Linux内核学习:EXT4 文件系统在 Linux 内核系统中的读写过程【转】
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32473685/article/details/103494398
目录
2.3 sys_write( ) 的核心部分 vfs_write( )
2.5 generic_file_write_iter( )
2.6 __generic_file_write_iter( )
2.7.1 ext4文件系统address_space_operations
2.7.2 ext4文件系统delay allocation机制
2.7.3 执行完 generate_write_back( )后
1 概述
用户进程通过系统调用write()往磁盘上写数据,但write()执行结束后,数据是否 立即写到磁盘上?内核读文件数据时,使用到了“提前读”;写数据时,则使用了“延迟写”, 即write()执行结束后,数据并没有立即立即将请求放入块设备驱动请求队列,然后写到 硬盘上。
跟踪的时候通过
dump_stack重新编译linux内核,跟踪函数执行过程。
2 虚拟文件系统 与 Ext4 文件系统
首先文件系统在内核中的读写过程是在 sys_write( ) 中定义的。
2.1 sys_write( ) 代码跟踪
sys_write( ) 定义在 include/linux/syscalls.h 中:
asmlinkage long sys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user *buf, 568 size_t count);
sys_write( )的具体实现在 fs/read_write.c 中:
-
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
-
size_t, count)
-
{
-
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
-
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
-
if (f.file) {
-
loff_t pos = file_pos_read(f.file);
-
ret = vfs_write(f.file, buf, count, &pos);
-
if (ret >= 0)
-
file_pos_write(f.file, pos);
-
fdput_pos(f);
-
}
-
return ret;
-
}
2.2 sys_write( ) 过程分析
可以看出在实现 sys_write( ) 的时候,分为如下几步:
1) 根据打开文件号 fd找到该已打开文件file结构:
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);2) 读取当前文件的读写位置:
loff_t pos = file_pos_read(f.file);3) 写入:
ret = vfs_write(f.file, buf, count, &pos);4) 根据读文件结果,更新文件读写位置 :
file_pos_write(f.file, pos);2)和 4)可以作为写入之前和之后的对应操作来看,一个是读取当前文件的位置,一个是根据写文件的结果,更新文件的读写位置,主要代码还是在 fs/read_write.c 中:
-
static inline loff_t file_pos_read(struct file *file)
-
{
-
return file->f_pos;
-
}
-
-
