大数据之Apache Flume
Apache Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的软件。Flume的核心是把数据从数据源(source)收集过来,再将收集到的数据送到指定的目的地(sink)。为了保证输送的过程一定成功,在送到目的地(sink)之前,会先缓存数据(channel),待数据真正到达目的地(sink)后,flume在删除自己缓存的数据。
Flume支持定制各类数据发送方,用于收集各类型数据;同时,Flume支持定制各种数据接受方,用于最终存储数据。一般的采集需求,通过对flume的简单配置即可实现。针对特殊场景也具备良好的自定义扩展能力。因此,flume可以适用于大部分的日常数据采集场景。
当前Flume有两个版本。Flume 0.9X版本的统称Flume OG(original generation),Flume1.X版本的统称Flume NG(next generation)。由于Flume NG经过核心组件、核心配置以及代码架构重构,与Flume OG有很大不同,使用时请注意区分。改动的另一原因是将Flume纳入 apache 旗下,Cloudera Flume 改名为 Apache Flume。
1. 运行机制
Flume系统中核心的角色是agent,agent本身是一个Java进程,一般运行在日志收集节点。
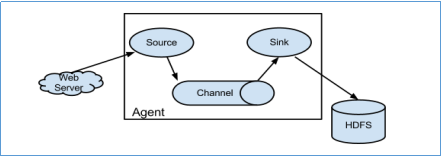
每一个agent相当于一个数据传递员,内部有三个组件:
Source:采集源,用于跟数据源对接,以获取数据;
Sink:下沉地,采集数据的传送目的,用于往下一级agent传递数据或者往最终存储系统传递数据;
Channel:agent内部的数据传输通道,用于从source将数据传递到sink;
在整个数据的传输的过程中,流动的是event,它是Flume内部数据传输的最基本单元。event将传输的数据进行封装。如果是文本文件,通常是一行记录,event也是事务的基本单位。event从source,流向channel,再到sink,本身为一个字节数组,并可携带headers(头信息)信息。event代表着一个数据的最小完整单元,从外部数据源来,向外部的目的地去。
一个完整的event包括:event headers、event body、event信息,其中event信息就是flume收集到的日记记录。
2. Flume采集系统结构图
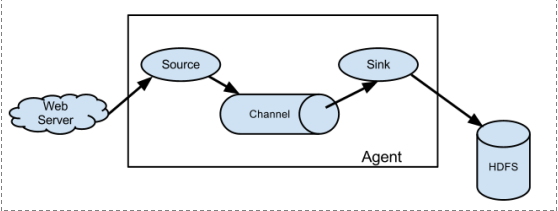
2.1. 简单结构
单个agent采集数据
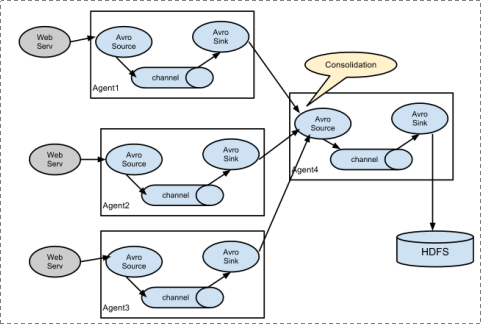
2.2. 复杂结构
3. Flume安装部署
Flume的安装非常简单,上传安装包到数据源所在节点上,然后解压 tar -zxvf apache-flume-1.8.0-bin.tar.gz,然后进入flume的目录,修改conf下的flume-env.sh,在里面配置JAVA_HOME
根据数据采集需求配置采集方案,描述在配置文件中(文件名可任意自定义),指定采集方案配置文件,在相应的节点上启动flume agent
先用一个最简单的例子来测试一下程序环境是否正常
1、先在flume的conf目录下新建一个文件
vim netcat-logger.conf
1 # 定义这个agent中各组件的名字 2 a1.sources = r1 3 a1.sinks = k1 4 a1.channels = c1 5 6 # 描述和配置source组件:r1 7 a1.sources.r1.type = netcat 8 a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost 9 a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 10 11 # 描述和配置sink组件:k1 12 a1.sinks.k1.type = logger 13 14 # 描述和配置channel组件,此处使用是内存缓存的方式 15 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 16 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 17 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 18 19 # 描述和配置source channel sink之间的连接关系 20 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 21 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
2、启动agent去采集数据
1 bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/netcat-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
-c conf 指定flume自身的配置文件所在目录
-f conf/netcat-logger.con 指定我们所描述的采集方案
-n a1 指定我们这个agent的名字
3、测试
先要往agent采集监听的端口上发送数据,让agent有数据可采。
随便在一个能跟agent节点联网的机器上:
telnet anget-hostname port (telnet localhost 44444)
telnet 通了之后可以通过发送数据来进行查看是否成功,成功的情况下是你在这边发送数据,任务启动那边可以马上看得到输出。
4.Flume简单案例
1. 采集目录到HDFS
采集需求:服务器的某特定目录下,会不断产生新的文件,每当有新文件出现,就需要把文件采集到HDFS中去
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
-
- 采集源,即source——监控文件目录 : spooldir
- 下沉目标,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
- source和sink之间的传递通道——channel,可用file channel 也可以用内存channel
配置文件编写:
1 # Name the components on this agent 2 a1.sources = r1 3 a1.sinks = k1 4 a1.channels = c1 5 6 # Describe/configure the source 7 ##注意:不能往监控目录中重复丢同名文件 8 a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir #监控模式,这里为监控文件夹目录 9 a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /root/logs #监控的目录 10 a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true #可配置为true或者false,表示在flume读取数据之后,是否在封装出来的event中将文件名添加到event的header中。 11 12 # Describe the sink 13 a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs 14 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/ 15 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events- 16 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #按照时间滚动文件夹 17 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 #多长时间创建一个新文件夹 18 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute #定义时间的单位 19 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3 #多久生成一个新文件秒为单位。设置为0表示不会因为时间间隔截断文件 20 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 20 #文件字节数超过20截断一个文件。设置为0就不因为文件大小截断文件 21 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 5 #每5个event截断一个文件。设置为0就不因为event数量截断文件 22 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1 #积攒到多少event后flush到hdfs一次 23 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #使用本地时间戳 24 #生成的文件类型,默认是Sequencefile,可用DataStream,则为普通文本 25 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream 26 27 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory 28 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 29 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 #默认通道允许的最大的event数量 30 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #每次最大可从source拿到或者传输到sink的数量 31 32 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 33 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 34 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动命令:bin/flume-ng agent -c ./conf -f ./conf/spool-hdfs.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
