ansible服务部署与使用
第1章 ssh+key实现基于密钥连接(ansible使用前提)
说明:
ansible其功能实现基于SSH远程连接服务
使用ansible需要首先实现ssh密钥连接
1.1 部署ssh key
1.1.1 第一个里程碑: 创建密钥对
ssh-keygen
-t 指定密钥类型 rsa1 dsa(常用) ecdsa
语法:
SYNOPSIS
ssh-keygen [-q] [-b bits] -t type [-N new_passphrase] [-C comment]
[-f output_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -p [-P old_passphrase] [-N new_passphrase] [-f keyfile]
ssh-keygen -i [-f input_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -e [-f input_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -y [-f input_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -c [-P passphrase] [-C comment] [-f keyfile]
ssh-keygen -l [-f input_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -B [-f input_keyfile]
ssh-keygen -D pkcs11
ssh-keygen -F hostname [-f known_hosts_file] [-l]
ssh-keygen -H [-f known_hosts_file]
ssh-keygen -R hostname [-f known_hosts_file]
ssh-keygen -r hostname [-f input_keyfile] [-g]
ssh-keygen -G output_file [-v] [-b bits] [-M memory] [-S start_point]
ssh-keygen -T output_file -f input_file [-v] [-a num_trials]
[-W generator]
ssh-keygen [-n] [-D smartcard]
ssh-keygen -s ca_key -I certificate_identity [-h] [-Z principals]
[-O option] [-V validity_interval] [-z serial_number] file ...
ssh-keygen -L [-f input_keyfile]
创建密钥的过程
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-keygen -t dsa Generating public/private dsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_dsa): #私钥创建后保存的路径 Created directory '/root/.ssh'. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #私钥需不需进行加密,设置密码 Enter same passphrase again: #私钥需不需进行加密,再次输入密码确认 Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_dsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 31:4a:4f:9f:97:b0:b6:ca:4c:53:78:70:89:83:5f:16 root@m01 The key's randomart image is: +--[ DSA 1024]----+ | E | | . . o | | o B * | | . = @ + . | | . S B o | | + o | | o . | | + o | | + | +-----------------+
创建出来的文件:
[root@m01 ~]# ll /root/.ssh/ total 8 -rw------- 1 root root 668 Oct 17 18:55 id_dsa #创建出来的私钥 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 598 Oct 17 18:55 id_dsa.pub #创建出来的公钥
1.1.2 第二个里程碑: 分发公钥文件
[root@m01 ~]# man ssh-copy-id ssh-copy-id - install your public key in a remote machine’s autho-rized_keys
注意:密钥分发命令属于openssh-clients软件包
[root@nfs01 ~]# rpm -qf `which ssh-copy-id` openssh-clients-5.3p1-122.el6.x86_64
语法格式
ssh-copy-id [-i [identity_file]] [user@]machine -i 指定要分发的公钥文件以及路径信息 [user@] 以什么用户身份进行分发 machine 将公钥分发到哪台主机上,远程主机IP地址 [root@m01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub root@172.16.1.41 The authenticity of host '172.16.1.41 (172.16.1.41)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is d3:41:bb:0d:43:88:da:a3:2c:e8:36:91:11:c9:e4:9c. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.41' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. root@172.16.1.41's password: Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh 'root@172.16.1.41'", and check in .ssh/authorized_keys to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
1.1.3 第三个里程碑: 基于密钥登陆测试
[root@m01 ~]# ssh 172.16.1.41 Last login: Tue Oct 17 18:38:47 2017 from 10.0.0.1 [root@backup ~]#
基于密钥登陆方式成功↑
[root@m01 ~]# ssh root@172.16.1.41 "hostname -i" 172.16.1.41
不用的登陆到远程主机直接执行命令,返回输出结果↑
说明:
管理主机一旦创建好秘钥对文件,给多个主机分发公钥时,公钥文件相同
1.1.4 ssh服务分发公钥实质执行过程
①. 管理服务器创建私钥和公钥(密钥对)
②. 将公钥文件远程传送复制到被管理服务器相应用户~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub下,并修改.ssh目录权限为700
③. 修改公钥文件文件名称为authorized_keys,授权权限为600
④. 利用ssh服务配置文件的配置参数,进行识别公钥文件authorized_keys
⑤. 进而实现基于密钥远程登录服务器(免密码登录/非交互方式登录)
1.2 默认端口号不是22,如何分发公钥
1.2.1 查询ssh-copy-id命令可以得知这是个脚本文件
[root@m01 ~]# file `which ssh-copy-id ` /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: POSIX shell script text executable
看看脚本内容发现传输方式
[root@m01 ~]# cat `which ssh-copy-id`|grep ssh ssh $1 "exec sh -c 'cd; umask 077; test -d .ssh || mkdir .ssh ; cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys && (test -x /sbin/restorecon && /sbin/restorecon .ssh .ssh/authorized_keys >/dev/null 2>&1 || true)'" || exit 1
说明:
1、切换用户到家目录下,临时设置umask值
2、判断客户端相应用户中有没有.ssh目录,如果没有.ssh 目录就进行创建
3、将管理端公钥文件内容添加到客户端~./ssh/authorized_keys, 默认authorized_keys文件不存在,需要创建,文件权限600
1.2.2 实现非22端口的分发
方法一: 修改脚本内容
ssh -p52113 $1 "exec sh -c 'cd; umask 077; test -d .ssh || mkdir .ssh ; cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys && (test -x /sbin/restorecon && /sbin/restorecon .ssh .ssh/authorized_keys >/dev/null 2>&1 || true)'" || exit 1
说明:根据命令脚本,修改$1传参信息,从而实现根据ssh不同端口传送公钥文件
方法二:将传入的参数上添加上端口信息(推荐)
[root@m01 scripts]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub "-p 52113 znix@172.16.1.250" Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '-p 52113 znix@172.16.1.250'", and check in: .ssh/authorized_keys to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
1.2.3 关于 /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id 脚本中 $1的说明
1.2.3.1 编写脚本shift
[root@m01 scripts]# cat shift.sh #!/bin/bash until [ $# -eq 0 ] do echo $* shift done
测试
[root@m01 scripts]# sh shift.sh 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 5 6 6
说明:
shift命令用于对参数的移动(左移),通常用于在不知道传入参数个数的情况下依次遍历每个参数然后进行相应处理(常见于Linux中各种程序的启动脚本)。
|
1
|
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub "-p 52113 znix@172.16.1.250" |
由于/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id 脚本中前面使用了两个shift 所有原本该为3的参数变为了3的参数变为了1.
