逆向工程 Python 逆向
逆向工程 Python 逆向
Salary python逆向
(选做)运行Salary.pyc,要求输出 flag 代表成功。
https://github.com/SKPrimin/HomeWork/tree/main/ReverseEngineering/lab1_python
直接运行发现RuntimeError,magic number,这是类UNIX系统上文件的前几个字节的内容,它标志着该文件的类型。
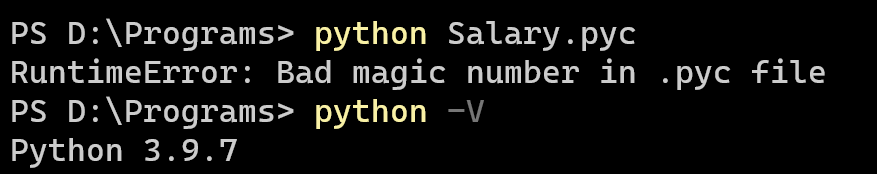
PS D:\Programs> python Salary.pyc
RuntimeError: Bad magic number in .pyc file
使用十六进制查看magic number,其为0x0D42 = 3394
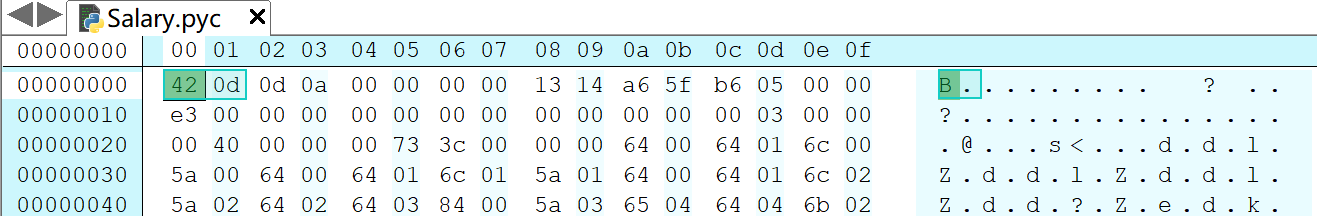
经过一番查找搜寻,我们发现所有的信息都在从importlib.util中的_RAW_MAGIC_NUMBER进入的配置文件里
# Python 3.7b5 3394 (restored docstring as the first stmt in the body;
# this might affected the first line number #32911)
此时我们当然可以直接下载python3.7版本,然后运行,但这不是捡了芝麻丢了西瓜吗?我们不能为了一题把整个电脑的配置环境搞得一团遭,好在此前我们曾经接触过anaconda,随后我们用如下命令创建一个python版本为3.7的虚拟环境:
conda create -n p37 python=3.7
经过一系列创建下载后,虚拟环境创建成功。
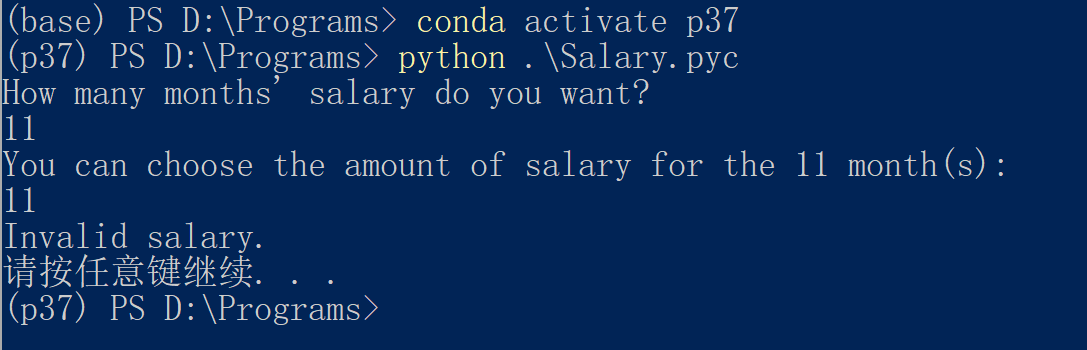
随后我们找到 anaconda自带的命令行,再次激活 p37并进入,能够成功运行,显然这需要逆向查看源代码。
(base) PS D:\Programs> conda info -e
# conda environments:
#
base * D:\Anaconda3
p37 D:\Anaconda3\envs\p37
conda activate p37
python Salary.pyc
我们直接使用uncompyle6反编译得到python代码,当然也可以在 https://tool.lu/pyc/ 网站上反编译
uncompyle6 Salary.pyc > Salary.py
对源代码做如下的分析
# uncompyle6 version 3.8.0
# Python bytecode 3.7.0 (3394)
# Decompiled from: Python 3.9.7 (default, Sep 16 2021, 16:59:28) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
# Embedded file name: Salary.py
# Compiled at: 2020-11-07 11:27:15
# Size of source mod 2**32: 1462 bytes
import hashlib, random, os
def run():
dword = [
465, 293, 555, 151, 760, 370, 315, 817, 676, 840, 976, 240, 660, 691, 218, 578, 80, 933, 786,
158, 622, 657, 952, 972, 924, 744, 635, 507, 451, 879]
s = ''
v12 = ''
seed = 0
print("How many months' salary do you want?")
