cpufreq概述【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lvzh/p/13169941.html
linux cpufreq
cpufreq概述
cpufreq的核心功能,是通过调整CPU的电压和频率,兼顾系统的性能和功耗。在不需要高性能时,降低电压和频率,以降低功耗;在需要高性能时,提高电压和频率,以提高性能。
cpufreq软件框架
对下,cpufreq基于clock、regulator、pmu等模块实现频率和电压的控制。
对上,cpufreq通过cpufreq core、cpufreq governor、cpufreq stats等模块以sysfs的形式向用户空间提供频率的查询、控制等接口。
内部,cpufreq内部分为core、governor、drivers等模块。

cpufreq调频策略
- Performance
性能优先,CPU固定工作在其支持的最高频率。
- Powersave
功耗优先,CPU固定工作在其支持的最低频率。
- Userspace
系统将变频策略的决策权交给用户态应用程序,并提供了相应的接口供用户态程序设置CPU 频率。
- Ondemand
按需动态调整CPU频率, 只要CPU负载超过阈值up_threshold就会立即设置为最大频率,其他时候根据负载计算出合适的频率。
- Conservative
与ondemand不同,Conservative不是一味追求最高频率,而是平滑地调整CPU频率,频率的升降是渐变式的。
cpufreq调测命令
- 查询
以下文件节点均可通过cat命令显示
# ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/
affected_cpus //当前策略作用于哪些online core
cpuinfo_cur_freq //当前CPU硬件频率
cpuinfo_max_freq //CPU硬件支持的最低频率
cpuinfo_min_freq //CPU硬件支持的最高频率
cpuinfo_transition_latency //硬件支持的切换频率最小间隔
related_cpus //online和offline core
scaling_available_frequencies //软件支持的频率列表
scaling_available_governors //支持的策略列表
scaling_cur_freq //软件设置的当前频率,通常与cpuinfo_cpus相同,如果出现硬件问题可能导致不一致
scaling_driver //当前使用的driver
scaling_governor //当前使用的governor
scaling_max_freq //软件governor设置的最高频率
scaling_min_freq //软件governor设置的最低频率
scaling_setspeed //需将governor类型切换为userspace,才会出现,通过echo修改数值,会切换主频
- 设置
可以通过 echo配置scaling_governor,scaling_max_freq,scaling_min_freq
例如:echo 1400 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_min_freq
cpufreq编译配置
#CPU Frequency scaling
CONFIG_CPU_FREQ=y #主开关
#CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_DEFAULT_GOV_SCHEDUTIL=y #default gov任选某个宏打开即可,决定了cpufreq初始化使用的governor,后续可在init.rc修改文件结点
#CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_DEFAULT_GOV_PERFORMANCE=y
#CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_DEFAULT_GOV_ONDEMAND=y
CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_STAT=y #维测开关,查看cpufreq统计信息:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/stats
performance/powersave策略
performance/powersave策略都是静态频率,performance设置为最高频,powersave设置为最低频。在切换governor的时候配置好频率:
cpufreq_set_policy->cpufreq_governor_limits
Userspace策略
用户写文件节点/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed时,调用store_scaling_setspeed函数修改频率。
Interactive策略
重要概念
hispeed_freq:当CPU频率较低且负载突然超过go_hispeed_load时,CPU跳到此频率,如果在
go_hispeed_load:hispeed_freq对应的负载
min_sample_time:在降频前需要在当前频率运行保持的时间
sampling_rate:interative管理器的采样间隔
target_loads:为每个CPU频率设置理想的CPU负载,以负载+频率的数组形式存储,如75:800:80:900:85:1300: 90:1500:95,含义是负载75以下时频率为800MHz,75~80时,频率为900MHz。
above_hispeed_delay:频率升高时的需要保持的时间,以频率+时间的数组形式存储
调频基本流程
设置sched的回调函数,每次发生调度变化时设置一个irq_work任务,在irq_work中重新计算目标频率
gov_set_update_util->cpufreq_add_update_util_hook->cpufreq_update_util->update_util_handler->irq_work_queue->eval_target_freq->update_load==choose_freq
update_load:以CPU idle运行时间,计算移动平均频率
choose_freq:使用平均负载频率,预估合适的目标频率
static u64 update_load(struct interactive_cpu *icpu, int cpu)
{
struct interactive_tunables *tunables = icpu->ipolicy->tunables;
u64 now_idle, now, active_time, delta_idle, delta_time;
now_idle = get_cpu_idle_time(cpu, &now, tunables->io_is_busy); /* 系统启动之后CPU处于idle的总时间 */