if [ "-i" = "$1" ]; then
shift
# check if we have 2 parameters left, if so the first is the new ID file
if [ -n "$2" ]; then
if expr "$1" : ".*\.pub" > /dev/null ; then
ID_FILE="$1"
else
ID_FILE="$1.pub"
fi
shift # and this should leave $1 as the target name
fi
else
1.3 实现自动分发公钥,远程管理多台主机
1.3.1 【预备知识】shell中三种循环
#for 循环
for n in (1..100)
do
xxx
done
#while循环:循环条件为真时,一直循环;为假时,停止循环
while [ture]
do
xxx
done
#until 循环: 循环条件为假时,一直循环;为真时,停止循环
until [ture]
do
xxx
done
1.3.2 实现自动分发公钥,远程管理多台主机的阻碍因素?
01.创建秘钥对需要进行交互
a.需要确认秘钥保存路径
b.需要确认密码信息
02.分发公钥时需要进行交互
a.需要进行确认yes|no
b.第一次分发公钥需要进行密码认证
1.3.3 解决阻碍因素
1.自动保存路径,并且不密码
ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -N "" -q
参数说明:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
-f filename Specifies the filename of the key file. 指定密钥文件保存的路径信息(免交互)-P passphrase Provides the (old) passphrase. 提供一个密码信息-N new_passphrase Provides the new passphrase. -P -N 都是免交互方式指定密码信息-q 安静的 不输出信息,减少信息输出 |
2.解决分发公钥时需要进行的交互
sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub " root@172.16.1.$ip -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no "
参数说明:
|
1
2
|
-o option 选择 (man 手册中可以查到有很多选项)StrictHostKeyChecking=no 对询问的回应(不进行对密钥检查) |
要实现免密码,需要一款软件 sshpass 该软件就是为ssh提供密码使用的
[root@m01 ~]# yum install sshpass -y
注意:密码与 -p之间不能有空格
1.3.4 最终批量分发脚本内容
[root@m01 scripts]# vim ssh-key.sh #!/bin/bash . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions # 创建密钥 \rm ~/.ssh/id_rsa* -f ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -N "" -q # 分发公钥 for ip in 31 41 8 do sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub " root@172.16.1.$ip -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no " &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then action "fenfa 172.16.1.$ip" /bin/true else action "fenfa 172.16.1.$ip" /bin/false fi echo "" done
脚本执行效果:
[root@m01 scripts]# sh ssh-key.sh fenfa 172.16.1.31 [ OK ] fenfa 172.16.1.41 [ OK ] fenfa 172.16.1.8 [ OK ]
说明:
脚本中引用 . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions 函数,可以显示执行结果的判断。
使用if语句进行判断,action 执行相应的动作。true/false
1.3.5 实现基于密钥的批量管理脚本
[root@m01 scripts]# vim piliang_guanli.sh #!/bin/bash CMD=$1 for ip in 8 31 41 do echo ========host 172.16.1.$ip======= ssh root@172.16.1.$ip "$CMD" echo ============END=============== echo "" done
脚本执行效果:
[root@m01 scripts]# sh piliang_guanli.sh date ======172.16.1.8====== Thu Oct 19 16:25:08 CST 2017 =========END============= ======172.16.1.31====== Thu Oct 19 16:25:08 CST 2017 =========END============= ======172.16.1.41====== Thu Oct 19 16:25:08 CST 2017 =========END=============
基于密钥登陆方式,分发的公钥文件会识别用户信息,所以能够实现免密码批量管理。
第2章 ansible软件介绍
- python 语言是运维人员必须会的语言
- ansible 是一个基于python 开发的自动化运维工具
- 其功能实现基于ssh远程连接服务
- ansible 可以实现批量系统配置,批量软件部署,批量文件拷贝,批量运行命令等功能
除了ansible之外,还有saltstack 等批量管理软件
2.1 自动化批量管理方式说明
2.1.1 ssh+key方式的说明
免密码登录验证是单向的,方向从私钥(钥匙) >==> 公钥(锁)
SSH免密码登录基于用户的,最好不要跨不同的用户
SSH连接慢解决;即修改sshd_config配罝文件参数信息
批量分发1000台初始都需要输入一次密码,并且第一次连接要确认(expect/sshpass)
expect批量管理服务器参考 http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com/2561410/1206238
2.1.2 企业级生产场景批量管理-自动化管理方案
①.最简单/最常用/最强大的选择是ssh key+shell/pssh方案,一般中小型企业会用(50-100台以下规模企业)
a.利用ssh key执行命令,并将命令放在脚本里面
b.利用ssh key执行命令,将命令放在脚本里面,并加上相应循环语句或判断语句
②.sina cfengine/puppet较早的批量管理工具;现在基本上没有企业用
③.门户级别比较流行的,puppet批量管理工具(复杂/笨重)
④.saltstack批量管理工具;特点:简单,功能强大(配罝复杂>---赶集网/小米/一些CDN公司 批量管理路线:ssh key-->cfengine-->puppet-->saltstack/ansible
PS:使用ansible软件的前提是ssh key公钥分发充成
2.1.3 如何完成成集群规模架构一键自动化实现(步骤说明)
①.1台服务器先配置好(kickstart,cobbler无人值守安装)。高级实现云计算(按需分配,动态调整)(openstack,kvm)
②.linux基本优化,包括ssh服务(可以自动化实现)。
创建密钥信息(自动化免交互创建)
ssh-keygen -t dsa -P "" -f ~/.ssh/id_dsa >/dev/null 2>&1
进行批量分发密钥(sshpass,expect自动化实现)
⑤.ansible软件安装(可以自动化实现)
⑥.网络服务自动化安装(ansible实现)
(搭建yum仓库,定制rpm包)
2.2 ansible软件特点概述
l 不需要单独安装客户端(no agents),基于系统自带的sshd服务,sshd就相当于ansible的客户端
l 不需要服务端(no sever)
l 需要依靠大量的模块实现批量管理
l 配置文件 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg (前期不用配置)
ansible软件相关参考链接信息
http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_installation.html
http://www.ansible.com.cn/