static inline void file_pos_write(struct file *file, loff_t pos)
-
{
-
file->f_pos = pos;
-
}
3) 是整个 sys_write( ) 中最为重要的一部分,下面我们仔细分析一下这个函数。
2.3 sys_write( ) 的核心部分 vfs_write( )
-
ssize_t vfs_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos){
-
ssize_t ret;
-
-
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))
-
return -EBADF;
-
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_WRITE))
-
return -EINVAL;
-
if (unlikely(!access_ok(VERIFY_READ, buf, count)))
-
return -EFAULT;
-
ret = rw_verify_area(WRITE, file, pos, count);
-
if (ret >= 0) {
-
count = ret;
-
file_start_write(file);
-
if (file->f_op->write)
-
ret = file->f_op->write(file, buf, count, pos);
-
else if (file->f_op->aio_write)
-
ret = do_sync_write(file, buf, count, pos);
-
else
-
ret = new_sync_write(file, buf, count, pos);
-
if (ret > 0) {
-
fsnotify_modify(file);
-
add_wchar(current, ret);
-
}
-
inc_syscw(current);
-
file_end_write(file);
-
}
-
-
return ret;
-
}
首先函数在 rw_verify_area(WRITE, file, pos, count); 检查文件是否从当前位置 pos 开始的 count 字节是否对写操作加上了 “强制锁”,这是通过调用函数完成的。
通过合法性检查后,就调用具体文件系统 file_operations中 write 的方法。对于ext4文件系统,file_operations方法定义在 fs/ext4/file.c 中。从定义中可知 write 方法实现函数为 do_sync_write( )。
下面是ext4文件系统操作的数据结构:
-
const struct file_operations ext4_file_operations = {
-
.llseek = ext4_llseek,
-
.read = new_sync_read,
-
.write = new_sync_write,
-
.read_iter = generic_file_read_iter,
-
.write_iter = ext4_file_write_iter,
-
.unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
-
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
-
.compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
-
#endif
-
.mmap = ext4_file_mmap,
-
.open = ext4_file_open,
-