# 第一个输入数据,循环次数,要求大于0
v5 = int(input())
if v5 <= 0:
print('You want too much!! Get Out!!')
return
print('You can choose the amount of salary for the', v5, 'month(s):')
for i in range(v5):
# 接收 v6 薪水数,取值(16, 65535)范围参与异或,一次则等效于直接赋值,低于16,seed直接出0
v6 = int(input())
if not v6 <= 16:
if v6 > 65535:
print('Invalid salary.')
return
seed = seed ^ v6
i = seed
v9 = 0
while True:
# i 不为0则参与运算
if i:
# v9 递增
v9 = v9 + 1
# i 同 i-1 与运算,根据性质,i为 2^n时直接清零,其余时:将二进制下最后一个1该为0
i &= i - 1
else:
break
# v9 必须等于 10,即要求i的二进制有 10 个 1,有多少个0无关紧要
if v9 != 10:
print("That's not for you.")
return
random.seed(seed) # 锁定随机数,随机数序列从此固定
v10 = hashlib.md5()
for i in range(30):
# 随机生成数字字符串并拼接
v9 = random.randint(0, 1000)
s = s + str(v9)
# md5.update 会将每次字符串拼接后再散列
v10.update(s.encode())
# v12 由随机数参与dword内容异或
v12 = v12 + chr(v9 ^ dword[i])
# 进行 MD5 验证,锁定只有一个能出来
v11 = v10.hexdigest()
if v11 != 'c29c475cae3bae204393f198b0cf33e3':
print('Try different salaries, Your decision is a bit hasty')
return
print("\nYou've chosen the most suitable salary and here is your reward: The flag is nullcon{", v12, '}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
os.system('pause')
# okay decompiling Salary.pyc
从此我们可知,我们需要得知seed的值,而seed值二进制表示中1的个数恒为10,这大大缩小了范围,如下是一种暴力破解方式。
import random
from hashlib import md5
seed = 1023
dword = [465, 293, 555, 151, 760, 370, 315, 817, 676, 840, 976, 240, 660, 691, 218, 578, 80, 933, 786, 158, 622, 657, 952, 972, 924, 744, 635, 507, 451, 879]