http://docs.ansible.com/modules_by_category.html
http://www.ansible.cn/docs/
2.2.1 ansible软件中查看模块相关信息方法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -l 列出所有模块信息 [root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -s cron 参看指定模块的帮助
2.3 部署ansible软件
2.3.1 第一个里里程碑:部署ssh+key免密码登录方式
2.3.2 第二个里程碑:被管理端安装ansible相关管理软件
[root@m01 ~]# yum install libselinux-python -y
该软件是用来对selinux进行设置的,确保即使服务器selinux服务开启,依旧能够通过ansible 软件管理。
2.3.3 第三个里程碑:管理端安装ansible软件,配置hosts文件
[root@m01 ~]# yum install ansible -y
软件安装完成,进行修改ansible下的hosts文件,注意文件的路径
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [clsn] 172.16.1.31 172.16.1.41 172.16.1.8
文件信息说明:
1.中括号中的名字代表组名
2.主机(hosts)部分可以使用域名、主机名、IP地址表示;一般此类配置中多使用IP地址;
3.组名下的主机地址就是ansible可以管理的地址
至此ansible 服务就部署完成 ↑
2.4 查看ansible软件相关信息
2.4.1 ansible实践部署地址规划
|
服务器名称 |
网卡eth0 |
网卡eth1 |
用途说明 |
|
m01 |
10.0.0.61 |
172.16.1.61 |
批量管理服务器 |
|
nfs01 |
10.0.0.31 |
172.16.1.31 |
nfs共享储存服务器 |
|
backup |
10.0.0.41 |
172.16.1.41 |
rsync备份服务器 |
|
web01 |
10.0.0.8 |
172.16.1.8 |
web服务器 |
|
说明:无特殊情况,子网掩码为255.255.255.0 |
|||
2.4.2 ansible软件的版本信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible --version ansible 2.3.2.0 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg configured module search path = Default w/o overrides python version = 2.6.6 (r266:84292, Aug 18 2016, 15:13:37) [GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-17)]
2.4.3 软件目前主要会用到的文件
[root@m01 ~]# rpm -ql ansible /etc/ansible/hosts #定义anisble软件可以管理的主机信息 /usr/bin/ansible #ansible执行命令 /usr/bin/ansible-playboot # ansible执行剧本命令
2.4.4 /etc/ansible下的文件
[root@m01 ansible]# ll total 28 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18066 Sep 6 06:38 ansible.cfg #ansible配置文件 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1016 Sep 6 06:38 hosts #定义ansible可以管理的主机信息 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 6 06:38 roles #主要在自动化的时候部署多台主机时使用
2.5 ansible软件的使用/参数
2.5.1 ansible远程批量执行命令
语法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
ansible clsn -a "uptime"ansible clsn -m command -a "uptime"ansible 定义的组/单个ip/域名/all -m command -a "uptime" |
说明:-m 指定使用的模块
-a 指定使用模块中相应的命令参数
命令参数只能是基本命令,并不支持管道操作
all 为hosts文件中的组全部管理
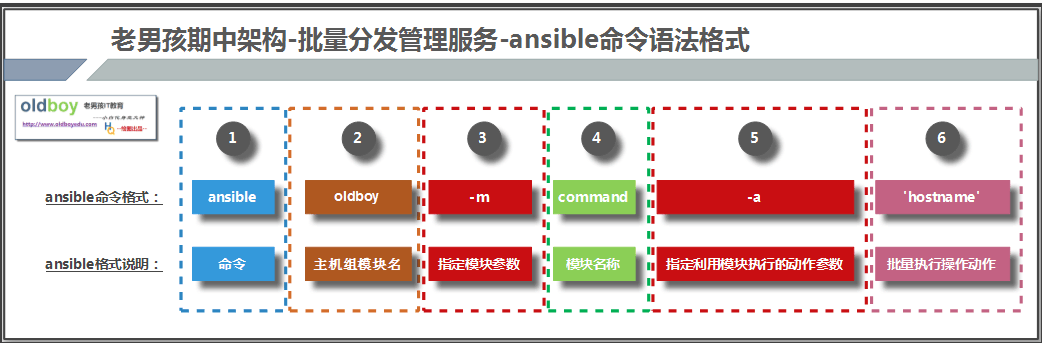
图2-1 ansible命令语法格式示意图
2.5.2 未分发公钥如何实现远程管理主机及指定ansible端口信息
配置hosts文件时配置上密码
vim /etc/ansible/hosts [clsn] 172.16.1.31:52113 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456 172.16.1.41 172.16.1.8
IP:端口 用户 密码
|
1
2
|
[znix]www.znix.top:52113 ansible_ssh_user=znix |
指定端口 用户名
测试修改端口后的结果 使用ping 模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible znix -m ping
www.znix.top | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
2.6 ansible软件常用参数表
|
命令参数 |
参数说明 |
|
-m MODULE_NAME |
-module-name=MODULE_NAME module name to execute (default=command) 相应名称的模块被执行(默认模块为command ); -m后边是模块的名宇 |
|
-a MODULE_ARGS |
-args=MODULE_ARGS module arguments 模块参数信息 -a后面是要执行的命令;也可以写个ip ,针对台机器来执行命令 |
|
-C, -checks |
don't make any changes, instead, try to predict some of the changes that may occurs 不做任何改变;反而,只是尝试预言些可能出现的改变 |
|
-syntax-checks |
perform a syntax check on the playbook, but do not execute ii*> 执行语法检查在剧本上,但是并不执行剧本 |
2.6.1 ansible命令执行结果色彩说明:
绿色:表示没有发生任何改变
红色:执行命令操作出现异常
黄色:执行命令后,对受控主机产生影响,发生了配置改变
第3章 ansible中的模块说明
3.1 ping 模块:测试连通性
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m ping
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
连接正常返回 pong 通过帮助信息可以获得 ↓
通过 ansible-doc -v ping 可以获得该模块的说明
ansible-doc -s file 参看模块的具体信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -v ping Using /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg as config file > PING (/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/ansible/modules/system/ping.py) A trivial test module, this module always returns `pong' on successful contact. It does not make sense in playbooks, but it is useful from `/usr/bin/ansible' to verify the ability to login and that a usable python is configured. This is NOT ICMP ping, this is just a trivial test module.
3.2 command 模块 默认模块
