从0到1了解babel背后的原理
概要
Babel 是一个工具链,主要用于将采用 ECMAScript 2015+ 语法编写的代码转换为向后兼容的 JavaScript 语法,以便能够运行在当前和旧版本的浏览器或其他环境中。本文主要抽丝剥茧深入了解babel内部的工作机制,而非对配置项的解释说明。
抽象语法树(AST)
要了解Babel的工作原理,那首先需要了解抽象语法树这一概念,想必了解过vue源码的同学应该接触过这一概念。而Babel插件正是基于抽象语法树进行工作的,把我们编写的代码在编译阶段解析成抽象语法树(AST),然后经过一系列的遍历和转换,再使转换后的抽象语法树生成为常规的js代码。下面这幅图可以表示Babel的工作流程:
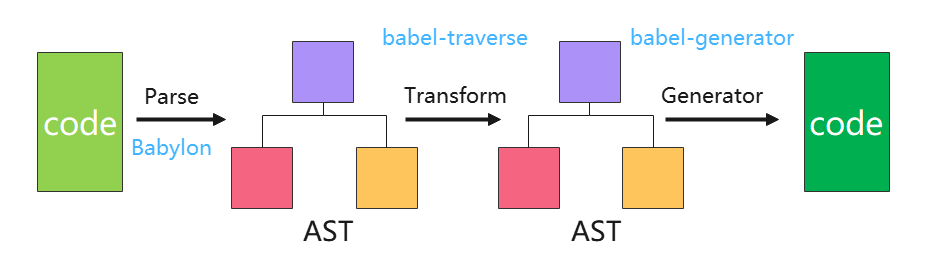
代码解析成AST的目的就是方便计算机更好地理解我们的代码。这里我们先写一段代码:
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
add(1, 2);
然后将代码解析成抽象语法树(在线工具),表示成JSON形式如下:
{
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 52,
"body": [
{
"type": "FunctionDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 40,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 9,
"end": 12,
"name": "add"
},
"expression": false,
"generator": false,
"params": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 13,
"end": 14,
"name": "x"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 16,
"end": 17,
"name": "y"
}
],
"body": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"start": 19,
"end": 40,
"body": [
{
"type": "ReturnStatement",
"start": 25,
"end": 38,
"argument": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"start": 32,
"end": 37,
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 32,
"end": 33,
"name": "x"
},
"operator": "+",
"right": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 36,
"end": 37,
"name": "y"
}
}
}
]
}
},
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"start": 42,
"end": 52,
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"start": 42,
"end": 51,
"callee": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 42,
"end": 45,
"name": "add"
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Literal",
"start": 46,
"end": 47,
"value": 1,
"raw": "1"
},
{
"type": "Literal",
"start": 49,
"end": 50,
"value": 2,
"raw": "2"
}
]
}
}
],
"sourceType": "module"
}
这里你会发现抽象语法树中不同层级有着相似的结构,比如:
{
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 52,
"body": [...]
}
{
"type": "FunctionDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 40,
"id": {...},
"body": {...}
}
{
"type": "BlockStatement",
"start": 19,
"end": 40,
"body": [...]
}
像这样的结构叫做节点(Node)。一个AST是由多个或单个这样的节点组成,节点内部可以有多个这样的子节点,构成一颗语法树,这样就可以描述用于静态分析的程序语法。
节点中的type字段表示节点的类型,比如上述AST中的"Program"、"FunctionDeclaration"、"ExpressionStatement"等等,当然每种节点类型会有一些附加的属性用于进一步描述该节点类型。
Babel的工作流程
上面那幅图已经描述了Babel的工作流程,下面我们再详细描述一下。Babel 的三个主要处理步骤分别是: 解析(parse),转换(transform),生成(generate)。
- 解析
将代码解析成抽象语法树(AST),每个js引擎(比如Chrome浏览器中的V8引擎)都有自己的AST解析器,而Babel是通过Babylon实现的。在解析过程中有两个阶段:词法分析和语法分析,词法分析阶段把字符串形式的代码转换为令牌(tokens)流,令牌类似于AST中节点;而语法分析阶段则会把一个令牌流转换成 AST的形式,同时这个阶段会把令牌中的信息转换成AST的表述结构。 - 转换
在这个阶段,Babel接受得到AST并通过babel-traverse对其进行深度优先遍历,在此过程中对节点进行添加、更新及移除操作。这部分也是Babel插件介入工作的部分。 - 生成
将经过转换的AST通过babel-generator再转换成js代码,过程就是深度优先遍历整个AST,然后构建可以表示转换后代码的字符串。
为了了解Babel在遍历时处理AST的具体过程,我们还需要了解下面几个重要知识点。
Visitor
当Babel处理一个节点时,是以访问者的形式获取节点信息,并进行相关操作,这种方式是通过一个visitor对象来完成的,在visitor对象中定义了对于各种节点的访问函数,这样就可以针对不同的节点做出不同的处理。我们编写的Babel插件其实也是通过定义一个实例化visitor对象处理一系列的AST节点来完成我们对代码的修改操作。举个栗子:
我们想要处理代码中用来加载模块的import命令语句
import { Ajax } from '../lib/utils';
那么我们的Babel插件就需要定义这样的一个visitor对象:
visitor: {
Program: {
enter(path, state) {
console.log('start processing this module...');
},
exit(path, state) {
console.log('end processing this module!');
}
},
ImportDeclaration (path, state) {
console.log('processing ImportDeclaration...');
// do something
}
}
当把这个插件用于遍历中时,每当处理到一个import语句,即ImportDeclaration节点时,都会自动调用ImportDeclaration()方法,这个方法中定义了处理import语句的具体操作。ImportDeclaration()都是在进入ImportDeclaration节点时调用的,我们也可以让插件在退出节点时调用方法进行处理。
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration: {
enter(path, state) {
console.log('start processing ImportDeclaration...');
// do something
},
exit(path, state) {
console.log('end processing ImportDeclaration!');
// do something
}
},
}
当进入ImportDeclaration节点时调用enter()方法,退出ImportDeclaration节点时调用exit()方法。上面的Program节点(Program节点可以通俗地解释为一个模块节点)也是一样的道理。值得注意的是,AST的遍历采用深度优先遍历,所以上述import代码块的AST遍历的过程如下:
─ Program.enter()
─ ImportDeclaration.enter()
─ ImportDeclaration.exit()
─ Program.exit()
所以当创建访问者时你实际上有两次机会来访问一个节点。
ps: 有关AST中各种节点类型的定义可以查看Babylon手册
Path
从上面的visitor对象中,可以看到每次访问节点方法时,都会传入一个path参数,这个path参数中包含了节点的信息以及节点和所在的位置,以供对特定节点进行操作。具体来说Path 是表示两个节点之间连接的对象。这个对象不仅包含了当前节点的信息,也有当前节点的父节点的信息,同时也包含了添加、更新、移动和删除节点有关的其他很多方法。具体地,Path对象包含的属性和方法主要如下:
── 属性
- node 当前节点
- parent 父节点
- parentPath 父path
- scope 作用域
- context 上下文
- ...
── 方法
- get 当前节点
- findParent 向父节点搜寻节点
- getSibling 获取兄弟节点
- replaceWith 用AST节点替换该节点
- replaceWithMultiple 用多个AST节点替换该节点
- insertBefore 在节点前插入节点
- insertAfter 在节点后插入节点
- remove 删除节点
- ...
具体的可以查看babel-traverse。
这里我们继续上面的例子,看看path参数的node属性包含哪些信息:
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration (path, state) {
console.log(path.node);
// do something
}
}
打印结果如下:
Node {
type: 'ImportDeclaration',
start: 5,
end: 41,
loc:
SourceLocation {
start: Position { line: 2, column: 4 },
end: Position { line: 2, column: 40 } },
specifiers:
[ Node {
type: 'ImportSpecifier',
start: 14,
end: 18,
loc: [SourceLocation],
imported: [Node],
local: [Node] } ],
source:
Node {
type: 'StringLiteral',
start: 26,
end: 40,
loc: SourceLocation { start: [Position], end: [Position] },
extra: { rawValue: '../lib/utils', raw: '\'../lib/utils\'' },
value: '../lib/utils'
}
}
可以发现除了type、start、end、loc这些常规字段,ImportDeclaration节点还有specifiers和source这两个特殊字段,specifiers表示import导入的变量组成的节点数组,source表示导出模块的来源节点。这里再说一下specifier中的imported和local字段,imported表示从导出模块导出的变量,local表示导入后当前模块的变量,还是有点费解,我们把import命令语句修改一下:
import { Ajax as ajax } from '../lib/utils';
然后继续打印specifiers第一个元素的local和imported字段:
Node {
type: 'Identifier',
start: 22,
end: 26,
loc:
SourceLocation {
start: Position { line: 2, column: 21 },
end: Position { line: 2, column: 25 },
identifierName: 'ajax' },
name: 'ajax' }
Node {
type: 'Identifier',
start: 14,
end: 18,
loc:
SourceLocation {
start: Position { line: 2, column: 13 },
end: Position { line: 2, column: 17 },
identifierName: 'Ajax' },