while seed:
if bin(seed).count('1') == 10:
s = ''
v12 = ''
random.seed(seed)
v10 = md5()
for i in range(30):
v9 = random.randint(0, 1000)
print(v9)
s = s + str(v9)
v10.update(s.encode())
v12 = v12 + chr(v9 ^ dword[i])
v11 = v10.hexdigest()
if v11 == 'c29c475cae3bae204393f198b0cf33e3':
print('seed = ',seed )
break
seed += 1
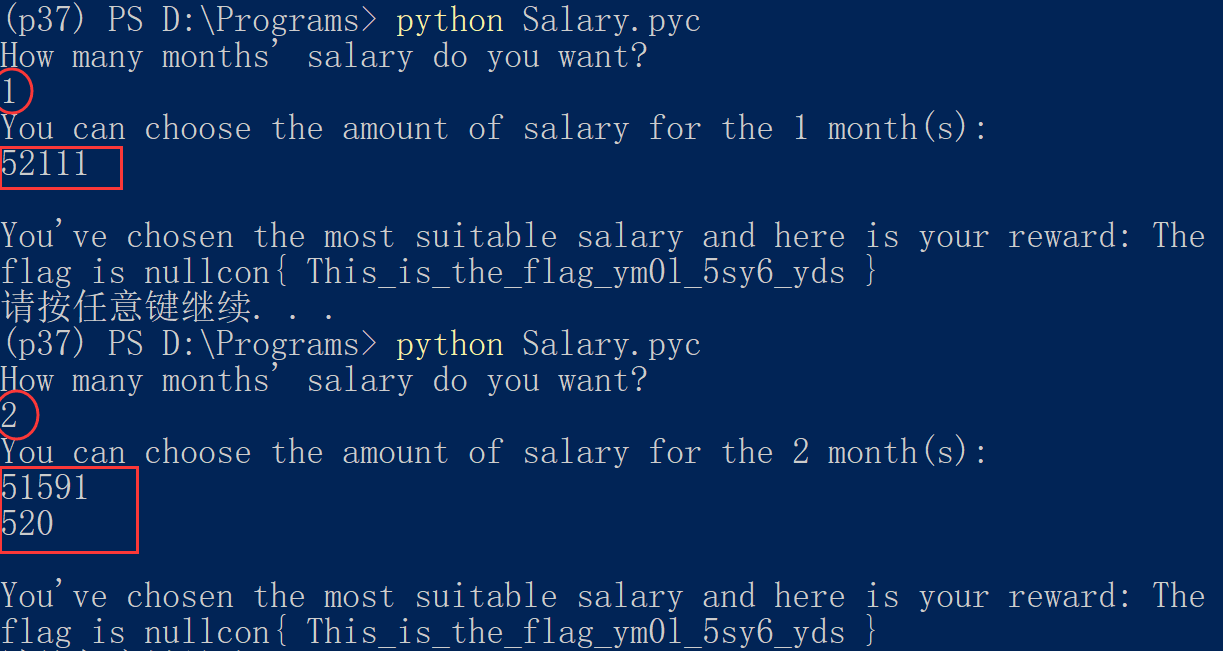
我们得到seed = 52111,即我们输入的几个数异或结果必须为52111。
我们可以轻而易举的找到无数个满足条件的数
1 52111
2 51591 520
……
elfpass 静态调试
把elfpass拷贝进seed虚拟机,设成root所有suid程序,用普通用户去攻击获得root权限。可以先静态分析,搞不定再用gdb动态调试。
直接使用IDA打开(后缀改为.elf),映入眼帘的缩略图显示这是一个只有主函数的简单程序。
进入主函数
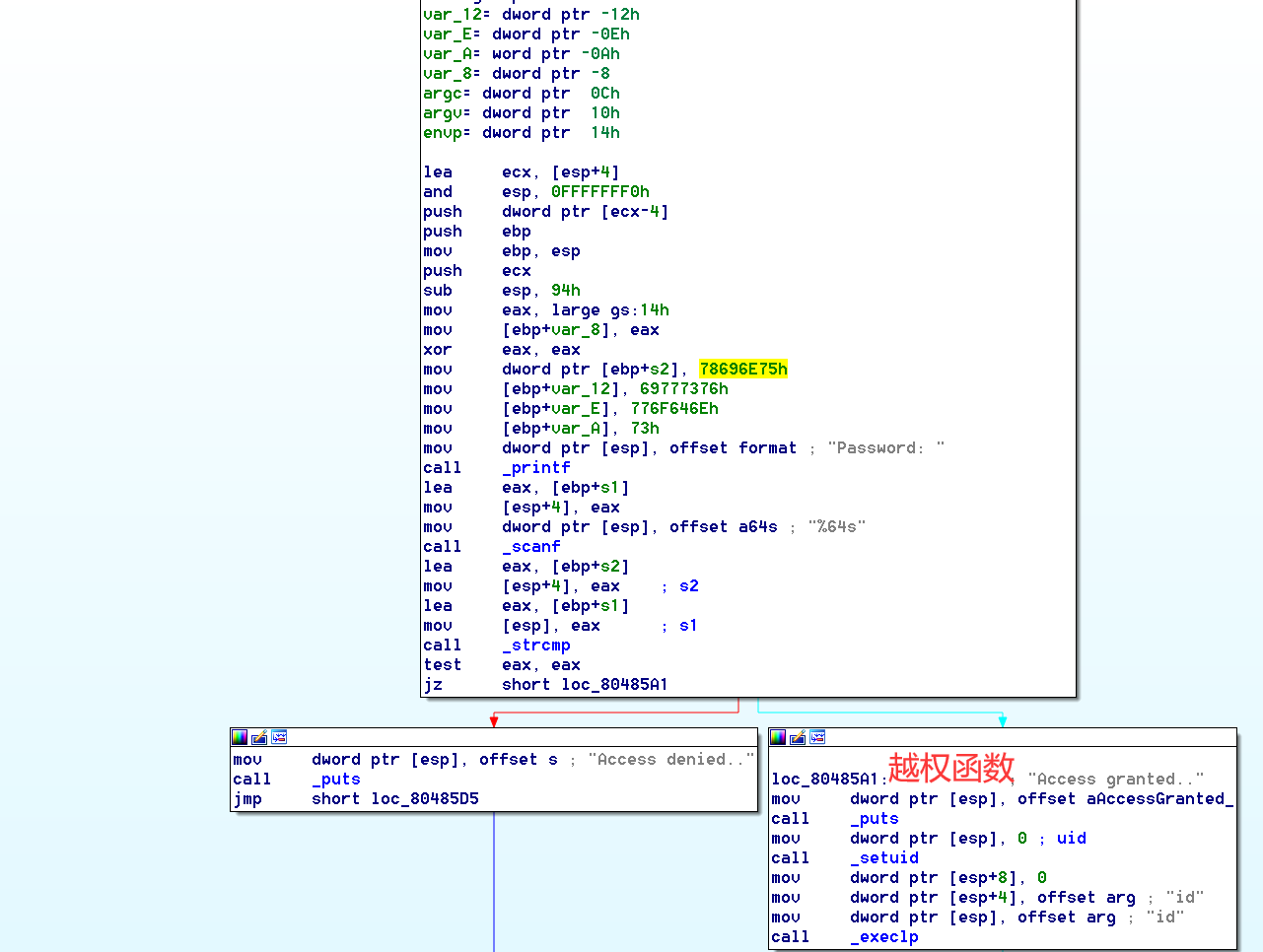
可见,程序进行了栈的初始化,开辟空间,并将几个数据压入栈中
.text:08048524 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
.text:08048524 public main
.text:08048524 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+17o
.text:08048524
.text:08048524 s1 = byte ptr -7Ah
.text:08048524 s2 = byte ptr -16h
.text:08048524 var_12 = dword ptr -12h
.text:08048524 var_E = dword ptr -0Eh
.text:08048524 var_A = word ptr -0Ah
.text:08048524 var_8 = dword ptr -8
.text:08048524 argc = dword ptr 0Ch
.text:08048524 argv = dword ptr 10h
.text:08048524 envp = dword ptr 14h
.text:08048524
.text:08048524 lea ecx, [esp+4]
.text:08048528 and esp, 0FFFFFFF0h
.text:0804852B push dword ptr [ecx-4]
.text:0804852E push ebp
.text:0804852F mov ebp, esp
.text:08048531 push ecx
.text:08048532 sub esp, 94h
.text:08048538 mov eax, large gs:14h
