C++STL 预定义函数对象和函数适配器
预定义函数对象和函数适配器
预定义函数对象基本概念:标准模板库STL提前定义了很多预定义函数对象,#include <functional> 必须包含。
1使用预定义函数对象:
void main()
{
plus<int> intAdd;
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
int z = intAdd(x, y); //等价于 x + y
cout << z << endl;
plus<string> stringAdd;
string myc = stringAdd("aaa", "bbb");
cout << myc << endl;
vector<string> v1;
v1.push_back("bbb");
v1.push_back("aaa");
v1.push_back("ccc");
v1.push_back("zzzz");
}
算术函数对象
预定义的函数对象支持加、减、乘、除、求余和取反。调用的操作符是与type相关联的实例
加法:plus<Types>
plus<string> stringAdd;
sres = stringAdd(sva1,sva2);
减法:minus<Types>
乘法:multiplies<Types>
除法divides<Tpye>
求余:modulus<Tpye>
取反:negate<Type>
negate<int> intNegate;
ires = intNegate(ires);
Ires= UnaryFunc(negate<int>(),Ival1);
关系函数对象
等于equal_to<Tpye>
equal_to<string> stringEqual;
sres = stringEqual(sval1,sval2);
不等于not_equal_to<Type>
大于 greater<Type>
大于等于greater_equal<Type>
小于 less<Type>
小于等于less_equal<Type>
void main()
{
vector<string> v1;
v1.push_back("bbb");
v1.push_back("aaa");
v1.push_back("ccc");
v1.push_back("zzzz");
v1.push_back("ccc");
string s1 = "ccc";
//int num = count_if(v1.begin(),v1.end(), equal_to<string>(),s1);
int num = count_if(v1.begin(),v1.end(),bind2nd(equal_to<string>(), s1));//bind2nd函数适配器
cout << num << endl;
}
逻辑函数对象
逻辑与 logical_and<Type>
logical_and<int> indAnd;
ires = intAnd(ival1,ival2);
dres=BinaryFunc( logical_and<double>(),dval1,dval2);
逻辑或logical_or<Type>
逻辑非logical_not<Type>
logical_not<int> IntNot;
Ires = IntNot(ival1);
Dres=UnaryFunc( logical_not<double>,dval1);
函数适配器

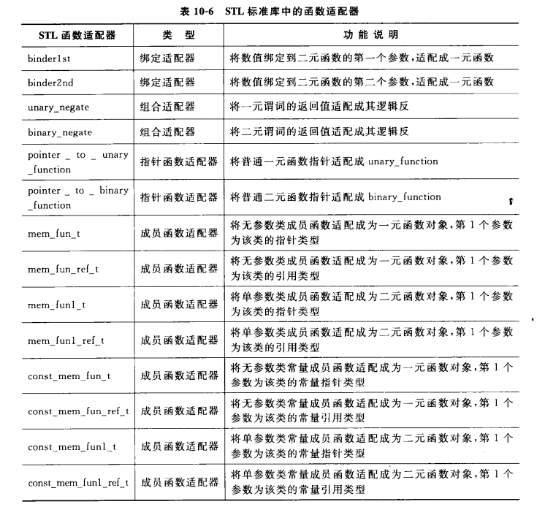


常用函数函数适配器
1绑定器(binder): binder通过把二元函数对象的一个实参绑定到一个特殊的值上,将其转换成一元函数对象。C++标准库提供两种预定义的binder适配器:bind1st和bind2nd,前者把值绑定到二元函数对象的第一个实参上,后者绑定在第二个实参上。
2取反器(negator) : negator是一个将函数对象的值翻转的函数适配器。标准库提供两个预定义的ngeator适配器:not1翻转一元预定义函数对象的真值,而not2翻转二元谓词函数的真值。
常用函数适配器列表如下:
bind1st(op, value)
bind2nd(op, value)
not1(op)
not2(op)
class IsGreat
{
public:
IsGreat(int i)
{
m_num = i;
}
bool operator()(int &num)
{
if (num > m_num)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected:
private:
int m_num;
};
void main()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i+1);
}
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it!=v1.end(); it ++)
{
cout << *it << " " ;
}
int num1 = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);
cout << "num1:" << num1 << endl;
//通过谓词求大于2的个数
int num2 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), IsGreat(2));
cout << "num2:" << num2 << endl;
//通过预定义函数对象求大于2的个数 greater<int>() 有2个参数
// param > 2
int num3 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(greater<int>(), 2 ) );
cout << "num3:" << num3 << endl;
//取模 能被2整除的数 求奇数
int num4 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(modulus <int>(), 2 ) );
cout << "奇数num4:" << num4 << endl;
int num5 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), not1( bind2nd(modulus <int>(), 2 ) ) );
cout << "偶数num5:" << num5 << endl;
return ;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号