name: 'Ajax' }
这样就很明显了。如果不使用as关键字,那么imported和local就是表示同一个变量的节点了。
State
State是visitor对象中每次访问节点方法时传入的第二个参数。如果看Babel手册里的解释,可能还是有点困惑,简单来说,state就是一系列状态的集合,包含诸如当前plugin的信息、plugin传入的配置参数信息,甚至当前节点的path信息也能获取到,当然也可以把babel插件处理过程中的自定义状态存储到state对象中。
Scopes(作用域)
这里的作用域其实跟js说的作用域是一个道理,也就是说babel在处理AST时也需要考虑作用域的问题,比如函数内外的同名变量需要区分开来,这里直接拿Babel手册里的一个例子解释一下。考虑下列代码:
function square(n) {
return n * n;
}
我们来写一个把 n 重命名为 x 的visitor。
visitor: {
FunctionDeclaration(path) {
const param = path.node.params[0];
paramName = param.name;
param.name = "x";
},
Identifier(path) {
if (path.node.name === paramName) {
path.node.name = "x";
}
}
}
对上面的例子代码这段访问者代码也许能工作,但它很容易被打破:
function square(n) {
return n * n;
}
var n = 1;
上面的visitor会把函数square外的n变量替换成x,这显然不是我们期望的。更好的处理方式是使用递归,把一个访问者放进另外一个访问者里面。
visitor: {
FunctionDeclaration(path) {
const updateParamNameVisitor = {
Identifier(path) {
if (path.node.name === this.paramName) {
path.node.name = "x";
}
}
};
const param = path.node.params[0];
paramName = param.name;
param.name = "x";
path.traverse(updateParamNameVisitor, { paramName });
},
}
到这里我们已经对Babel工作流程大概有了一些了解,下面我们再说一下Babel的工具集。
Babel的工具集
Babel 实际上是一组模块的集合,在上面介绍Babel工作流程中也都提到过。
Babylon
“Babylon 是 Babel的解析器。最初是从Acorn项目fork出来的。Acorn非常快,易于使用,并且针对非标准特性(以及那些未来的标准特性) 设计了一个基于插件的架构。”。这里直接引用了手册里的说明,可以说Babylon定义了把代码解析成AST的一套规范。引用一个例子:
import * as babylon from "babylon";
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
babylon.parse(code);
// Node {
// type: "File",
// start: 0,
// end: 38,
// loc: SourceLocation {...},
// program: Node {...},
// comments: [],
// tokens: [...]
// }
babel-traverse
babel-traverse用于维护操作AST的状态,定义了更新、添加和移除节点的操作方法。之前也说到,path参数里面的属性和方法都是在babel-traverse里面定义的。这里还是引用一个例子,将babel-traverse和Babylon一起使用来遍历和更新节点:
import * as babylon from "babylon";
import traverse from "babel-traverse";
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
if (
path.node.type === "Identifier" &&
path.node.name === "n"
) {
path.node.name = "x";
}
}
});
babel-types
babel-types是一个强大的用于处理AST节点的工具库,“它包含了构造、验证以及变换AST节点的方法。该工具库包含考虑周到的工具方法,对编写处理AST逻辑非常有用。”这个工具库的具体的API可以参考Babel官网
这里我们还是用import命令来演示一个例子,比如我们要判断import导入是什么类型的导入,这里先写出三种形式的导入:
import { Ajax } from '../lib/utils';
import utils from '../lib/utils';
import * as utils from '../lib/utils';
在AST中用于表示上面导入的三个变量的节点是不同的,分别叫做ImportSpecifier、ImportDefaultSpecifier和ImportNamespaceSpecifier。具体可以参考这里。
如果我们只对导入指定变量的import命令语句做处理,那么我们的babel插件就可以这样写:
function plugin () {
return ({ types }) => ({
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration (path, state) {
const specifiers = path.node.specifiers;
specifiers.forEach((specifier) => {
if (!types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifier) && !types.isImportNamespaceSpecifier(specifier)) {
// do something
}
})
}
}
}
到这里,关于Babel的原理差不多都讲完了,下面我们尝试写一个具体功能的Babel插件。
Babel插件实践
这里我们尝试实现这样一个功能:当使用UI组件库时,我们常常只会用到组件库中的部分组件,就像这样:
import { Select, Pagination } from 'xxx-ui';
但是这样却引入了整个组件库,那么打包的时候也会把整个组件库的代码打包进去,这显然是不太合理的,所以我们希望能够在打包的时候只打包我们需要的组件。
Let's do it!