.text:0804853E mov [ebp+var_8], eax
.text:08048541 xor eax, eax
.text:08048543 mov dword ptr [ebp+s2], 78696E75h
.text:0804854A mov [ebp+var_12], 69777376h
.text:08048551 mov [ebp+var_E], 776F646Eh
.text:08048558 mov [ebp+var_A], 73h
_printf 和 _scanf即为输出函数与输入函数,可通过scanf参数%64s得知接收的是字符s1,并将收到的字符压入栈中
mov dword ptr [esp], offset format ; "Password: "
call _printf
lea eax, [ebp+s1]
mov [esp+4], eax
mov dword ptr [esp], offset a64s ; "%64s"
call _scanf
_strcmp函数为字符串比较函数,此处使用lea和mov将s2 s1的地址送入栈中,s2在初始化时即已经存在于栈中。
lea eax, [ebp+s2]
mov [esp+4], eax ; s2
lea eax, [ebp+s1]
mov [esp], eax ; s1
call _strcmp
而想要执行特权函数loc_80485A1就必须通过下面两条指令
test eax, eax
jz short loc_80485A1
est对两个参数(目标,源)执行AND逻辑操作,jz结果为0则设置ZF零标志为1,跳转。- 在此处意思即当eax的值等于0时跳转。
至此,我们大致可以推断出,该程序,将输入的字符与原有的进行对比,如果相同,则会跳转到特权函数。我们将字符值提取出来为。0x78696e75,0x69777376,0x776f646e,0x73转为字符即:xinu,iwsv,wodn,s
再转为正确的顺序,即可得到:unixvswindows
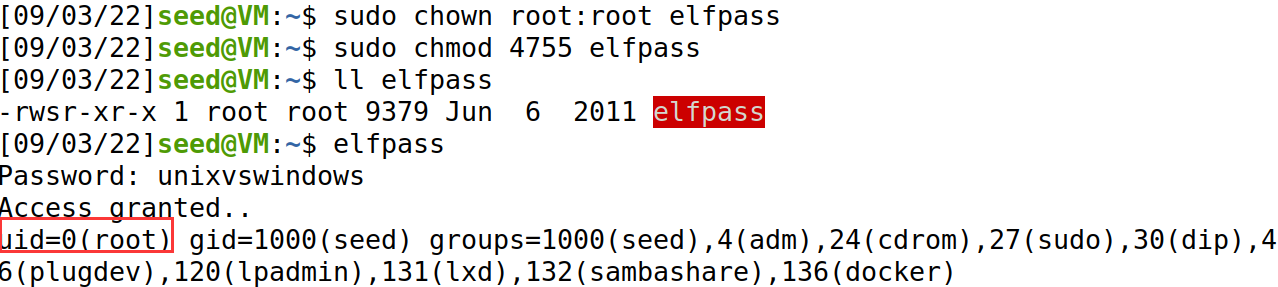
运行,获得root权限
sudo chown root:root elfpass
sudo chmod 4755 elfpass
elfpass
我们也可以找到主函数main,一键F5反汇编
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
int result; // eax@4
int v4; // edx@4
char s1; // [sp+1Eh] [bp-7Ah]@1
char s2[4]; // [sp+82h] [bp-16h]@1
int v7; // [sp+90h] [bp-8h]@1
v7 = *MK_FP(__GS__, 20);
strcpy(s2, "unixvswindows");
printf("Password: ");
scanf("%64s", &s1);
if ( !strcmp(&s1, s2) )
{
puts("Access granted..");
setuid(0);
execlp("id", "id", 0);
}
else
{
puts("Access denied..");