3.2.1 command命令常用参数说明
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
chdir |
在执行命令之前,通过cd命令进入到指定目录中 # ansible clsn -m command -a "chdir=/tmp ls" |
|
create |
定义一个文件是否存在,如果不存在运行相应命令;如果存在跳过此步骤 |
|
executable |
改变shell使用command进行执行,并且执行时要使用绝对路径 |
|
free_form |
命令模块采用自由形式命令运行;即可以输入任意linux命令 |
|
removes |
定义一个文件是否存在,如果存在运行相应命令;如果不存在跳过此步骤 |
|
warn (added in 1.8) |
如果ansible配置文件中定义了命令警告,如果参数设置了no/false,将不会警告此行命令 |
不指定模块的时候默认使用的模块就是command ↓
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -a "date" 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:15 CST 2017 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:15 CST 2017 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:15 CST 2017
使用ansible自带模块执行命令 如果要用 > < | & ' ' 使用shell模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m command -a "date" 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:27 CST 2017 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:28 CST 2017 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Thu Oct 19 17:12:27 CST 2017
chdir参数的使用:
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m command -a "chdir=/tmp pwd" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> /tmp 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> /tmp 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> /tmp
creates 文件是否存在,不存在就执行命令
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m command -a "creates=/etc/hosts date" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> skipped, since /etc/hosts exists
removes 文件是否存在,不存在就不执行命令,
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m command -a "removes=/etc/hosts date" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Fri Oct 20 13:32:40 CST 2017
3.3 shell模块 万能模块
执行linux命令时可以用
远程节点执行命令
说明: shell 模块在远程执行脚本时,远程主机上一定要有相应的脚本
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m shell -a "/bin/sh /server/scripts/ssh-key.sh" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> fenfa 172.16.1.31 [ OK ] fenfa 172.16.1.41 [ OK ] fenfa 172.16.1.8 [ OK ]
3.4 script 模块 执行脚本模块
在本地执行脚本时,将脚本中的内容传输到远程节点上运行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m script -a "/server/scripts/free.sh"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 172.16.1.8 closed.\r\n",
"stdout": " total used free shared buffers cached\r\nMem: 474M 377M 97M 532K 54M 202M\r\n-/+ buffers/cache: 120M 354M\r\nSwap: 767M 0B 767M\r\n",
"stdout_lines": [
" total used free shared buffers cached",
"Mem: 474M 377M 97M 532K 54M 202M",
"-/+ buffers/cache: 120M 354M",
"Swap: 767M 0B 767M"
]
}
说明:
使用scripts模块,不用将脚本传输到远程节点,脚本本身不用进行授权,即可利用script模块执行。直接执行脚本即可,不需要使用sh
3.5 copy模块 把本地文件发送到远端
3.5.1 copy模块常用参数
|
选项参数 |
选项说明 |
|
backup(重要参数) |
在覆盖远端服务器文件之前,将远端服务器源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息。有两个选项:yes|no |
|
content |
用于替代"src”,可以直接设定指定文件的值 |
|
dest |
必选项。要将源文件复制到的远程主机的绝对路径,如果源文件是一个目录,那么该路径也必须是个目录 |
|
directory_mode |
递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限 |
|
forces |
如果目标主机包含该文件,但内容不同,如果设置为yes,则强制覆盖。 如果为no,则只有当目标主机的目标位置不存在该文件时,才复制。默认为yes。别名:thirsty |
|
others |
所有的file模块里的选项都可以在这里使用 |
|
src |
被复制到远程主机的本地文件,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,它将递归复制。在这种情况下,如果路径使用"/"来结尾,则只复制目录里的内容,如果没有使用"/"来结尾,则包含目录在内的整个内容全部复制,类似于rsync。 |
|
mode |
定义文件或目录的权限;注意:是4位 |
|
owner |
修改属主 |
|
group |
修改属组 |
说明: src和content不能同时使用
3.5.2 copy常用命令参数测试
使用copy 模块,将/etc/hosts 文件 传输到各个服务器送,权限修改为0600 属主属组为clsn
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/ mode=0600 owner=clsn group=clsn "
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "b3c1ab140a1265cd7f6de9175a962988d93c629b",
"dest": "/tmp/hosts",
"gid": 500,
"group": "clsn",
"md5sum": "8c2b120b4742a806dcfdc8cfff6b6308",
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "clsn",
"size": 357,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1508410846.63-224022812989166/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 500
}
……
检查结果