.release = ext4_release_file,
-
.fsync = ext4_sync_file,
-
.splice_read = generic_file_splice_read,
-
.splice_write = iter_file_splice_write,
-
.fallocate = ext4_fallocate,
-
};
下面是do_sync_write( )的具体代码,也在fs/read_write.c中:
-
ssize_t do_sync_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
-
{
-
struct iovec iov = { .iov_base = (void __user *)buf, .iov_len = len };
-
struct kiocb kiocb;
-
ssize_t ret;
-
init_sync_kiocb(&kiocb, filp);
-
kiocb.ki_pos = *ppos;
-
kiocb.ki_nbytes = len;
-
ret = filp->f_op->aio_write(&kiocb, &iov, 1, kiocb.ki_pos);
-
if (-EIOCBQUEUED == ret)
-
ret = wait_on_sync_kiocb(&kiocb);
-
*ppos = kiocb.ki_pos;
-
return ret;
-
}
-
EXPORT_SYMBOL(do_sync_write);
异步I/O允许用户空间来初始化操作而不必等待它们的完成,因此,一个应用程序可以在他的I/O处理进行中做其他的处理。
块和网络驱动在整个时间是完全异步的,因此只有字符驱动对于明确的异步I/O支持是候选的。实现异步I/O操作的file_operations方法,都使用I/O Control Block,其定义在 include/linux/aio.h中
定义了一个临时变量iov,这个变量记录了用户空间缓冲区地址buf和所要写的字节数len,用户空间的缓冲区地址buf是保存在iov中的。初始化异步I/O数据结构后,就用file_operations 中的aio_write方法。拓展到ext4文件中的时,该方法就是ext4_file_operations结构体中的ext4_file_write( )。
下面就具体到ext4的文件系统,这个函数也是aio_write( ) 的延展。
2.4 ext4_file_write( )
2.4.1 ext4文件系统的extent
Ext2/3等老Linux文件系统使用间接映射模式 (block mapping), 文件的每一个块都要被记录下来,这使得大文件操作(删除)效率低下。Ext4 引入extents这一概念来代替 Ext2/3 使用的传统的块映射方式。ext4中一个extent最大可以映射128MB的连续物理存储空间。
Ext3采用间接块映射,当操作大文件的时候,效率极其低下,比如一个100MB大小的文件,在Ext3中要建立25600个数据块的映射表,每个数据块大小为4KB,而Ext4引入了extents,每个extent为一组连续的数据块,上述文件表示为,该文件数据保存在接下来的25600个数据块中,提高了不少效率。
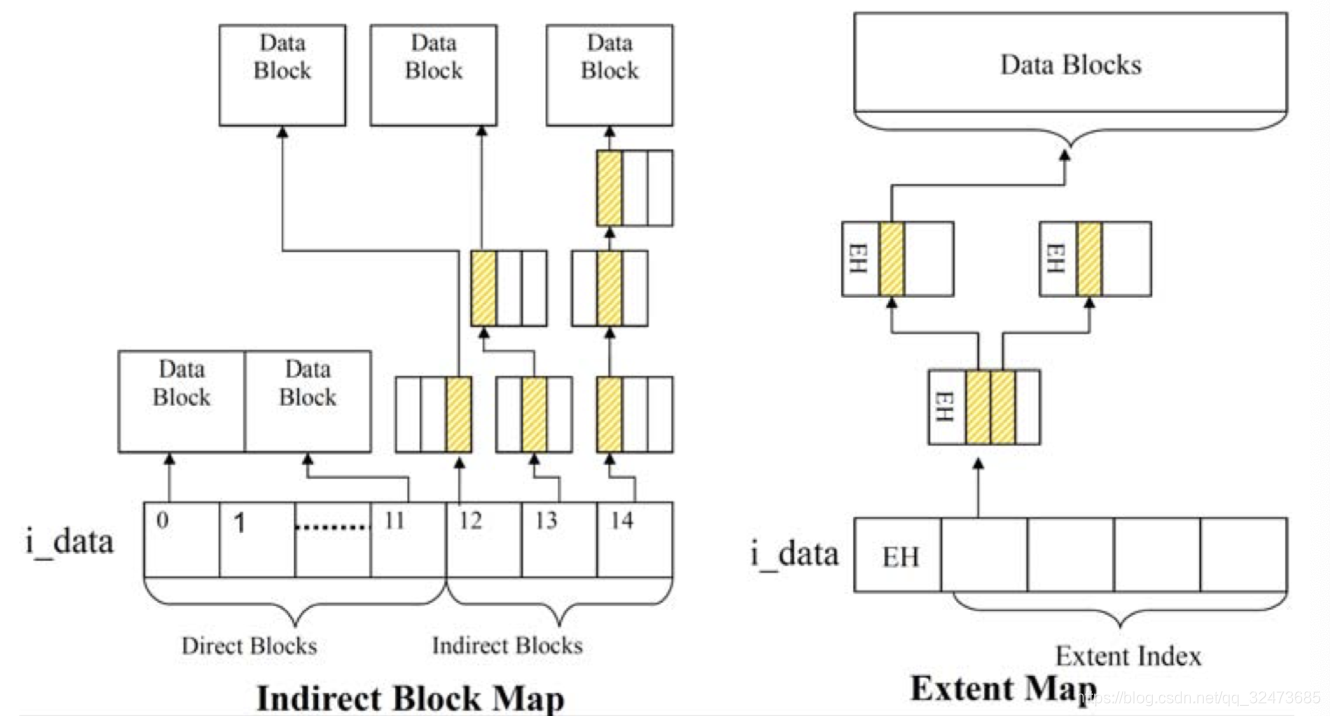
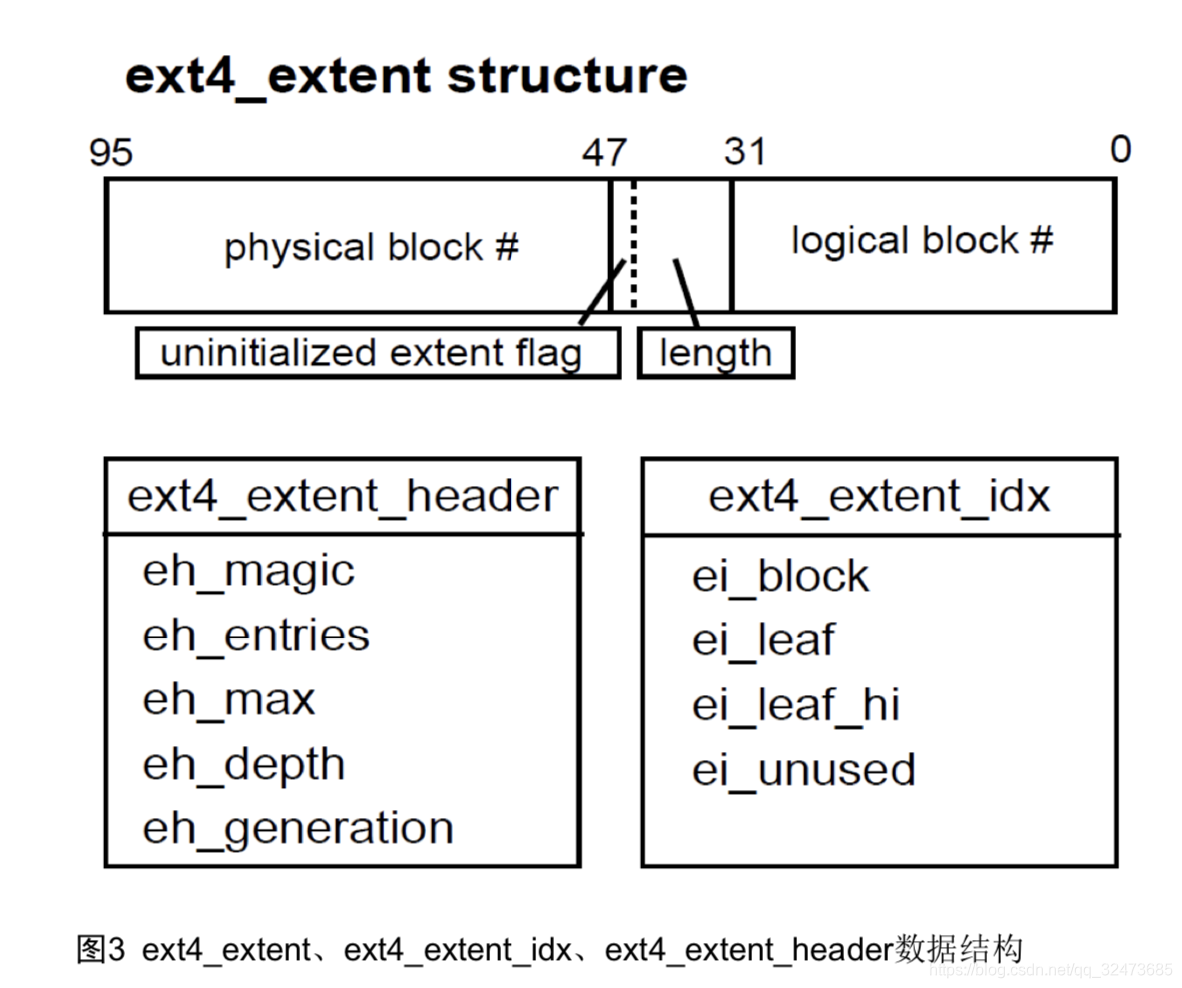
Extent模式主要数据结构包括ext4_extent, ext4_extent_idx, ext4_extent_header,均定义在文件fs/ext4/ext4_extents.h文件中。
-
/*
-
* This is the extent on-disk structure.