}
result = 0;
v4 = *MK_FP(__GS__, 20) ^ v7;
return result;
}
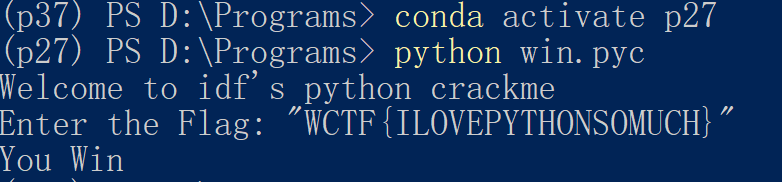
win python 逆向
3运行win.pyc,要求输出'You Win'代表成功。
uncompyle6 win.pyc > win.py
反编译得到如下所示:
# uncompyle6 version 3.8.0
# Python bytecode 2.7 (62211)
# Decompiled from: Python 3.9.7 (default, Sep 16 2021, 16:59:28) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
# Embedded file name: d:/idf.py
# Compiled at: 2014-12-21 10:28:24
def encrypt(key, seed, string):
rst = []
for v in string:
rst.append((ord(v) + seed ^ ord(key[seed])) % 255)
seed = (seed + 1) % len(key)
return rst
if __name__ == '__main__':
print "Welcome to idf's python crackme"
flag = input('Enter the Flag: ')
KEY1 = 'Maybe you are good at decryptint Byte Code, have a try!'
KEY2 = [124, 48, 52, 59, 164, 50, 37, 62, 67, 52, 48, 6, 1, 122, 3, 22, 72, 1, 1, 14, 46, 27, 232]
en_out = encrypt(KEY1, 5, flag)
if KEY2 == en_out:
print 'You Win'
else:
print 'Try Again !'
# okay decompiling win.pyc
通过分析关键过程
num = (ord(v) + seed ^ ord(key[seed])) % 255
num = (ord(v) + seed ^ ord(key[seed])) % 255
↓
ord(v) + seed = num ^ ord(key[seed]) %255
↓
ord(v) = ((num ^ key[seed]) % 255) - seed
得到解密核心
((num ^ key[seed]) % 255) - seed
写出解密程序
def decrypt(key, seed, KEY2):
rst = []
for num in KEY2:
rst.append(((num ^ key[seed]) % 255) - seed)
seed = (seed + 1) % len(key)
return rst
if __name__ == '__main__':
KEY1 = b'Maybe you are good at decryptint Byte Code, have a try!'