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "ls -l /tmp/hosts" 172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> -rw------- 1 clsn clsn 357 Oct 19 19:00 /tmp/hosts 172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> -rw------- 1 clsn clsn 357 Oct 11 15:12 /tmp/hosts 172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> -rw------- 1 clsn clsn 357 Oct 19 19:00 /tmp/hosts
移动远程主机上的文件 remote_src=true 参数
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m copy -a " src=/server/scripts/ssh-key.sh dest=/tmp/ remote_src=true"
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "d27bd683bd37e15992d2493b50c9410e0f667c9c",
"dest": "/tmp/ssh-key.sh",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "dc88a3a419e3657bae7d3ef31925cbde",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 397,
"src": "/server/scripts/ssh-key.sh",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
定义文件中的内容 content=clsnedu.com 默认没有换行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m copy -a "content=clsnedu.com dest=/tmp/clsn666.txt"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "291694840cd9f9c464263ea9b13421d8e74b7d00",
"dest": "/tmp/clsn666.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "0a6bb40847793839366d0ac014616d69",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 13,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1508466752.1-24733562369639/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
3.6 file模块 设置文件属性
3.6.1 file模块常用参数
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
|
owner |
设置复制传输后的数据属主信息 |
|
|
group |
设置复制传输后的数据属组信息 |
|
|
mode |
设置文件数据权限信息 |
|
|
dest |
要创建的文件或目录命令,以及路径信息 |
|
|
src |
指定要创建软链接的文件信息 |
|
|
state |
state参数信息 |
|
|
directory |
创建目录 |
|
|
file |
创建文件 |
|
|
link |
创建软链接 |
|
|
hard |
创建出硬链接 |
|
|
absent |
目录将被递归删除以及文件,而链接将被取消链接 |
|
|
touch |
创建文件;如果路径不存在将创建一个空文件 |
|
注意:重命名和创建多级目录不能同时实现
3.6.2 常用参数测试
创建目录
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m file -a "dest=/tmp/clsn_dir state=directory"
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/tmp/clsn_dir",
"size": 4096,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
创建文件
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m file -a "dest=/tmp/clsn_file state=touch"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/clsn_file",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
创建软连接
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m file -a "src=/tmp/clsn_file dest=/tmp/clsn_file_link state=link"
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/clsn_file_link",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"size": 16,
"src": "/tmp/clsn_file",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
删除目录文件信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m file -a "dest=/tmp/clsn_dir state=absent"
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"path": "/tmp/clsn_dir",
"state": "absent"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m file -a "dest=/tmp/clsn_file state=absent"
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"path": "/tmp/clsn_file",
"state": "absent"
创建多级目录
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/01/0/0/0/0/0/0/0/"
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "b3c1ab140a1265cd7f6de9175a962988d93c629b",
"dest": "/tmp/01/0/0/0/0/0/0/0/hosts",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "8c2b120b4742a806dcfdc8cfff6b6308",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 357,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1508466973.39-99676412390473/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
注意:重命名和创建多级目录不能同时实现
3.7 fetch 模块 拉取文件
3.7.1 fetch常用参数说明
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
dest |
将远程主机拉取过来的文件保存在本地的路径信息 |
|
src |
指定从远程主机要拉取的文件信息,只能拉取文件 |
|
flat |
默认设置为no,如果设置为yes,将不显示172.16.1.8/etc/信息 |
3.7.2 常用参数实例
从远程拉取出来文件
[root@m01 cp]# ansible clsn -m fetch -a "dest=/tmp/backup src=/etc/hosts"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "b3c1ab140a1265cd7f6de9175a962988d93c629b",
"dest": "/tmp/backup/172.16.1.8/etc/hosts",
"md5sum": "8c2b120b4742a806dcfdc8cfff6b6308",