-
* It's used at the bottom of the tree.
-
*/
-
struct ext4_extent {
-
__le32 ee_block; /* first logical block extent covers */
-
__le16 ee_len; /* number of blocks covered by extent */
-
__le16 ee_start_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */
-
__le32 ee_start_lo; /* low 32 bits of physical block */
-
};
-
-
/*
-
* This is index on-disk structure.
-
* It's used at all the levels except the bottom.
-
*/
-
struct ext4_extent_idx {
-
__le32 ei_block; /* index covers logical blocks from 'block' */
-
__le32 ei_leaf_lo; /* pointer to the physical block of the next *
-
* level. leaf or next index could be there */
-
__le16 ei_leaf_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */
-
__u16 ei_unused;
-
};
-
-
/*
-
* Each block (leaves and indexes), even inode-stored has header.
-
*/
-
struct ext4_extent_header {
-
__le16 eh_magic; /* probably will support different formats */
-
__le16 eh_entries; /* number of valid entries */
-
__le16 eh_max; /* capacity of store in entries */
-
__le16 eh_depth; /* has tree real underlying blocks? */
-
__le32 eh_generation; /* generation of the tree */
-
};
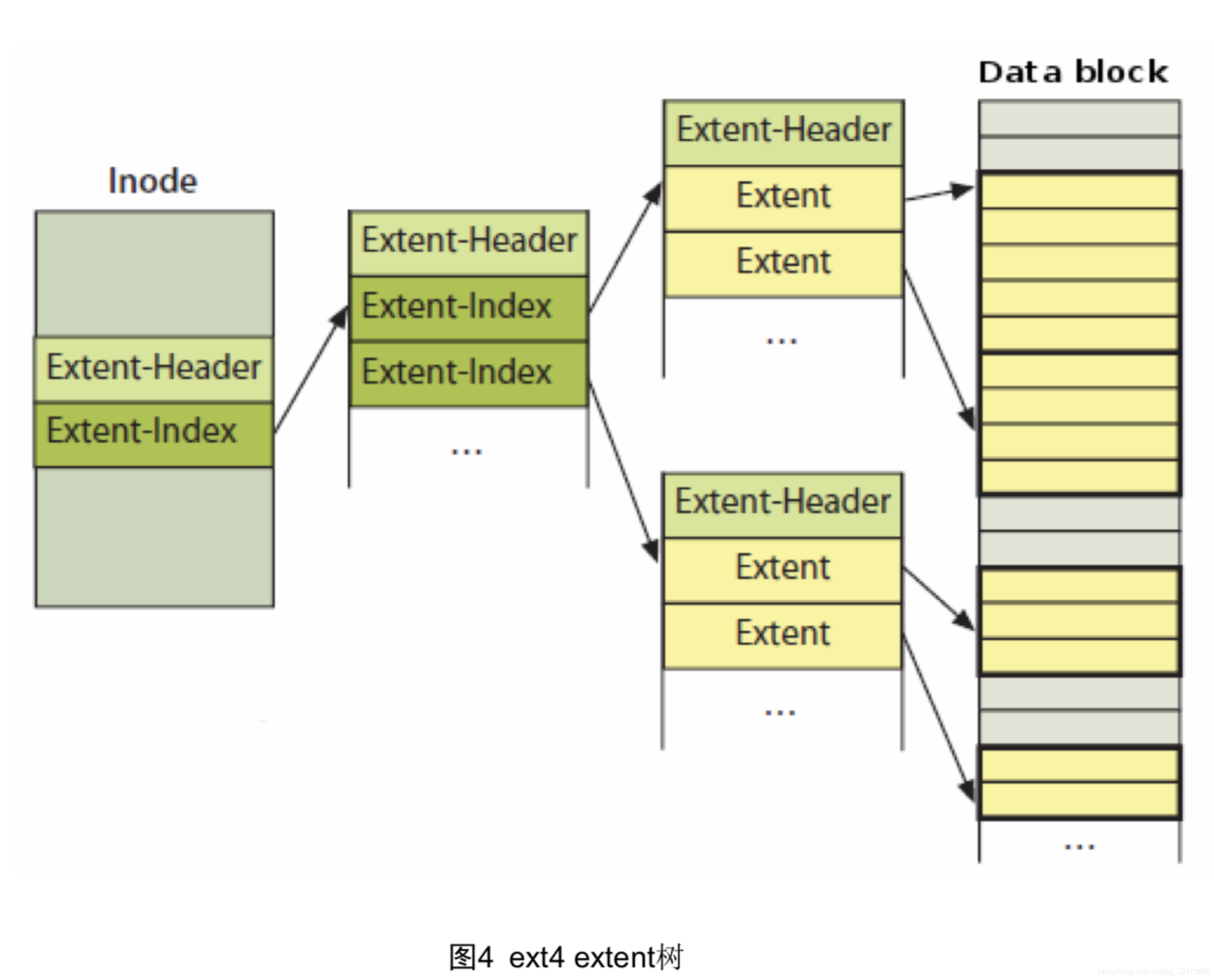
2.4.2 ext4_file_write( )
-
static ssize_t
-
ext4_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
-
{
-
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
-
struct inode *inode = file_inode(iocb->ki_filp);
-
struct mutex *aio_mutex = NULL;
-
struct blk_plug plug;
-
int o_direct = io_is_direct(file);
-
int overwrite = 0;
-
size_t length = iov_iter_count(from);
-
ssize_t ret;
-
loff_t pos = iocb->ki_pos;
-
-
/*
-
* Unaligned direct AIO must be serialized; see comment above
-
* In the case of O_APPEND, assume that we must always serialize
-
*/
-
if (o_direct &&
-
ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS) &&
-
!is_sync_kiocb(iocb) &&
-
(file->f_flags & O_APPEND ||
-
ext4_unaligned_aio(inode, from, pos))) {