KEY2 = [124, 48, 52, 59, 164, 50, 37, 62, 67, 52, 48, 6, 1, 122, 3, 22, 72, 1, 1, 14, 46, 27, 232]
de_out = decrypt(KEY1, 5, KEY2)
s = ''.join([chr(i) for i in de_out])
print(s)
运行得到:
WCTF{ILOVEPYTHONSOMUCH}
随后接着使用anaconda创建python2.7的虚拟环境
conda create -n p27 python=2.7
conda activate p37
python Salary.pyc
crackme 逆向
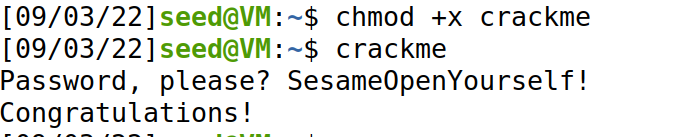
- (选做)crackme文件拷贝进seed虚拟机,运行,要求输出'Congratulations!'代表成功。
使用IDA静态调试,发现程序结构更为简单
发现关键函数
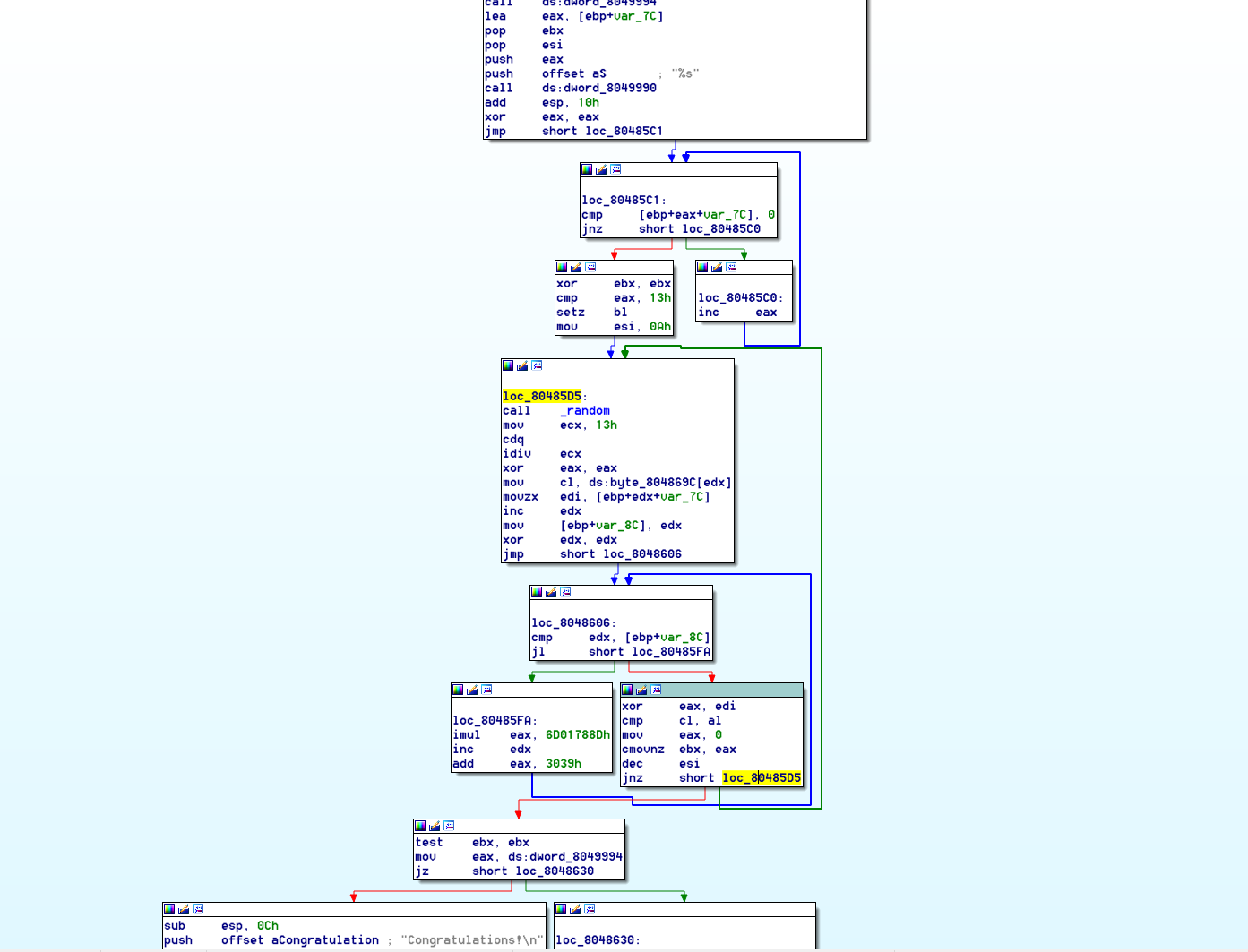
对其反编译发现,如下
int sub_8048591()
{
int i; // eax@1
int v1; // ebx@4
signed int v2; // esi@4
__int32 v3; // edx@5
int v4; // eax@5
char v5; // cl@5
char v6; // di@5
int v7; // edx@5
int result; // eax@12
int v9; // [sp+18h] [bp-8Ch]@5
char v10[124]; // [sp+28h] [bp-7Ch]@1
dword_8049994("Password, please? ");
dword_8049990("%s", v10);
for ( i = 0; v10[i]; ++i )
; // 获取 v10的长度
v1 = i == 19; // 判断 v10的长度是否为19
v2 = 10;
do
{
v3 = random() % 19;
v4 = 0;
v5 = byte_804869C[v3];
v6 = v10[v3];
v9 = v3 + 1;
v7 = 0;
while ( v7 < v9 ) //根据v3值确定v4值
{
++v7;
v4 = 1828812941 * v4 + 12345;
}
if ( v5 != ((unsigned __int8)v6 ^ (unsigned __int8)v4) ) //byte_804869C[v3] != v10[v3] ^ v4
v1 = 0;
--v2;
}
while ( v2 ); // 执行 v2=10 次循环
if ( v1 ) // 若 输入19个 且 byte_804869C[v3] == v10[v3] ^ v4 一直成立,成功
result = dword_8049994("Congratulations!\n");
else
result = dword_8049994("Oops..\n");
return result;
}
一路追查发现数组

推理