2. 采集文件到HDFS
采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
-
- 采集源,即source——监控文件内容更新 : exec ‘tail -F file’
- 下沉目标,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
- Source和sink之间的传递通道——channel,可用file channel 也可以用 内存channel
1 # Name the components on this agent 2 a1.sources = r1 3 a1.sinks = k1 4 a1.channels = c1 5 6 # Describe/configure the source 7 a1.sources.r1.type = exec #监控模式,监控某个具体文件 8 a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /root/logs/test.log #被监控的文件,监控新增的数据 9 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 10 11 # Describe the sink 12 a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs 13 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/tailout/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/ 14 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events- 15 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true 16 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 17 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute 18 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3 19 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 20 20 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 5 21 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1 22 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true 23 #生成的文件类型,默认是Sequencefile,可用DataStream,则为普通文本 24 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream 25 26 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory 27 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 28 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 29 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 30 31 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 32 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 33 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动命令:bin/flume-ng agent -c ./conf -f ./conf/exec-hdfs.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5. Flume的load-balance、failover
负载均衡是用于解决一台机器(一个进程)无法解决所有请求而产生的一种算法。Load balancing Sink Processor能够实现load balance功能,如下图Agent1是一个路由节点,负责将Channel暂存的Event均衡到对应的多个Sink组件上,而每个Sink组件分别连接到一个独立的Agent上,示例配置,如下所示:
#agent1 name agent1.channels = c1 agent1.sources = r1 agent1.sinks = k1 k2 #set gruop agent1.sinkgroups = g1 #set channel agent1.channels.c1.type = memory agent1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 agent1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 agent1.sources.r1.channels = c1 agent1.sources.r1.type = exec agent1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /root/logs/123.log # set sink1 agent1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 agent1.sinks.k1.type = avro agent1.sinks.k1.hostname = node-2 agent1.sinks.k1.port = 52020 # set sink2 agent1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 agent1.sinks.k2.type = avro agent1.sinks.k2.hostname = node-3 agent1.sinks.k2.port = 52020 #set sink group agent1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 #set failover agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true #如果开启,则将失败的sink放入黑名单
agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin #另外还支持random
agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector.maxTimeOut=10000#在黑名单放置的超时时间,超时结束时,若仍然无法接收,则超时时间呈指数增长
启动代码:bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/exec-avro.conf -n agent1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
Failover Sink Processor能够实现failover功能,具体流程类似load balance,但是内部处理机制与load balance完全不同。
Failover Sink Processor维护一个优先级Sink组件列表,只要有一个Sink组件可用,Event就被传递到下一个组件。故障转移机制的作用是将失败的Sink降级到一个池,在这些池中它们被分配一个冷却时间,随着故障的连续,在重试之前冷却时间增加。一旦Sink成功发送一个事件,它将恢复到活动池。 Sink具有与之相关的优先级,数量越大,优先级越高。