"remote_checksum": "b3c1ab140a1265cd7f6de9175a962988d93c629b",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
[root@m01 cp]# tree /tmp/backup/
/tmp/backup/
├── 172.16.1.31
│ └── etc
│ └── hosts
├── 172.16.1.41
│ └── etc
│ └── hosts
└── 172.16.1.8
└── etc
└── hosts
flat 参数,拉去的时候不创建目录(同名文件会覆盖)
[root@m01 tmp]# ansible clsn -m fetch -a "dest=/tmp/backup/ src=/etc/hosts flat=yes"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"checksum": "b3c1ab140a1265cd7f6de9175a962988d93c629b",
"dest": "/tmp/backup/hosts",
"file": "/etc/hosts",
"md5sum": "8c2b120b4742a806dcfdc8cfff6b6308"
3.8 mount模块 配置挂载点模块
3.8.1 mount模块常用参数
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
|
fstype |
指定挂载文件类型 -t nfs == fstype=nfs |
|
|
opts |
设定挂载的参数选项信息 -o ro == opts=ro |
|
|
path |
挂载点路径 path=/mnt |
|
|
src |
要被挂载的目录信息 src=172.16.1.31:/data |
|
|
state |
state状态参数 |
|
|
unmounted |
加载/etc/fstab文件 实现卸载 |
|
|
absent |
在fstab文件中删除挂载配置 |
|
|
present |
在fstab文件中添加挂载配置 |
|
|
mounted |
1.将挂载信息添加到/etc/fstab文件中 2.加载配置文件挂载 |
|
3.8.2 mount参数实例
挂载
[root@m01 tmp]# ansible 172.16.1.8 -m mount -a "fstype=nfs opts=rw path=/mnt/ src=172.16.1.31:/data/ state=mounted"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dump": "0",
"fstab": "/etc/fstab",
"fstype": "nfs",
"name": "/mnt/",
"opts": "rw",
"passno": "0",
"src": "172.16.1.31:/data/"
}
卸载
[root@m01 tmp]# ansible 172.16.1.8 -m mount -a "fstype=nfs opts=rw path=/mnt/ src=172.16.1.31:/data/ state=unmounted"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"dump": "0",
"fstab": "/etc/fstab",
"fstype": "nfs",
"name": "/mnt/",
"opts": "rw",
"passno": "0",
"src": "172.16.1.31:/data/"
}
3.9 cron模块 定时任务
3.9.1 cron模块常用参数
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
|
minute 分 |
Minute when the job should run ( 0-59, *, */2, etc ) |
|
|
hour 时 |
Hour when the job should run ( 0-23, *, */2, etc ) |
|
|
day 日 |
Day of the month the job should run ( 1-31, *, */2, etc ) |
|
|
month 月 |
Month of the year the job should run ( 1-12, *, */2, etc ) |
|
|
weekday 周 |
Day of the week that the job should run ( 0-6 for Sunday-Saturday, *, etc ) |
|
|
job |
工作 ;要做的事情 |
|
|
name |
定义定时任务的描述信息 |
|
|
disabled |
注释定时任务 |
|
|
state |
state 状态参数 |
|
|
absent |
删除定时任务 |
|
|
present |
创建定时任务 |
|
|
默认为present |
||
3.9.2 cron模块参数实践
添加定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m cron -a "minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/hostname.sh &>/dev/null' name=clsn01"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"clsn01"
]
}
删除定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m cron -a "minute=00 hour=00 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/hostname.sh &>/dev/null' name=clsn01 state=absent"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
只用名字就可以删除
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m cron -a "name=clsn01 state=absent"
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
注释定时任务
注意: 注释定时任务的时候必须有job的参数
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m cron -a "name=clsn01 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/hostname.sh &>/dev/null' disabled=yes"
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"clsn01"
]
}
取消注释
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m cron -a "name=clsn01 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/hostname.sh &>/dev/null' disabled=no"
172.16.1.41 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"clsn01"
]
}
3.10 yum 模块
3.10.1 yum 模块常用参数
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
name=name |
指定安装的软件 |
|
state=installed |
安装 |
3.10.2 yum模块参数实践
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m yum -a "name=nmap state=installed "
