->p_Next;
temp = temp->p_Next->p_Next;
}
else
{
temp = temp->p_Next;
flag = 1;//是奇数
}
}
return result;
}
void Test(const char* testName, ListNode* pHead)
{
if (testName)
std::cout << testName << " begins :\n";
int signal = 0;
ListNode* results = FindMidNode(pHead, signal);
if (results == nullptr)
std::cout << "The list is empty!\n";
else
{
if (signal == 0)
{
std::cout << "The middle nodes are: \n";
std::cout << results->m_Value << " and " << results->p_Next->m_Value << std::endl;
}
else if (signal == 1)
{
std::cout << "The middle node is: \n";
std::cout << results->m_Value << '\n';
}
}
}
void Test1()
{
ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1);
ListNode* pNode2 = CreateListNode(2);
ListNode* pNode3 = CreateListNode(3);
ListNode* pNode4 = CreateListNode(4);
ListNode* pNode5 = CreateListNode(5);
ConnectListNodes(pNode1, pNode2);
ConnectListNodes(pNode2, pNode3);
ConnectListNodes(pNode3, pNode4);
ConnectListNodes(pNode4, pNode5);
Test("Test1", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
void Test2()
{
ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1);
ListNode* pNode2 = CreateListNode(2);
ListNode* pNode3 = CreateListNode(3);
ListNode* pNode4 = CreateListNode(4);
ListNode* pNode5 = CreateListNode(5);
ListNode* pNode6 = CreateListNode(6);
ConnectListNodes(pNode1, pNode2);
ConnectListNodes(pNode2, pNode3);
ConnectListNodes(pNode3, pNode4);
ConnectListNodes(pNode4, pNode5);
ConnectListNodes(pNode5, pNode6);
Test("Test2", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
void Test3()
{
Test("Test3", nullptr);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
return 0;
}
【华为OD机试真题】可以转到CSDN相关专栏订阅学习:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45541762/article/details/129903356



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号