例如,具有优先级为100的sink在优先级为80的Sink之前被激活。如果在发送事件时汇聚失败,则接下来将尝试下一个具有最高优先级的Sink发送事件。如果没有指定优先级,则根据在配置中指定Sink的顺序来确定优先级。
示例配置如下所示
1 #agent1 name 2 agent1.channels = c1 3 agent1.sources = r1 4 agent1.sinks = k1 k2 5 6 #set gruop 7 agent1.sinkgroups = g1 8 9 #set channel 10 agent1.channels.c1.type = memory 11 agent1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 12 agent1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 13 14 agent1.sources.r1.channels = c1 15 agent1.sources.r1.type = exec 16 agent1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /root/logs/456.log 17 18 # set sink1 19 agent1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 20 agent1.sinks.k1.type = avro 21 agent1.sinks.k1.hostname = node-2 22 agent1.sinks.k1.port = 52020 23 24 # set sink2 25 agent1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 26 agent1.sinks.k2.type = avro 27 agent1.sinks.k2.hostname = node-3 28 agent1.sinks.k2.port = 52020 29 30 #set sink group 31 agent1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 32 33 #set failover 34 agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover 35 agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 10 #优先级值越大优先级越高 36 agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 1 37 agent1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000 #失败时Sink最大的回退期
启动代码:bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/exec-avro.conf -n agent1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
6. Flume拦截器实战案例
6.1. 日志的采集和汇总
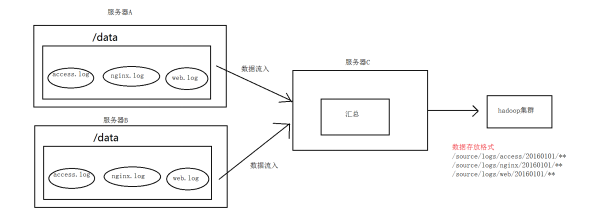
6.1.1. 案例场景
A、B两台日志服务机器实时生产日志主要类型为access.log、nginx.log、web.log
现在要求:
把A、B 机器中的access.log、nginx.log、web.log 采集汇总到C机器上然后统一收集到hdfs中。
但是在hdfs中要求的目录为:
/source/logs/access/20160101/**
/source/logs/nginx/20160101/**
/source/logs/web/20160101/**
6.1.2. 案例场景
6.1.3.定义静态拦截器
1 # Name the components on this agent 2 a1.sources = r1 r2 r3 3 a1.sinks = k1 4 a1.channels = c1 5 6 # Describe/configure the source 7 a1.sources.r1.type = exec 8 a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /root/logs/access.log 9 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 #设置拦截器 10 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = static #指定拦截器类型,static类型的拦截器就是往采集到的数据的event header里面插入下面定义的键值队 11 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.key = type #事件头的key 12 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.value = access #key的value 13 14 a1.sources.r2.type = exec 15 a1.sources.r2.command = tail -F /root/logs/nginx.log 16 a1.sources.r2.interceptors = i2 17 a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.type = static 18 a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.key = type 19 a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.value = nginx 20 21 a1.sources.r3.type = exec 22 a1.sources.r3.command = tail -F /root/logs/web.log 23 a1.sources.r3.interceptors = i3 24 a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.type = static 25 a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.key = type 26 a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.value = web 27 28 # Describe the sink 29 a1.sinks.k1.type = avro 30 a1.sinks.k1.hostname = node-2 31 a1.sinks.k1.port = 41414 32 33 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory 34 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 35 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 2000 36 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 37 38 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 39 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 40 a1.sources.r2.channels = c1 41 a1.sources.r3.channels = c1 42 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
6.1.4 定义时间拦截器