172.16.1.31 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, security\nSetting up Install Process\nLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile\n * base: mirrors.aliyun.com\n * epel: mirrors.aliyun.com\n * extras: mirrors.aliyun.com\n * updates: mirrors.aliyun.com\nResolving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package nmap.x86_64 2:5.51-6.el6 will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n nmap x86_64 2:5.51-6.el6 base 2.8 M\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package(s)\n\nTotal download size: 2.8 M\nInstalled size: 9.7 M\nDownloading Packages:\nRunning rpm_check_debug\nRunning Transaction Test\nTransaction Test Succeeded\nRunning Transaction\n\r Installing : 2:nmap-5.51-6.el6.x86_64 1/1 \n\r Verifying : 2:nmap-5.51-6.el6.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n nmap.x86_64 2:5.51-6.el6 \n\nComplete!\n"
]
}
3.11 service模块 服务管理
3.11.1 service模块常用参数说明
|
参数 |
参数说明 |
|
name=service name |
服务的名称 |
|
state=参数 |
停止服务 服务状态信息为过去时 stared/stoped/restarted/reloaded |
|
enabled=yes |
设置开机自启动 |
说明 :service 管理的服务必须存在在/etc/init.d/下有的服务脚本
3.11.2 service 模块参数实践
重启定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible clsn -m service -a "name=crond state=restarted"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"name": "crond",
"state": "started"
}
3.12 ansible中的常用模块
|
常用模块 |
模块说明 |
|
command (重要模块) |
执行命令模块,ansible命令执行默认模块 |
|
shell (重要模块) |
行shell脚本模块 |
|
script (重要模块) |
把脚本发到客户端,然后执行;执行脚本命令在远端服务器上 |
|
copy (重要模块) |
把本地文件发送到远端 |
|
file |
设定文件属性模块 |
|
services |
系统服务管理模块 |
|
cron |
计划任务管理模块 |
|
yum |
yum软件包安装管理模块 |
|
synchronize |
使用rsync同步文件模块 |
|
mount |
挂载模块 |
3.13 其他模块补充
3.13.1 hostname 修改主机名模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.8 -m hostname -a "name=web01"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "etiantian.org",
"ansible_fqdn": "www.etiantian.org",
"ansible_hostname": "web01",
"ansible_nodename": "web01"
},
"changed": false,
"name": "web01"
}
3.13.2 selinux 管理模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.8 -m selinux -a "state=disabled"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"configfile": "/etc/selinux/config",
"msg": "",
"policy": "targeted",
"state": "disabled"
}
3.13.3 get_url 模块 == 【wget】
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.8 -m get_url -a "url=http://lan.znix.top/RDPWrap-v1.6.1.zip dest=/tmp/"
172.16.1.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum_dest": null,
"checksum_src": "ad402705624d06a6ff4b5a6a98c55fc2453b3a70",
"dest": "/tmp/RDPWrap-v1.6.1.zip",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "b04dde546293ade71287071d187ed92d",
"mode": "0644",
"msg": "OK (1567232 bytes)",
"owner": "root",
"size": 1567232,
"src": "/tmp/tmp4X4Von",
"state": "file",
"status_code": 200,
"uid": 0,
"url": "http://lan.znix.top/RDPWrap-v1.6.1.zip"
}
url= 下载文件的地址 dest 下载到哪里
timeout 超时时间
url_password 密码
url_username 用户名
第4章 ansible-playbook 剧本
4.1 ansible基础知识部分补充
4.1.1 ansible软件特点:
· 可以实现批量管理
· 可以实现批量部署
· ad-hoc(批量执行命令)---针对临时性的操作
ansible clsn -m command -a "hostname" <- 批量执行命令举例
· 编写剧本-脚本(playbook)---针对重复性的操作
4.1.2 ansible核心功能:
pyYAML-----用于ansible编写剧本所使用的语言格式(saltstack---python)
rsync-ini语法 sersync-xml语法 ansible-pyYAML语法
paramiko---远程连接与数据传输
Jinja2-----用于编写ansible的模板信息
4.2 ansible剧本编写规则说明
4.2.1 pyYAML语法规则:
规则一:缩进
yaml使用一个固定的缩进风格表示数据层结构关系,Saltstack需要每个缩进级别由两个空格组成。一定不能使用tab键
注意:编写yaml文件,就忘记键盘有tab
规则二:冒号
CMD="echo"
yaml:
mykey:
每个冒号后面一定要有一个空格(以冒号结尾不需要空格,表示文件路径的模版可以不需要空格)
规则三:短横线
想要表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一个列表的一部分
核心规则:有效的利用空格进行剧本的编写,剧本编写是不支持tab的
4.3 剧本书写格式
### 剧本的开头,可以不写 - hosts: all <- 处理所有服务器,找到所有服务器; -(空格)hosts:(空格)all tasks: <- 剧本所要干的事情; (空格)(空格)task: - command: echo hello clsn linux. (空格)(空格)空格)(空格)-(空格)模块名称:(空格)模块中对应的功能
ansible all -m command -a "echo hello clsn linux"
剧本编写内容扩展:剧本任务定义名称
- hosts: 172.16.1.7 <- 处理指定服务器 -(空格)hosts:(空格)all task: <- 剧本所要干的事情; (空格)(空格)task: - name: command: echo hello clsn linux. (空格)(空格)空格)(空格)-(空格)模块名称:(空格)模块中对应的功能
4.3.1 剧本格式示例
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# vim rsync_sever.yml
- hosts: 172.16.1.41
tasks:
- name: install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
4.4 剧本编写后检查方法
01:ansible-playbook --syntax-check 01.yml
--- 进行剧本配置信息语法检查
02:ansible-playbook -C 01.yml
--- 模拟剧本执行(彩排)
4.4.1 语法检查
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check 01.yml playbook: 01.yml