首先我们需要告诉Babel怎么找到对应组件的路径,也就是说我们需要自定义一个规则告诉Babel根据指定名称加载对应组件,这里我们定义一个方法:
"customSourceFunc": componentName =>(`./xxx-ui/src/components/ui-base/${componentName}/${componentName}`)}
这个方法作为这个插件的配置参数,可以配置到.babelrc(准确来说是.babelrc.js)或者babel-loader里面。 接下来我们需要定义visitor对象,有了之前的铺垫,这里直接上代码:
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration (path, { opts }) {
const specifiers = path.node.specifiers;
const source = path.node.source;
// 判断传入的配置参数是否是数组形式
if (Array.isArray(opts)) {
opts.forEach(opt => {
assert(opt.libraryName, 'libraryName should be provided');
});
if (!opts.find(opt => opt.libraryName === source.value)) return;
} else {
assert(opts.libraryName, 'libraryName should be provided');
if (opts.libraryName !== source.value) return;
}
const opt = Array.isArray(opts) ? opts.find(opt => opt.libraryName === source.value) : opts;
opt.camel2UnderlineComponentName = typeof opt.camel2UnderlineComponentName === 'undefined'
? false
: opt.camel2UnderlineComponentName;
opt.camel2DashComponentName = typeof opt.camel2DashComponentName === 'undefined'
? false
: opt.camel2DashComponentName;
if (!types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifiers[0]) && !types.isImportNamespaceSpecifier(specifiers[0])) {
// 遍历specifiers生成转换后的ImportDeclaration节点数组
const declarations = specifiers.map((specifier) => {
// 转换组件名称
const transformedSourceName = opt.camel2UnderlineComponentName
? camel2Underline(specifier.imported.name)
: opt.camel2DashComponentName
? camel2Dash(specifier.imported.name)
: specifier.imported.name;
// 利用自定义的customSourceFunc生成绝对路径,然后创建新的ImportDeclaration节点
return types.ImportDeclaration([types.ImportDefaultSpecifier(specifier.local)],
types.StringLiteral(opt.customSourceFunc(transformedSourceName)));
});
// 将当前节点替换成新建的ImportDeclaration节点组
path.replaceWithMultiple(declarations);
}
}
}
其中opts表示的就是之前在.babelrc.js或babel-loader中传入的配置参数,代码中的camel2UnderlineComponentName和camel2DashComponentName可以先不考虑,不过从字面上也能猜到是什么功能。这个visitor主要就是遍历模块内所有的ImportDeclaration节点,找出specifier为ImportSpecifier类型的节点,利用传入customSourceFunc得到其绝对路径的导入方式,然后替换原来的ImportDeclaration节点,这样就可以实现组件的按需加载了。
我们来测试一下效果,
const babel = require('babel-core');
const types = require('babel-types');
const plugin = require('./../lib/index.js');
const visitor = plugin({types});
const code = `
import { Select as MySelect, Pagination } from 'xxx-ui';
import * as UI from 'xxx-ui';
`;
const result = babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [
[
visitor,
{
"libraryName": "xxx-ui",
"camel2DashComponentName": true,
"customSourceFunc": componentName =>(`./xxx-ui/src/components/ui-base/${componentName}/${componentName}`)}
}
]
]
});
console.log(result.code);
// import MySelect from './xxx-ui/src/components/ui-base/select/select';
// import Pagination from './xxx-ui/src/components/ui-base/pagination/pagination';
// import * as UI from 'xxx-ui';

 Babel 是一个工具链,主要用于将采用 ECMAScript 2015+ 语法编写的代码转换为向后兼容的 JavaScript 语法,以便能够运行在当前和旧版本的浏览器或其他环境中。本文主要抽丝剥茧深入了解babel内部的工作机制,而非对配置项的解释说明。
Babel 是一个工具链,主要用于将采用 ECMAScript 2015+ 语法编写的代码转换为向后兼容的 JavaScript 语法,以便能够运行在当前和旧版本的浏览器或其他环境中。本文主要抽丝剥茧深入了解babel内部的工作机制,而非对配置项的解释说明。


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)