-
aio_mutex = ext4_aio_mutex(inode);
-
mutex_lock(aio_mutex);
-
ext4_unwritten_wait(inode);
-
}
-
mutex_lock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
if (file->f_flags & O_APPEND)
-
iocb->ki_pos = pos = i_size_read(inode);
-
-
/*
-
* If we have encountered a bitmap-format file, the size limit
-
* is smaller than s_maxbytes, which is for extent-mapped files.
-
*/
-
if (!(ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS))) {
-
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi = EXT4_SB(inode->i_sb);
-
-
if ((pos > sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes) ||
-
(pos == sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes && length > 0)) {
-
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
ret = -EFBIG;
-
goto errout;
-
}
-
-
if (pos + length > sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes)
-
iov_iter_truncate(from, sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes - pos);
-
}
-
-
iocb->private = &overwrite;
-
if (o_direct) {
-
blk_start_plug(&plug);
-
/* check whether we do a DIO overwrite or not */
-
if (ext4_should_dioread_nolock(inode) && !aio_mutex &&
-
!file->f_mapping->nrpages && pos + length <= i_size_read(inode)) {
-
struct ext4_map_blocks map;
-
unsigned int blkbits = inode->i_blkbits;
-
int err, len;
-
-
map.m_lblk = pos >> blkbits;
-
map.m_len = (EXT4_BLOCK_ALIGN(pos + length, blkbits) >> blkbits)
-
- map.m_lblk;
-
len = map.m_len;
-
-
err = ext4_map_blocks(NULL, inode, &map, 0);
-
/*
-
* 'err==len' means that all of blocks has
-
* been preallocated no matter they are
-
* initialized or not. For excluding
-
* unwritten extents, we need to check
-
* m_flags. There are two conditions that
-
* indicate for initialized extents. 1) If we
-
* hit extent cache, EXT4_MAP_MAPPED flag is
-
* returned; 2) If we do a real lookup,
-
* non-flags are returned. So we should check
-
* these two conditions.