4.4.2 模拟剧本执行
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# ansible-playbook -C 01.yml PLAY [all] **************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] **************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.41] ok: [172.16.1.8] ok: [172.16.1.31] TASK [cron] *************************************************************** ok: [172.16.1.8] ok: [172.16.1.41] ok: [172.16.1.31] PLAY RECAP **************************************************************** 172.16.1.31 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 172.16.1.41 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 172.16.1.8 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
4.5 剧本示例
4.5.1 剧本编写内容扩展:剧本任务编写多个任务
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: restart-network
cron: name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1'
- name: sync time
cron: name='sync time' minute=*/5 job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.com >/dev/null 2>&1"
4.5.2 剧本编写内容扩展:剧本任务编写多个主机
- hosts: 172.16.1.7
tasks:
- name: restart-network
cron: name='restart network' minute=00 hour=00 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1'
- name: sync time
cron: name='sync time' minute=*/5 job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate pool.ntp.com >/dev/null 2>&1"
- hosts: 172.16.1.31
tasks:
- name: show ip addr to file
shell: echo $(hostname -i) >> /tmp/ip.txt
4.6 剧本编写方式
01 多主机单任务编写方式
02 多主机多任务编写方式
03 不同主机多任务编写方式
第5章 常见错误
5.1 ansible编写剧本排错思路
1. ansible-playbook编写完,检査语法和模拟测试运行
2. 打开剧本,定位异常问題原因,将剧本中的内容转换命令执行一次
|
1
2
|
cron: name=clsn64 minute=ee hour=03 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null'ansible clsn -m cron -a "name=clsn64 minute=00 hour=03 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh &>/dev/null |
3. 将参数中的脚本文件推送到远程屎务器,在远程服务器本地执行脚本 sh -x test.sh
说明:ansible执行时,加1上-vvvv显示ansible详细执行过程,也可以定位异常原因!
5.1.1 排错逻辑
01. 剧本执行中的错误
02. 把剧本中的内容转换为ansible命令执行
ansible clsn -m yum -a "name=rsync state=installed"
03. 把ansible服务器上执行的命令放在被管理主机上执行
yum install -y rsync
5.2 ansible 无法正常使用
5.2.1 在被控端上 root@notty 进程一直存在
[root@backup ~]# ps -ef|grep sshd root 35274 1 0 15:25 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd root 37004 35274 0 16:23 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/2 root 37062 35274 0 16:55 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@notty root 37154 37006 0 16:55 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd
5.2.2 解决办法
首先,将该进程干掉
kill pid
5.2.3 然后使用ansible的 -vvvv 参数查看执行的错误信息
Loading callback plugin minimal of type stdout, v2.0 from /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/ansible/plugins/callback/__init__.pyc META: ran handlers Using module file /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/ansible/modules/system/ping.py <172.16.1.8> ESTABLISH SSH CONNECTION FOR USER: None <172.16.1.8> SSH: EXEC ssh -vvv -C -o ControlMaster=auto -o ControlPersist=60s -o KbdInteractiveAuthentication=no -o PreferredAuthentications=gssapi-with-mic,gssapi-keyex,hostbased,publickey -o PasswordAuthentication=no -o ConnectTimeout=10 -o ControlPath=/root/.ansible/cp/923ebeb605 172.16.1.8 '/bin/sh -c '"'"'echo ~ && sleep 0'"'"'' ……
找到在哪里出错。
5.2.4 可能的错误
在 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 文件中的第132行为空,导致sftp 无法连接,出错~
|
1
|
133 Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server |
5.3 常见问题二:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@m01 ~]# ansible -k 172.16.1.51 -m pingSSH password:[WARNING]: No hosts matched, nothing to do |
原因分析:
在ansible的hosts文件中,没有配置相应主机地址信息
5.3.1 常见问题三:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# ansible -k 172.16.1.51 -m pingSSH password:172.16.1.51|FAILED! => {"failed": true,"msg": "Using a SSH password instead of a key is not possible because Host Key checking is enabled and sshpass does not support this. Please add this host's fingerprint to your known_hosts file to manage this host."} |
原因分析:
因为没有受控端的指纹信息,在known_hosts文件中