1 #定义agent名, source、channel、sink的名称 2 a1.sources = r1 3 a1.sinks = k1 4 a1.channels = c1 5 6 #定义source 7 a1.sources.r1.type = avro 8 a1.sources.r1.bind = node-2 9 a1.sources.r1.port =41414 10 11 #添加时间拦截器 12 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 13 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = org.apache.flume.interceptor.TimestampInterceptor$Builder #设置拦截器类型为时间戳类型,读取文件时把时间戳写入到event header上 14 15 #定义channels 16 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 17 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 20000 18 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 10000 19 20 #定义sink 21 a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs 22 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=hdfs://node-1:9000/source/logs/%{type}/%Y%m%d 23 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix =events 24 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream 25 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat = Text 26 #时间类型 27 #a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true 28 #生成的文件不按条数生成 29 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 30 #生成的文件不按时间生成 31 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 20 32 #生成的文件按大小生成 33 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 10485760 34 #批量写入hdfs的个数 35 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 20 36 flume操作hdfs的线程数(包括新建,写入等) 37 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.threadsPoolSize=10 38 #操作hdfs超时时间 39 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.callTimeout=30000 40 41 #组装source、channel、sink 42 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 43 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动代码: bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/avro_source_hdfs_sink.conf -name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
7. Flume自定义拦截器
7.1. 案例背景介绍
Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统,Flume支持在日志系统中定制各类数据发送方,用于收集数据;同时,Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(可定制)的能力。Flume有各种自带的拦截器,比如: TimestampInterceptor、HostInterceptor、RegexExtractorInterceptor等,通过使用不同的拦截器,实现不同的功能。但是以上的这些拦截器,不能改变原有日志数据的内容或者对日志信息添加一定的处理逻辑,当一条日志信息有几十个甚至上百个字段的时候,在传统的Flume处理下,收集到的日志还是会有对应这么多的字段,也不能对你想要的字段进行对应的处理。
7.2. 自定义拦截器
根据实际业务的需求,为了更好的满足数据在应用层的处理,通过自定义Flume拦截器,过滤掉不需要的字段,并对指定字段加密处理,将源数据进行预处理。减少了数据的传输量,降低了存储的开销。
7.3. 功能实现
本技术方案核心包括二部分:
- 编写java代码,自定义拦截器
内容包括:
- 定义一个类CustomParameterInterceptor实现Interceptor接口。
- 在CustomParameterInterceptor类中定义变量,这些变量是需要到 Flume的配置文件中进行配置使用的。每一行字段间的分隔符(fields_separator)、通过分隔符分隔后,所需要列字段的下标(indexs)、多个下标使用的分隔符(indexs_separator)、多个下标使用的分隔符(indexs_separator)。
- 添加CustomParameterInterceptor的有参构造方法。并对相应的变量进行处理。将配置文件中传过来的unicode编码进行转换为字符串。
- 写具体的要处理的逻辑intercept()方法,一个是单个处理的,一个是批量处理。
- 接口中定义了一个内部接口Builder,在configure方法中,进行一些参数配置。并给出,在flume的conf中没配置一些参数时,给出其默认值。通过其builder方法,返回一个CustomParameterInterceptor对象。
- 定义一个静态类,类中封装MD5加密方法
- 通过以上步骤,自定义拦截器的代码开发已完成,然后打包成jar, 放到Flume的根目录下的lib中
定义Flume配置信息
1 #定义agent名, source、channel、sink的名称 2 a1.channels = c1 3 a1.sources = r1 4 a1.sinks = s1 5 6 #定义channel 7 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 8 a1.channels.c1.capacity=100000 9 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=50000 10 11 #定义source 12 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 13 a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir 14 a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /root/data/ 15 a1.sources.r1.batchSize= 50 16 a1.sources.r1.inputCharset = UTF-8 17 #定义拦截器 18 a1.sources.r1.interceptors =i1 i2 19 #指定拦截器调用的类 20 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type =cn.zhoucheng.interceptor.CustomParameterInterceptor$Builder 21 #定义原始字段分隔符 22 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.fields_separator=\\u0009 23 #定义取字段的下标 24 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.indexs =0,1,3,5,6 25 #指定字段索引之间的分隔符,就是采到数据用什么拼接 26 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.indexs_separator =\\u002c 27 #指定需要加密的下标 28 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.encrypted_field_index =0 29 30 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type = org.apache.flume.interceptor.TimestampInterceptor$Builder 31 32 33 #sink 34 a1.sinks.s1.channel = c1 35 a1.sinks.s1.type = hdfs 36 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path =hdfs://192.168.200.101:9000/flume/%Y%m%d 37 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix = event 38 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileSuffix = .log 39 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize = 10485760 40 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval =20 41 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 