机器学习聚类算法之DBSCAN
一、概念
DBSCAN是一种基于密度的聚类算法,DBSCAN需要两个参数,一个是以P为中心的邻域半径;另一个是以P为中心的邻域内的最低门限点的数量,即密度。
优点:
1、不需要提前设定分类簇数量,分类结果更合理;
2、可以有效的过滤干扰。
缺点:
1、对高维数据处理效果较差;
2、算法复杂度较高,资源消耗大于K-means。
二、计算
1、默认使用第一个点作为初始中心;
2、通过计算点到中心的欧氏距离和领域半径对比,小于则是邻域点;
3、计算完所有点,统计邻域内点数量,小于于最低门限点数量则为噪声;
4、循环统计各个点的邻域点数,只要一直大于最低门限点数量,则一直向外扩展,直到不再大于。
5、一个簇扩展完成,会从剩下的点中重复上述操作,直到所有点都被遍历。
三、实现
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt cs = ['black', 'blue', 'brown', 'red', 'yellow', 'green'] class NpCluster(object): def __init__(self): self.key = [] self.value = [] def append(self, data): if str(data) in self.key: return self.key.append(str(data)) self.value.append(data) def exist(self, data): if str(data) in self.key: return True return False def __len__(self): return len(self.value) def __iter__(self): self.times = 0 return self def __next__(self): try: ret = self.value[self.times] self.times += 1 return ret except IndexError: raise StopIteration() def create_sample(): np.random.seed(10) # 随机数种子,保证随机数生成的顺序一样 n_dim = 2 num = 100 a = 3 + 5 * np.random.randn(num, n_dim) b = 30 + 5 * np.random.randn(num, n_dim) c = 60 + 10 * np.random.randn(1, n_dim) data_mat = np.concatenate((np.concatenate((a, b)), c)) ay = np.zeros(num) by = np.ones(num) label = np.concatenate((ay, by)) return {'data_mat': list(data_mat), 'label': label} def region_query(dataset, center_point, eps): result = NpCluster() for point in dataset: if np.sqrt(sum(np.power(point - center_point, 2))) <= eps: result.append(point) return result def dbscan(dataset, eps, min_pts): noise = NpCluster() visited = NpCluster() clusters = [] for point in dataset: cluster = NpCluster() if not visited.exist(point): visited.append(point) neighbors = region_query(dataset, point, eps) if len(neighbors) < min_pts: noise.append(point) else: cluster.append(point) expand_cluster(visited, dataset, neighbors, cluster, eps, min_pts) clusters.append(cluster) for data in clusters: print(data.value) plot_data(np.mat(data.value), cs[clusters.index(data)]) if noise.value: plot_data(np.mat(noise.value), 'green') plt.show() def plot_data(samples, color, plot_type='o'): plt.plot(samples[:, 0], samples[:, 1], plot_type, markerfacecolor=color, markersize=14) def expand_cluster(visited, dataset, neighbors, cluster, eps, min_pts): for point in neighbors: if not visited.exist(point): visited.append(point) point_neighbors = region_query(dataset, point, eps) if len(point_neighbors) >= min_pts: for expand_point in point_neighbors: if not neighbors.exist(expand_point): neighbors.append(expand_point) if not cluster.exist(point): cluster.append(point) init_data = create_sample() dbscan(init_data['data_mat'], 10, 3)
聚类结果:
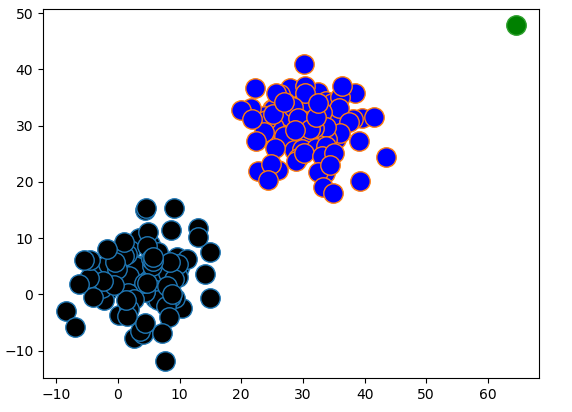
可以看到,点被很好的聚类为两个簇,右上角是噪声。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号