C++ 面经 :哈希/无序哈希,集合/无序集合 Some conclusions about compare map with set / compare unordered_map with unordered_set / compare unordered_ with ordered
1.What is the difference between set vs map in C++ ?
👉stl - C++中的设置与地图有什么区别?- 堆栈溢出 (stackoverflow.com)
- The're fullfilling different purposes, one is a map, one is a set. If you need a map, use the map. If you need a set, use the set. performance and memory are not the relevant differences. 这完全是不同的目的,一个是地图,一个是集合。如果需要地图,请使用地图。如果需要集合,请使用集合。性能和内存不是相关差异。
- You can kind of think of a set as a hash where only the key is used and the value not utilized. 可以将集合视为仅使用键而不使用值的哈希。
- Conceptually, a set is a collection of things, whereas a map is a mapping of keys to values 从概念上讲,集合是事物的集合,而映射是键到值的映射。
- A
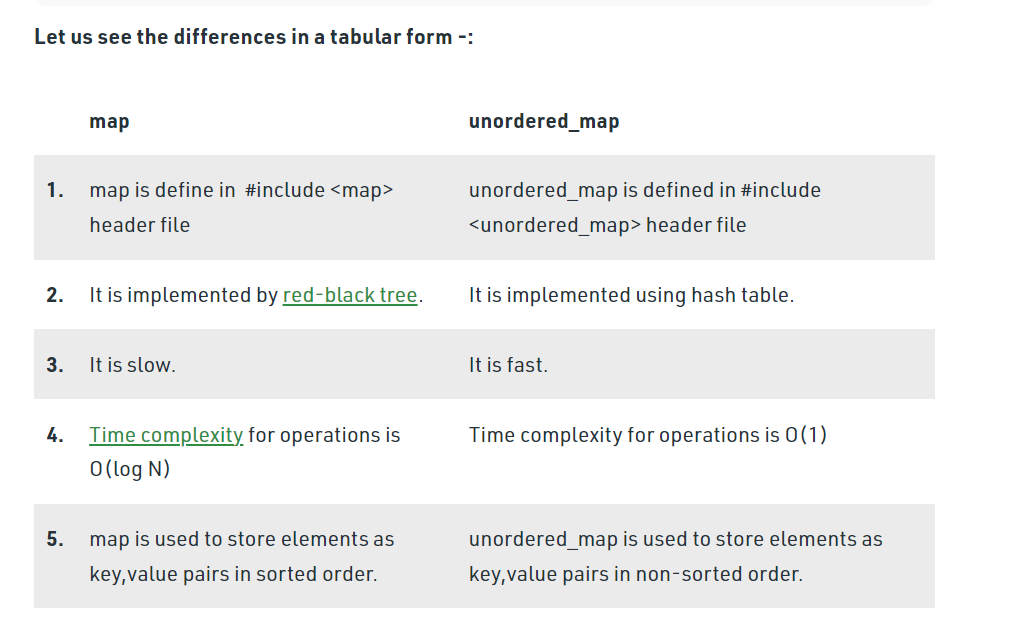
mapstores keys sorted. It maps keys to values. Usually it is implemented as a binary search tree (red-black tree) for keys. Asetis a map where values are irrelevant.unordered_mapandunordered_set(new in C++11) store keys unsorted and use hash table for search.地图存储排序的键。它将键映射到值。通常它被实现为键的二叉搜索树(红黑树)。集合是值无关紧要的映射。unordered_map和unordered_set(C++11 中的新功能)存储未排序的键,并使用哈希表进行搜索。
2.Comparing unordered_map vs unordered_set ?
👉c++ - Comparing unordered_map vs unordered_set - Stack Overflow
- The difference between an unordered_map and an unordered_set is that an unordered_map contains elements only in the form of (key-value) pairs while an unordered_set does not necessarily contain elements in the form of key-value pairs.
- Since an unordered_map has elements in the form of key-value pairs, we use the operator ([]) to extract the corresponding value of a key present in the map. While in an unordered_set, there is no such operator. The searching for an element is done using a find function.
3.Is there any advantage of using map over unordered_map ?