42 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.batchSize = 1500 43 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.round = true 44 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute 45 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.threadsPoolSize = 25 46 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true 47 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 48 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType =DataStream 49 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat = Text 50 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.callTimeout = 60000 51 a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.idleTimeout =60
启动:
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/spool-interceptor-hdfs.conf -name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
8. Flume高阶自定义组件
8.1. Flume自定义Source
8.1.1. 自定义Source说明
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。官方提供的source类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些source。
如:实时监控MySQL,从MySQL中获取数据传输到HDFS或者其他存储框架,所以此时需要我们自己实现MySQLSource。
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:
官网说明:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source
8.1.2. 自定义Source原理
根据官方说明自定义mysqlsource需要继承AbstractSource类并实现Configurable和PollableSource接口。
实现相应方法:
getBackOffSleepIncrement() //暂不用
getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() //暂不用
configure(Context context) //初始化context
process() //获取数据(从mysql获取数据,业务处理比较复杂,所以我们定义一个专门的类——QueryMysql来处理跟mysql的交互),封装成event并写入channel,这个方法被循环调用
stop() //关闭相关的资源
8.1.3.实现步骤
1.创建MySQL数据库,以及表。并初始化数据。
2.创建maven工程导入pom依赖
1 <dependencies> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId> 4 <artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId> 5 <version>1.8.0</version> 6 <scope>provided</scope> 7 </dependency> 8 9 <dependency> 10 <groupId>mysql</groupId> 11 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 12 <version>5.1.38</version> 13 </dependency> 14 <dependency> 15 <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> 16 <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> 17 <version>3.6</version> 18 </dependency> 19 </dependencies>
3.定义QueryMysql工具类

1 package cn.itcast.flumesource; 2 3 import org.apache.flume.Context; 4 import org.apache.flume.conf.ConfigurationException; 5 import org.apache.http.ParseException; 6 import org.slf4j.Logger; 7 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 8 9 import java.sql.*; 10 import java.util.ArrayList; 11 import java.util.List; 12 import java.util.Properties; 13 14 public class QueryMySql { 15 private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(QueryMySql.class); 16 17 private int runQueryDelay, //两次查询的时间间隔 18 startFrom, //开始id 19 currentIndex, //当前id 20 recordSixe = 0, //每次查询返回结果的条数 21 maxRow; //每次查询的最大条数 22 23 24 private String table, //要操作的表 25 columnsToSelect, //用户传入的查询的列 26 customQuery, //用户传入的查询语句 27 query, //构建的查询语句 28 defaultCharsetResultSet;//编码集 29 30 //上下文,用来获取配置文件 31 private Context context; 32 33 //为定义的变量赋值(默认值),可在flume任务的配置文件中修改 34 private static final int DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY = 10000; 35 private static final int DEFAULT_START_VALUE = 0; 36 private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_ROWS = 2000; 37 private static final String DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT = "*"; 38 private static final String DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET = "UTF-8"; 39 40 private static Connection conn = null; 41 private static PreparedStatement ps = null; 42 private static String connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword; 43 44 //加载静态资源 45 static { 46 Properties p = new Properties(); 47 try { 48 p.load(QueryMySql.