-
*/
-
if (err == len && (map.m_flags & EXT4_MAP_MAPPED))
-
overwrite = 1;
-
}
-
}
-
-
ret = __generic_file_write_iter(iocb, from);
-
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
-
if (ret > 0) {
-
ssize_t err;
-
err = generic_write_sync(file, iocb->ki_pos - ret, ret);
-
if (err < 0)
-
ret = err;
-
}
-
if (o_direct)
-
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
-
-
errout:
-
if (aio_mutex)
-
mutex_unlock(aio_mutex);
-
return ret;
-
}
首先检查文件是否为ext4的extent模式,若为传统的块映射方式,先检查文件是否过大。若当前文件位置加上待写的数据长度,大小若超过最大文件限制,则要做相应的调整,最终文件大小不能超过sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes。
-
if (!(ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS))) {
-
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi = EXT4_SB(inode->i_sb);
-
-
if ((pos > sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes) ||
-
(pos == sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes && length > 0)) {
-
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
ret = -EFBIG;
-
goto errout;
-
}
-
-
if (pos + length > sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes)
-
iov_iter_truncate(from, sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes - pos);
-
}
generic_file_aio_write( ) 就是ext4_file_write( )的主体执行语句,若I/O不是块对齐,写操作完成后,还要对i_aio_mutex解锁。
-
ret = __generic_file_write_iter(iocb, from);
-
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
-
if (ret > 0) {
-
ssize_t err;
-
err = generic_write_sync(file, iocb->ki_pos - ret, ret);
-
if (err < 0)
-
ret = err;
-
}
-
if (o_direct)
-
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
2.5 generic_file_write_iter( )
generic_file_aio_write( )源码如下:
-
/**
-
* generic_file_write_iter - write data to a file
-
* @iocb: IO state structure
-
* @from: iov_iter with data to write
-
*
-
* This is a wrapper around __generic_file_write_iter() to be used by most
-
* filesystems. It takes care of syncing the file in case of O_SYNC file
-
* and acquires i_mutex as needed.
-
*/
-
ssize_t generic_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
-
{
-
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
-
struct inode *inode = file->f_mapping->host;
-
ssize_t ret;
-
-
mutex_lock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
ret = __generic_file_write_iter(iocb, from);
-
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
-
if (ret > 0) {
-
ssize_t err;
-
-
err = generic_write_sync(file, iocb->ki_pos - ret, ret);
-
if (err < 0)
-
ret = err;
-
}
-
return ret;
-
}
-
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_file_write_iter);
在do_sync_write()中已经将当前文件写的起始位置记录在iocb->ki_pos。接下来执行主体函数__generic_file_write_iter( ),执行写操作前要加锁,完成后解锁,若写操作成功,就返回写完成的字节数,返回值大于0;写操作出现错误,就返回相应的错误码。接下来就要调用generic_write_sync()将数据刷新到硬盘上。
2.6 __generic_file_write_iter( )
-
/**
-
* __generic_file_write_iter - write data to a file
-
* @iocb: IO state structure (file, offset, etc.)
-
* @from: iov_iter with data to write
-
*
-
* This function does all the work needed for actually writing data to a
-
* file. It does all basic checks, removes SUID from the file, updates
-
* modification times and calls proper subroutines depending on whether we
-
* do direct IO or a standard buffered write.
-
*
-
* It expects i_mutex to be grabbed unless we work on a block device or similar
-
* object which does not need locking at all.
-
*
-
* This function does *not* take care of syncing data in case of O_SYNC write.
-
* A caller has to handle it. This is mainly due to the fact that we want to
-
* avoid syncing under i_mutex.
-
* 此功能完成了将数据实际写入文件所需的所有工作。它会进行所有基本检查,从文件中删除SUID,更新修改
-
* 时间并根据我们执行直接I/O还是标准缓冲写入来调用适当的子例程。除非我们在完全不需要锁定的块设备或
-
* 类似对象上工作,否则它预计将获取i_mutex。如果是O_SYNC写操作,此功能不会负责同步数据。呼叫者必
-
* 须处理它。这主要是由于我们要避免在i_mutex下进行同步。
-
*/
-
-
ssize_t __generic_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
-
{
-
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
-
struct address_space * mapping = file->f_mapping;
-
struct inode *inode = mapping->host;
-
loff_t pos = iocb->ki_pos;
-
ssize_t written = 0;
-
ssize_t err;
-
ssize_t status;
-
size_t count = iov_iter_count(from);
-
-
/* We can write back this queue in page reclaim */
-
current->backing_dev_info = inode_to_bdi(inode);
-
err = generic_write_checks(file, &pos, &count, S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode));
-
if (err)
-
goto out;
-
-
if (count == 0)
-
goto out;
-
iov_iter_truncate(from, count);
-
-
err = file_remove_suid(file);
-
if (err)
-
goto out;
-
-
err = file_update_time(file);
-
if (err)
-
goto out;
-
-
if (io_is_direct(file)) {
-
loff_t endbyte;
-
-
written = generic_file_direct_write(iocb, from, pos);
-
/*
-
* If the write stopped short of completing, fall back to
-
* buffered writes. Some filesystems do this for writes to
-
* holes, for example. For DAX files, a buffered write will
-
* not succeed (even if it did, DAX does not handle dirty
-
* page-cache pages correctly).