byte_array = [0x6a, 0xfb, 0x4c, 0x8d, 0x58, 0x0F, 0xD4, 0xE8, 0x94, 0x98, 0xEE, 0x6B, 0x18, 0x30, 0xE0, 0x55, 0xC5, 0x28, 0x0E, 0x90]
v4 = 0
result = []
for i in range(19):
v4 = -115 * v4 + 57
v4 &= 255
result.append(chr(byte_array[i] ^ v4))
print(''.join(result))
SesameOpenYourself!
赋权执行
chmod +x crackme
LEC RSA
cipher text
704796792, 752211152, 274704164, 18414022, 368270835, 483295235, 263072905, 459788476, 483295235, 459788476, 663551792, 475206804, 459788476, 428313374, 475206804, 459788476, 425392137, 704796792, 458265677, 341524652, 483295235, 534149509, 425392137, 428313374, 425392137, 341524652, 458265677, 263072905, 483295235, 828509797, 341524652, 425392137, 475206804, 428313374, 483295235, 475206804, 459788476, 306220148
{920139713,19}我们猜测可能是RSA的公钥{N, e},其中第一个数920139713 = 18443 × 49891两个质数相乘,第二个数是质数。更加印证了我们的猜想。随后逐个破解密文。
import gmpy2
cipher = [704796792, 752211152, 274704164, 18414022, 368270835, 483295235, 263072905, 459788476, 483295235, 459788476, 663551792, 475206804, 459788476, 428313374, 475206804, 459788476, 425392137, 704796792, 458265677, 341524652, 483295235, 534149509, 425392137, 428313374, 425392137, 341524652, 458265677, 263072905, 483295235, 828509797, 341524652, 425392137, 475206804, 428313374, 483295235, 475206804, 459788476, 306220148]
n = 920139713
e = 19
p, q = 49891, 18443
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = gmpy2.invert(e, phi)
for c in cipher:
print(chr(gmpy2.powmod(c, d, n)), end="")
得到
flag