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties")); 49 connectionURL = p.getProperty("dbUrl"); 50 connectionUserName = p.getProperty("dbUser"); 51 connectionPassword = p.getProperty("dbPassword"); 52 Class.forName(p.getProperty("dbDriver")); 53 } catch (Exception e) { 54 LOG.error(e.toString()); 55 } 56 } 57 58 //获取JDBC连接 59 private static Connection InitConnection(String url, String user, String pw) { 60 try { 61 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw); 62 if (conn == null) 63 throw new SQLException(); 64 return conn; 65 } catch (SQLException e) { 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } 68 return null; 69 } 70 71 //构造方法 72 QueryMySql(Context context) throws ParseException { 73 //初始化上下文 74 this.context = context; 75 76 //有默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数,读不到的采用默认值 77 this.columnsToSelect = context.getString("columns.to.select", DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT); 78 this.runQueryDelay = context.getInteger("run.query.delay", DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY); 79 this.startFrom = context.getInteger("start.from", DEFAULT_START_VALUE); 80 this.defaultCharsetResultSet = context.getString("default.charset.resultset", DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET); 81 82 //无默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数 83 this.table = context.getString("table"); 84 this.customQuery = context.getString("custom.query"); 85 connectionURL = context.getString("connection.url"); 86 connectionUserName = context.getString("connection.user"); 87 connectionPassword = context.getString("connection.password"); 88 conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword); 89 90 //校验相应的配置信息,如果没有默认值的参数也没赋值,抛出异常 91 checkMandatoryProperties(); 92 //获取当前的id 93 currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom); 94 //构建查询语句 95 query = buildQuery(); 96 } 97 98 //校验相应的配置信息(表,查询语句以及数据库连接的参数) 99 private void checkMandatoryProperties() { 100 if (table == null) { 101 throw new ConfigurationException("property table not set"); 102 } 103 if (connectionURL == null) { 104 throw new ConfigurationException("connection.url property not set"); 105 } 106 if (connectionUserName == null) { 107 throw new ConfigurationException("connection.user property not set"); 108 } 109 if (connectionPassword == null) { 110 throw new ConfigurationException("connection.password property not set"); 111 } 112 } 113 114 //构建sql语句 115 private String buildQuery() { 116 String sql = ""; 117 //获取当前id 118 currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom); 119 LOG.info(currentIndex + ""); 120 if (customQuery == null) { 121 sql = "SELECT " + columnsToSelect + " FROM " + table; 122 } else { 123 sql = customQuery; 124 } 125 StringBuilder execSql = new StringBuilder(sql); 126 //以id作为offset 127 if (!sql.contains("where")) { 128 execSql.append(" where "); 129 execSql.append("id").append(">").append(currentIndex); 130 return execSql.toString(); 131 } else { 132 int length = execSql.toString().length(); 133 return execSql.toString().substring(0, length - String.valueOf(currentIndex).length()) + currentIndex; 134 } 135 } 136 137 //执行查询 138 List<List<Object>> executeQuery() { 139 try { 140 //每次执行查询时都要重新生成sql,因为id不同 141 customQuery = buildQuery(); 142 //存放结果的集合 143 List<List<Object>> results = new ArrayList<>(); 144 if (ps == null) { 145 // 146 ps = conn.prepareStatement(customQuery); 147 } 148 ResultSet result = ps.executeQuery(customQuery); 149 while (result.next()) { 150 //存放一条数据的集合(多个列) 151 List<Object> row = new ArrayList<>(); 152 //将返回结果放入集合 153 for (int i = 1; i <= result.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) { 154 row.add(result.getObject(i)); 155 } 156 results.add(row); 157 } 158 LOG.info("execSql:" + customQuery + "\nresultSize:" + results.size()); 159 return results; 160 } catch (SQLException e) { 161 LOG.error(e.toString()); 162 // 重新连接 163 conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword); 164 } 165 return null; 166 } 167 168 //将结果集转化为字符串,每一条数据是一个list集合,将每一个小的list集合转化为字符串 169 List<String> getAllRows(List<List<Object>> queryResult) { 170 List<String> allRows = new ArrayList<>(); 171 if (queryResult == null || queryResult.isEmpty()) 172 return allRows; 173 StringBuilder row = new StringBuilder(); 174 for (List<Object> rawRow : queryResult) { 175 Object value = null; 176 for (Object aRawRow : rawRow) { 177 value = aRawRow; 178 if (value == null) { 179 row.append(","); 180 } else { 181 row.append(aRawRow.toString()).append(","); 182 } 183 } 184 allRows.add(row.toString()); 185 row = new StringBuilder(); 186 } 187 return allRows; 188 } 189 190 //更新offset元数据状态,每次返回结果集后调用。