- Don't forget that keeps its elements ordered. If you can't give that up, obviously you can't use .
mapunordered_map
Something else to keep in mind is that generally uses more memory. just has a few house-keeping pointers, and memory for each object. Contrarily, has a big array (these can get quite big in some implementations), and then additional memory for each object. If you need to be memory-aware, should prove better, because it lacks the large array.unordered_mapmapunordered_mapmap
So, if you need pure lookup-retrieval, I'd say is the way to go. But there are always trade-offs, and if you can't afford them, then you can't use it.unordered_map
Just from personal experience, I found an enormous improvement in performance (measured, of course) when using instead of in a main entity look-up table.unordered_mapmap
On the other hand, I found it was much slower at repeatedly inserting and removing elements. It's great for a relatively static collection of elements, but if you're doing tons of insertions and deletions the hashing + bucketing seems to add up. (Note, this was over many iterations.)
Use std::map when
- You need ordered data.
- You would have to print/access the data (in sorted order).
- You need predecessor/successor of elements.
- See advantages of BST over Hash Table for more cases.
Use std::unordered_map when
- You need to keep count of some data (Example – strings) and no ordering is required.
- You need single element access i.e. no traversal.

Benefits of Unordered_map in C++
- The unordered_map has the ability to store data in the form of key-value pairs.
- The insertion, deletion, and the updation operations have O(1) average time complexity, making unordered_map a fast data structure.
- The searching in the unordered_map is also very fast (O(1) average time complexity), which makes it very useful in the real world.
Is unordered_map faster than a map?
- In the best case and the average case scenario, an unordered_map is faster than a map because the best case and the average case time complexities of all the operations in an unordered_map (O(1)) are less than the time complexity for all the operations in a map (O(log n)).
- But in the worst-case scenario, the unordered_map is slower than a map because the worst time complexity of all the operations in an unordered_map (O(n)) is greater than the time complexity for all the operations in a map (O(log n)).
- In the average case, the unordered_map is faster than a map since it uses a hash table, while a map is implemented using a self-balancing binary tree like a Red-Black tree.
Conclusion:
- An unordered_map is a data structure that stores data in the form of key-value pairs.
- The best case and the average case complexity for all the operations in an unordered_map is O(1). While in the worst case, the time complexity for all the operations in an unordered_map is O(n).
- The difference between an unordered_map and an unordered_set is that an unordered_map stores data only in the form of key-value pair while an unordered_set can store data that is not necessarily in the form of key-value pairs (for example, integer, string, etc.).
- The difference between an unordered_map and a map is that the data stored in an unordered_map is completely unordered (i.e., not sorted), while in a map, the data is stored in increasing order of keys of the key-value pairs that are stored in it.
- An unordered_map is implemented using a hash table, while a map is implemented using a self-balancing binary search tree like the Red-Black tree.
Whenever you prefer a tree to a hash table.
For instance, hash tables are "O(n)" at worst case. O(1) is the average case. Trees are "O(log n)" at worst.
4.Why would anyone use set instead of unordered_set?
Unordered sets have to pay for their O(1) average access time in a few ways:
setuses less memory than to store the same number of elements.unordered_set- For a small number of elements, lookups in a might be faster than lookups in an .
setunordered_set - Even though many operations are faster in the average case for , they are often guaranteed to have better worst case complexities for (for example ).
unordered_setsetinsert - That sorts the elements is useful if you want to access them in order.
set - You can lexicographically compare different s with , , and . s are not required to support these operations.
set<<=>>=unordered_set
translate:
无序集合必须以几种方式为其 O(1) 平均访问时间付费:
set使用的内存比存储相同数量的元素少。unordered_set- 对于少量元素,在 a 中查找可能比在 an 中查找更快。
setunordered_set - 尽管许多操作在平均情况下速度更快,但它们通常可以保证具有更好的最坏情况复杂性(例如)。
unordered_setsetinsert - 如果要按顺序访问元素,则对元素进行排序很有用。
set - 您可以按字典顺序比较差异,并且不需要支持这些操作。
set<<=>>=unordered_set
Use set when:
- We need ordered data(distinct elements).
- We would have to print/access the data (in sorted order).
- We need predecessor/successor of elements.
Use unordered_set when:
- We need to keep a set of distinct elements and no ordering is required.
- We need single element access i.e. no traversal.
本文来自博客园,作者:slowlydance2me,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/slowlydance2me/p/16899644.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本