常系数线性差分方程的求解
1. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/f191d2ea102de2bd960588ae.html
2. https://www.zhihu.com/question/25217301
3. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/9716c9f9770bf78a65295431.html
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
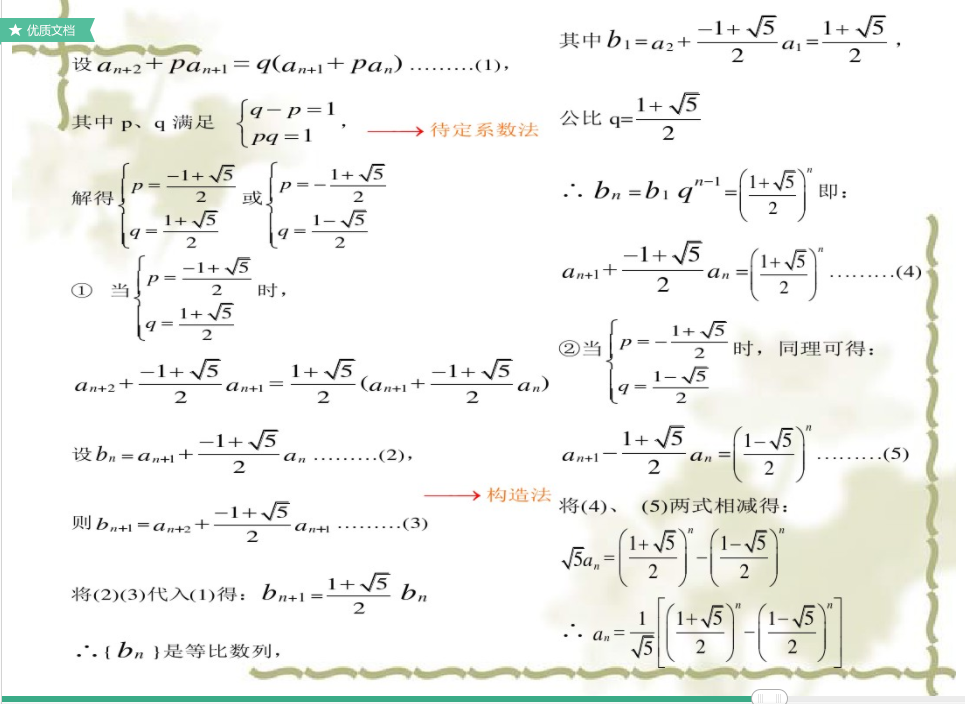
( 这里用 代表斐波那契数列第
项,且约定
)
设有一个矩阵 使得
设 就有
直接令 ,再令
,得到
把 特征分解,就可以求出
的通项式
解特征方程 得到
的特征值
然后得到两个的特征向量
所以
相同的方法可以求形如 递推式的通项公式,
只要让 ,剩下的步骤一模一样
甚至还可以扩展到更高维度的矩阵求形如 的通项公式
当然,前提是 非奇异,且拥有
个线性无关的特征向量
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
解差分方程
求逆Z变换
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/25217301/answer/158753864
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
感谢大家的点赞和评论!在这里统一向各位说声抱歉,我把这个解答称为初等方法确实不够严谨,看似初等的方法里面实际上隐藏了并不初等的概念。确切地说,如果要正确理解下面这个等式
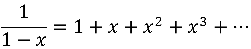
需要一些形式幂级数环的简单知识(包括环的概念,环中可逆元的概念)。
因为考虑的是形式幂级数,在向形式变元代入具体的数之前并不牵涉收敛性问题,也无需使用泰勒展开等工具。因此,我仍然认为这是一个中学生可以接受的解答,再加上生成函数非常有价值,应该介绍给大家。
至于“初等”与“高等”之争,我认为是一件好事,因为大家所熟知的初等数学里,也有很多事情需要借助高等数学的知识才能说清楚,而我们国家的中学数学教材与大学数学教材其实脱节很严重。但状况并不应该如此,中学数学里的内容有一些非常有趣而深刻的背景可以挖掘出来,而不是只教大家做题。最近在对这方面的内容做一个梳理和总结,系列文章
奇葩数学史 - 知乎专栏 新鲜上线,希望大家多提意见!
以下是原答。
------------------分割线-------------------
纯手工初等方法。记斐波那契数列第项为
,则
。
构造一个与有关的幂级数
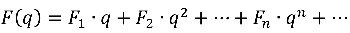
这个函数被称为斐波那契数列的生成函数,因为它的幂级数展开完全决定了 ,展开式中
的系数就是斐波那契数列的第
项。
对于一般数列的生成函数,我们暂且按下不表,先来看看有没有办法求这个特殊的。我们没有别的选择,唯一的条件是
,这个等式应该能够诱导出一个
满足的方程。
确实如此,是
的系数,
和
则分别是
和
的系数,要想让它们匹配在一起,就要想办法让它们对应同一个
。这其实很容易办到,
中
的系数就是
,同理,
中
的系数就是
。
于是,中
的所有高于
的幂次前的系数都变成了
,只剩下了
。从而
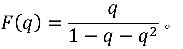
如果你能把 展开成幂级数的形式,就自然求出了斐波那契数列的通项。
现在,让我们回忆一个中学里十分常用的技巧
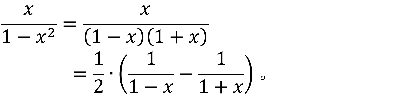
这件事情的本质是将分母中的多项式作因式分解,将分母含有二次项的分式转换成分母只含一次项,而分母只含一次项的分式很容易写成幂级数
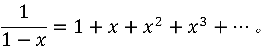
回到 ,我们可以用待定系数法完成上面的过程,设
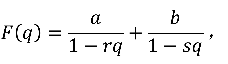
于是
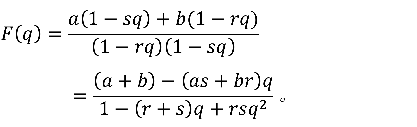
我们得到一个四元方程组
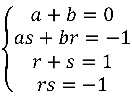
这个方程组的难度只能称为小喽喽级别,凭借后两个方程解出
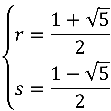
代入到前两个方程中即得 ,
。
所以
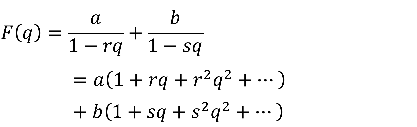
蕴含了斐波那契数列的通项为
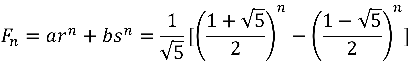
看起来不太像整数,但确实如此。
生成函数是处理数列的常用工具,是离散走向连续的桥梁,很多人们关心的离散信息都复刻在这样一条DNA上。你们一定很奇怪我在定义时用的自变量是
而不是
,事实上我想通过这种方式提醒大家无穷展开的广泛性,当
被某种具有周期性的基本函数替代时,我们就得到了傅立叶展开。作为著名的费马大定理证明核心的谷山-志村-韦伊猜想说的就是某种刻画了椭圆曲线模
点个数信息的生成函数可以与模形式的傅立叶展开对应起来,有机会再跟大家详聊。
以上。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号