必须记录每次查询的offset值,为程序中断续跑数据时使用,以id为offset 191 void updateOffset2DB(int size) { 192 //以source_tab做为KEY,如果不存在则插入,存在则更新(每个源表对应一条记录) 193 String sql = "insert into flume_meta(source_tab,currentIndex) VALUES('" 194 + this.table 195 + "','" + (recordSixe += size) 196 + "') on DUPLICATE key update source_tab=values(source_tab),currentIndex=values(currentIndex)"; 197 LOG.info("updateStatus Sql:" + sql); 198 execSql(sql); 199 } 200 201 //执行sql语句 202 private void execSql(String sql) { 203 try { 204 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 205 LOG.info("exec::" + sql); 206 ps.execute(); 207 } catch (SQLException e) { 208 e.printStackTrace(); 209 } 210 } 211 212 //获取当前id的offset 213 private Integer getStatusDBIndex(int startFrom) { 214 //从flume_meta表中查询出当前的id是多少 215 String dbIndex = queryOne("select currentIndex from flume_meta where source_tab='" + table + "'"); 216 if (dbIndex != null) { 217 return Integer.parseInt(dbIndex); 218 } 219 //如果没有数据,则说明是第一次查询或者数据表中还没有存入数据,返回最初传入的值 220 return startFrom; 221 } 222 223 //查询一条数据的执行语句(当前id) 224 private String queryOne(String sql) { 225 ResultSet result = null; 226 try { 227 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 228 result = ps.executeQuery(); 229 while (result.next()) { 230 return result.getString(1); 231 } 232 } catch (SQLException e) { 233 e.printStackTrace(); 234 } 235 return null; 236 } 237 238 //关闭相关资源 239 void close() { 240 try { 241 ps.close(); 242 conn.close(); 243 } catch (SQLException e) { 244 e.printStackTrace(); 245 } 246 } 247 248 int getCurrentIndex() { 249 return currentIndex; 250 } 251 252 void setCurrentIndex(int newValue) { 253 currentIndex = newValue; 254 } 255 256 int getRunQueryDelay() { 257 return runQueryDelay; 258 } 259 260 String getQuery() { 261 return query; 262 } 263 264 String getConnectionURL() { 265 return connectionURL; 266 } 267 268 private boolean isCustomQuerySet() { 269 return (customQuery != null); 270 } 271 272 Context getContext() { 273 return context; 274 } 275 276 public String getConnectionUserName() { 277 return connectionUserName; 278 } 279 280 public String getConnectionPassword() { 281 return connectionPassword; 282 } 283 284 String getDefaultCharsetResultSet() { 285 return defaultCharsetResultSet; 286 } 287 }
4.定义MySqlSource主类

1 package cn.itcast.flumesource; 2 3 import org.apache.flume.Context; 4 import org.apache.flume.Event; 5 import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException; 6 import org.apache.flume.PollableSource; 7 import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable; 8 import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent; 9 import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource; 10 import org.slf4j.Logger; 11 12 import java.util.ArrayList; 13 import java.util.HashMap; 14 import java.util.List; 15 16 import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.*; 17 18 public class MySqlSource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource { 19 20 //打印日志 21 private static final Logger LOG = getLogger(MySqlSource.class); 22 //定义sqlHelper 23 private QueryMySql sqlSourceHelper; 24 25 26 @Override 27 public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() { 28 return 0; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() { 33 return 0; 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public void configure(Context context) { 38 //初始化 39 sqlSourceHelper = new QueryMySql(context); 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 public PollableSource.Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { 44 try { 45 //查询数据表 46 List<List<Object>> result = sqlSourceHelper.executeQuery(); 47 //存放event的集合 48 List<Event> events = new ArrayList<>(); 49 //存放event头集合 50 HashMap<String, String> header = new HashMap<>(); 51 //如果有返回数据,则将数据封装为event 52 if (!result.isEmpty()) { 53 List<String> allRows = sqlSourceHelper.getAllRows(result); 54 Event event = null; 55 for (String row : allRows) { 56 event = new SimpleEvent(); 57 event.setBody(row.getBytes()); 58 event.setHeaders(header); 59 events.add(event); 60 } 61 //将event写入channel 62 this.getChannelProcessor().processEventBatch(events); 63 //更新数据表中的offset信息 64 sqlSourceHelper.updateOffset2DB(result.size()); 65 } 66 //等待时长 67 Thread.sleep(sqlSourceHelper.getRunQueryDelay()); 68 return Status.READY; 69 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 70 LOG.error("Error procesing row", e); 71 return Status.BACKOFF; 72 } 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public synchronized void stop() { 77 LOG.info("Stopping sql source {} ...", getName()); 78 try { 79 //关闭资源 80 sqlSourceHelper.close(); 81 } finally { 82 super.stop(); 83 } 84 } 85 }