delta_idle = (now_idle - icpu->time_in_idle); /* 本次与上次进入update_load之间,CPU处于idle的总时间 */
delta_time = (now - icpu->time_in_idle_timestamp); /* 本次与上次进入update_load时间只差 */
if (delta_time <= delta_idle)
active_time = 0;
else
active_time = delta_time - delta_idle;
icpu->cputime_speedadj += active_time * icpu->ipolicy->policy->cur; /* 移动平均值,代表CPU实际需要的频率值 */
icpu->time_in_idle = now_idle;
icpu->time_in_idle_timestamp = now;
return now;
}
/* Re-evaluate load to see if a frequency change is required or not */
static void eval_target_freq(struct interactive_cpu *icpu)
{
...
spin_lock_irqsave(&icpu->load_lock, flags);
now = update_load(icpu, smp_processor_id());
delta_time = (unsigned int)(now - icpu->cputime_speedadj_timestamp);
cputime_speedadj = icpu->cputime_speedadj;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&icpu->load_lock, flags);
spin_lock_irqsave(&icpu->target_freq_lock, flags);
do_div(cputime_speedadj, delta_time);
/* loadadjfreq = (cputime_speedadj + active_time * policy->cur) / delta_time *100 ≈ cur_load * cur_freq;表示在周期内CPU需要的平均负载频率 */
loadadjfreq = (unsigned int)cputime_speedadj * 100;
/* cpu_load = (cputime_speedadj / policy->cur + active_time ) / * delta_time) *100 ≈ active_time/delta_time*100≈cur_load;表示CPU平均负载*/
cpu_load = loadadjfreq / policy->cur;
....
/* choose_freq中使用loadadjfreq、target_loads的负载和频率,计算预期的频率 */
choose_freq(icpu, loadadjfreq);
...
}
/*
* If increasing frequencies never map to a lower target load then
* choose_freq() will find the minimum frequency that does not exceed its
* target load given the current load.
*/
static unsigned int choose_freq(struct interactive_cpu *icpu, unsigned int loadadjfreq)
{
struct cpufreq_policy *policy = icpu->ipolicy->policy;
struct cpufreq_frequency_table *freq_table = policy->freq_table;
unsigned int prevfreq, freqmin = 0, freqmax = UINT_MAX, tl;
unsigned int freq = policy->cur;
int index;
do {
prevfreq = freq;
tl = freq_to_targetload(icpu->ipolicy->tunables, freq); /* 根据目标freq返回目标负载 */
/*
* Find the lowest frequency where the computed load is less
* than or equal to the target load.
* target_frqe = loadadjfreq / tl = cur_freq * cur_load / tl; /* 根据这个公式逐渐收缩,多次调整找到最佳tl和目标freq */
*/
index = cpufreq_frequency_table_target(policy, loadadjfreq / tl, CPUFREQ_RELATION_L);
freq = freq_table[index].frequency;
if (freq > prevfreq) {
/* The previous frequency is too low */
...
} else if (freq < prevfreq) {
/* The previous frequency is high enough. */
...
}
/* If same frequency chosen as previous then done. */
} while (freq != prevfreq);
return freq;
}
Schedutil策略
基本思想
cpufreq_add_update_util_hook注册回调函数,当负载变化时通知调频
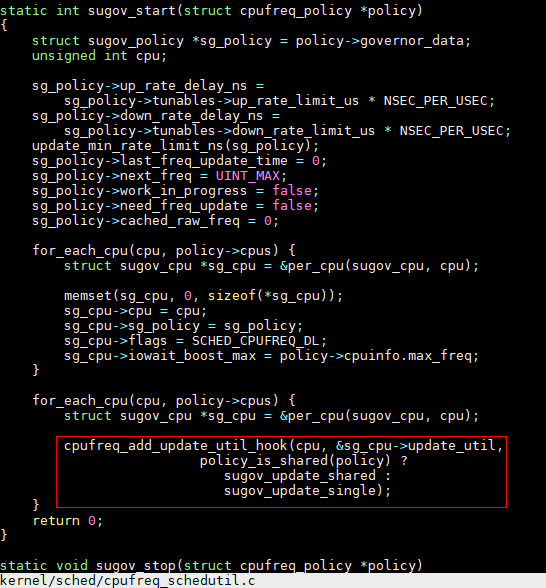
负载变化时调用这个函数
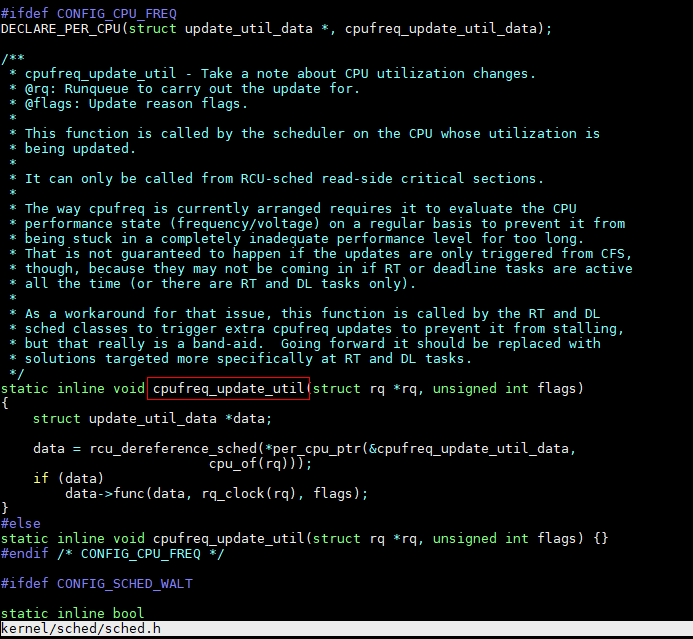



以下都会调用update_load_avg。
enqueue_entity
dequeue_entity
set_next_entity
put_prev_entity
entity_tick
enqueue_task_fair
dequeue_task_fair
update_blocked_averages
propagate_entity_cfs_rq
detach_entity_cfs_rq
attach_entity_cfs_rq
init_tg_cfs_entry
sched_group_set_shares
schedutil介绍
https://blog.csdn.net/wukongmingjing/article/details/81784727
根据下面文档做一下cpufreq的总结
Documentation/admin-guide/pm/cpufreq.rst
load和util的区别



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号