-
*/
-
if (written < 0 || written == count || IS_DAX(inode))
-
goto out;
-
-
pos += written;
-
count -= written;
-
-
status = generic_perform_write(file, from, pos);
-
/*
-
* If generic_perform_write() returned a synchronous error
-
* then we want to return the number of bytes which were
-
* direct-written, or the error code if that was zero. Note
-
* that this differs from normal direct-io semantics, which
-
* will return -EFOO even if some bytes were written.
-
*/
-
if (unlikely(status < 0)) {
-
err = status;
-
goto out;
-
}
-
iocb->ki_pos = pos + status;
-
/*
-
* We need to ensure that the page cache pages are written to
-
* disk and invalidated to preserve the expected O_DIRECT
-
* semantics.
-
*/
-
endbyte = pos + status - 1;
-
err = filemap_write_and_wait_range(file->f_mapping, pos, endbyte);
-
if (err == 0) {
-
written += status;
-
invalidate_mapping_pages(mapping,
-
pos >> PAGE_CACHE_SHIFT,
-
endbyte >> PAGE_CACHE_SHIFT);
-
} else {
-
/*
-
* We don't know how much we wrote, so just return
-
* the number of bytes which were direct-written
-
*/
-
}
-
} else {
-
written = generic_perform_write(file, from, pos);
-
if (likely(written >= 0))
-
iocb->ki_pos = pos + written;
-
}
-
out:
-
current->backing_dev_info = NULL;
-
return written ? written : err;
-
}
-
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__generic_file_write_iter);
更新检查后的实际可写入数据大小(大多数情况下不变,只有待写的数据超出文件大小限制,count值才会变化)。
generic_write_checks( )来检查对该文件的是否有相应的写权限,这个和系统中是否对文件大小有限制有关,将文件的suid标志清0,而且如果是可执行文件的话,就将sgid标志也清0,既然写文件,那么文件就会被修改(或创建),修改文件的时间是要记录在inode中的,并且将inode标记为脏(回写到磁盘上)。
若写方式为Direct IO,前面的工作都是一些合法性检查、记录文件改变、修改时间。而写文件的主要工作是调用函数 generic_perform_write( ) 来完成。
2.7 generic_perform_write( )
-
ssize_t generic_perform_write(struct file *file,
-
struct iov_iter *i, loff_t pos)
-
{
-
struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;
-
const struct address_space_operations *a_ops = mapping->a_ops;
-
long status = 0;
-
ssize_t written = 0;
-
unsigned int flags = 0;
-
-
/*
-
* Copies from kernel address space cannot fail (NFSD is a big user).
-
*/
-
if (!iter_is_iovec(i))
-
flags |= AOP_FLAG_UNINTERRUPTIBLE;
-
-
// 若当前I/O操作是属于在内核中进行,显然是不能被中断的(用户态的I/O操作可以被中断),就要设置AOP_FLAG_UNINTERRUPTIBLE标志
-
do {
-
struct page *page;
-
unsigned long offset; /* Offset into pagecache page */
-
unsigned long bytes; /* Bytes to write to page */
-
size_t copied; /* Bytes copied from user */
-
void *fsdata;
-
-
offset = (pos & (PAGE_CACHE_SIZE - 1));
-
bytes = min_t(unsigned long, PAGE_CACHE_SIZE - offset,
-
iov_iter_count(i));
-
// index:当前pos位置在pagecache的索引(以页面大小为单位)
-
// offset:为在页面内的偏移
-
// bytes:要从用户空间拷贝的数据大小
-
again:
-
/*
-
* Bring in the user page that we will copy from _first_.
-
* Otherwise there's a nasty deadlock on copying from the
-
* same page as we're writing to, without it being marked
-
* up-to-date.
-
*
-
* Not only is this an optimisation, but it is also required
-
* to check that the address is actually valid, when atomic
-
* usercopies are used, below.