5.功能测试
使用maven对工程进行打包,需要将mysql的依赖包一起打到jar包里,然后将打包好的jar包放到flume的lib目录下。
编辑flume的配置文件如下:
1 a1.sources = r1 2 a1.sinks = k1 3 a1.channels = c1 4 5 # Describe/configure the source 6 a1.sources.r1.type = cn.itcast.flumesource.MySqlSource 7 a1.sources.r1.connection.url = jdbc:mysql://node-1:3306/mysqlsource 8 a1.sources.r1.connection.user = root 9 a1.sources.r1.connection.password = hadoop 10 a1.sources.r1.table = student 11 a1.sources.r1.columns.to.select = * 12 a1.sources.r1.incremental.column.name = id 13 a1.sources.r1.incremental.value = 0 14 a1.sources.r1.run.query.delay=3000 15 16 # Describe the sink 17 a1.sinks.k1.type = logger 18 19 # Describe the channel 20 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 21 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 22 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 23 24 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 25 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 26 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动flume并查看结果:
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/mysqlsource.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
8.2 Flume自定义Sink
8.2.1. 自定义Sink说明
同自定义source类似,对于某些sink如果没有我们想要的,我们也可以自定义sink实现将数据保存到我们想要的地方去,例如kafka,或者mysql,或者文件等等都可以
需求:从网络端口当中发送数据,自定义sink,使用sink从网络端口接收数据,然后将数据保存到本地文件当中去。
8.2.2. 自定义Sink原理实现

1 public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable { 2 private Context context ; 3 private String filePath = ""; 4 private String fileName = ""; 5 private File fileDir; 6 7 //这个方法会在初始化调用,主要用于初始化我们的Context,获取我们的一些配置参数 8 @Override 9 public void configure(Context context) { 10 try { 11 this.context = context; 12 filePath = context.getString("filePath"); 13 fileName = context.getString("fileName"); 14 fileDir = new File(filePath); 15 if(!fileDir.exists()){ 16 fileDir.mkdirs(); 17 } 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 //这个方法会被反复调用 23 @Override 24 public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { 25 Event event = null; 26 Channel channel = this.getChannel(); 27 Transaction transaction = channel.getTransaction(); 28 transaction.begin(); 29 while(true){ 30 event = channel.take(); 31 if(null != event){ 32 break; 33 } 34 } 35 byte[] body = event.getBody(); 36 String line = new String(body); 37 try { 38 FileUtils.write(new File(filePath+File.separator+fileName),line,true); 39 transaction.commit(); 40 } catch (IOException e) { 41 transaction.rollback(); 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 return Status.BACKOFF; 44 }finally { 45 transaction.close(); 46 } 47 return Status.READY; 48 } 49 }
8.2.3 功能测试
将代码使用打包插件,打成jar包,注意一定要将commons-langs这个依赖包打进去,放到flume的lib目录下
开发flume的配置文件:
1 a1.sources = r1 2 a1.sinks = k1 3 a1.channels = c1 4 # Describe/configure the source 5 a1.sources.r1.type = netcat 6 a1.sources.r1.bind = node-1 7 a1.sources.r1.port = 5678 8 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 9 # Describe the sink 10 a1.sinks.k1.type = cn.itcast.flumesink.MySink 11 a1.sinks.k1.filePath=/export/servers 12 a1.sinks.k1.fileName=filesink.txt 13 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory 14 a1.channels.c1.type = memory 15 a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 16 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 17 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 18 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 19 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动flume,并且使用telnet测试:
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/filesink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
Telnet node-1 5678 连接到机器端口上输入数据。
岁月静好,负重前行。莫叫人间忽晚,山河已秋



