标准IO函数
#include <stdio.h>
FILE *fopen(const char *path, const char *mode);
The fopen() function opens the file whose name is the string pointed to by path and associates a stream with it.
int fclose(FILE *fp);
打开标准I/O流的mode参数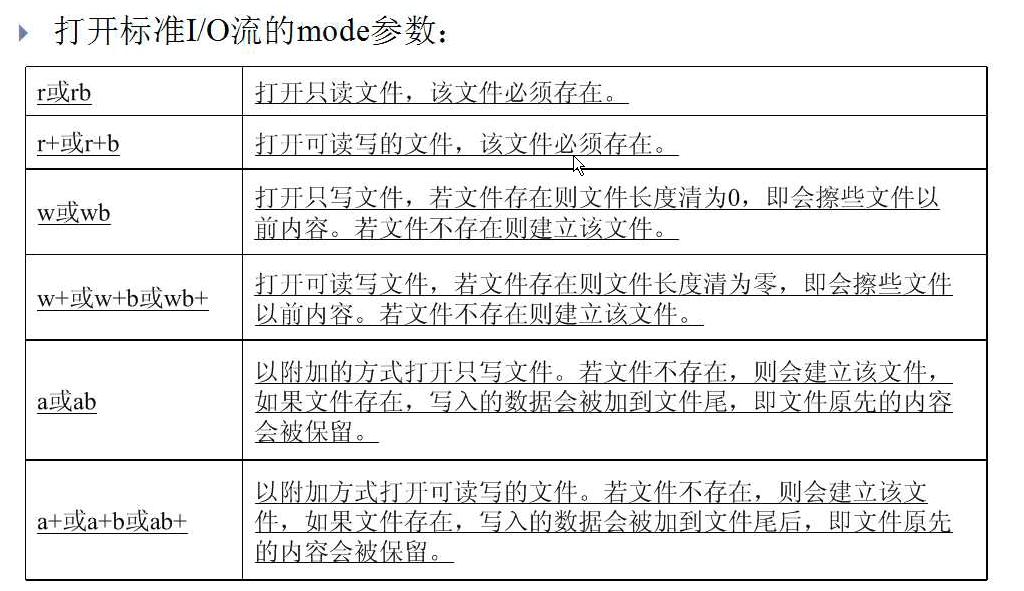

SYNOPSIS
#include <stdio.h>
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
DESCRIPTION
The function fread() reads nmemb elements of data, each size bytes
long, from the stream pointed to by stream, storing them at the loca‐
tion given by ptr.
The function fwrite() writes nmemb elements of data, each size bytes
long, to the stream pointed to by stream, obtaining them from the loca‐
tion given by ptr.
RETURN VALUE
fread() and fwrite() return the number of items successfully read or
written (i.e., not the number of characters). If an error occurs, or
the end-of-file is reached, the return value is a short item count (or
zero).
#include <stdio.h>
int fgetc(FILE *stream);
char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);
fgetc() reads the next character from stream and returns it as an
unsigned char cast to an int, or EOF on end of file or error.
fgets() reads in at most one less than size characters from stream and
stores them into the buffer pointed to by s. Reading stops after an
EOF or a newline. If a newline is read, it is stored into the buffer.
A terminating null byte ('\0') is stored after the last character in
the buffer.
#include <stdio.h>
int fputc(int c, FILE *stream);
int fputs(const char *s, FILE *stream);
fputc() writes the character c, cast to an unsigned char, to stream.
fputs() writes the string s to stream, without its terminating null
byte ('\0').
#include <stdio.h>
int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence);
The fseek() function sets the file position indicator for the stream
pointed to by stream. The new position, measured in bytes, is obtained
by adding offset bytes to the position specified by whence. If whence
is set to SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR, or SEEK_END, the offset is relative to
the start of the file, the current position indicator, or end-of-file,
respectively. A successful call to the fseek() function clears the
end-of-file indicator for the stream and undoes any effects of the
ungetc(3) function on the same stream.