-
*/
-
if (unlikely(iov_iter_fault_in_readable(i, bytes))) {
-
status = -EFAULT;
-
break;
-
}
-
-
// 调用索引节点(file->f_mapping)中address_space对象的write_begin方法,write_begin方法会为该页分配和初始化缓冲区首部,稍后,我们会详细分析ext4文件 系统实现的write_begin方法ext4_da_write_begin()。
-
-
status = a_ops->write_begin(file, mapping, pos, bytes, flags,
-
&page, &fsdata);
-
if (unlikely(status < 0))
-
break;
-
-
if (mapping_writably_mapped(mapping))
-
flush_dcache_page(page);
-
-
// mapping->i_mmap_writable 记录 VM_SHAREE 共享映射数。若mapping_writably_mapped()不等于0,则说明该页面被多个共享使用,调用flush_dcache_page()。flush_dcache_page()将dcache相应的page里的数据写到memory里去,以保证dcache内的数据与memory内的数据的一致性。但在x86架构中,flush_dcache_page() 的实现为空,不做任何操作。
-
-
copied = iov_iter_copy_from_user_atomic(page, i, offset, bytes);
-
flush_dcache_page(page);
-
-
status = a_ops->write_end(file, mapping, pos, bytes, copied,
-
page, fsdata);
-
if (unlikely(status < 0))
-
break;
-
copied = status;
-
-
cond_resched();
-
-
//将待写的数据拷贝到内核空间后,调用ext4文件系统的address_space_operations的 write_end方法。前面看到ext4文件系统有4种模式:writeback、ordered、journalled和delay allocation。加载ext4分区时,默认方式为delay allocation。对应的write_end方法为 ext4_da_write_end()。
-
cond_resched()检查当前进程的TIF_NEED_RESCHED标志,若该标志为设置,则 调用schedule函数,调度一个新程序投入运行。
-
-
iov_iter_advance(i, copied);
-
if (unlikely(copied == 0)) {
-
/*
-
* If we were unable to copy any data at all, we must
-
* fall back to a single segment length write.
-
*
-
* If we didn't fallback here, we could livelock
-
* because not all segments in the iov can be copied at
-
* once without a pagefault.
-
*/
-
bytes = min_t(unsigned long, PAGE_CACHE_SIZE - offset,
-
iov_iter_single_seg_count(i));
-
goto again;
-
}
-
//当a_ops->write_end()执行完成后,写数据操作完成了(注意,此时数据不一定真正写到磁盘上,因为大多数数据写为异步I/O)。接下来就要更新iov_iter结构体里的信息,包括文件的位置、写数据大小、数据所在位置。若copied值为0,说明没能将数据从用户态拷贝到内核态,就要再次尝试写操作。
-
pos += copied;
-
written += copied;
-
//更新文件位置pos和已完成写的数据大小
-
balance_dirty_pages_ratelimited(mapping);
-
if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {
-
status = -EINTR;
-
break;
-
}
-
} while (iov_iter_count(i));
-
//调用 balance_dirty_pages_ratelimited() 来检查页面Cache中的脏页比例是否超过一 个阀值(通常为系统中页的40%)。若超过阀值,就调用 writeback_inodes() 来刷新几十页到磁盘上
-
return written ? written : status;
-
}
-
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_perform_write);
2.7.1 ext4文件系统address_space_operations
2.7.2 ext4文件系统delay allocation机制
延时分配(Delayed allocation)该技术也称为allocate-on-flush,可以提升文件系统的性能。只有buffer I/O中每次写操作都会涉及的磁盘块分配过程推迟到数据回写时再进行,即数据将要被真正写入磁盘时,文件系统才为其分配块,这与其它文件系统在早期就分配好必要的块是不同的。另外,由于ext4的这种做法可以根据真实的文件大小做块分配决策,它还减少了碎片的产生。
通常在进行Buffer Write时,系统的实际操作仅仅是为这些数据在操作系统内分配内存页(page cache)并保存这些数据,等待用户调用fsync等操作强制刷新或者等待系统触发定时回写过程。在数据拷贝到page cache这一过程中,系统会为这些数据在磁盘上分配对应的磁盘块。
而在使用delalloc(delay allocation)后,上面的流程会略有不同,在每次buffer Write时,数据会被保存到page cache中,但是系统并不会为这些数据分配相应的磁盘块,仅仅会查询是否有已经为这些数据分配过磁盘块,以便决定后面是否需要为这些数据分配磁盘 块。在用户调用fsync或者系统触发回写过程时,系统会尝试为标记需要分配磁盘块的这些 数据分配磁盘块。这样文件系统可以为这些属于同一个文件的数据分配尽量连续的磁盘空间,从而优化后续文件的访问性能。
2.7.3 执行完 generate_write_back( )后
在generic_perform_write()函数执行完成后,我们应知道以下两点:
(1) 写数据已从用户空间拷贝到页面Cache中(内核空间);
(2) 数据页面标记为脏;
(3) 数据还未写到磁盘上去,这就是“延迟写”技术。后面我们会分析何时、在哪里、怎样将数据写到磁盘上的




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架