死锁的避免 银行家算法 java实现
死锁的避免 死锁的避免 银行家算法 java python 实现
实验内容
模拟进程的资源分配算法,了解死锁的产生和避免的办法。
实验目的
了解系统的资源分配情况,保证进程的资源请求和系统不会出现死锁。
实验题目
用银行家算法实现资源分配。
https://github.com/SKPrimin/HomeWork/tree/main/OperatingSystem/banker
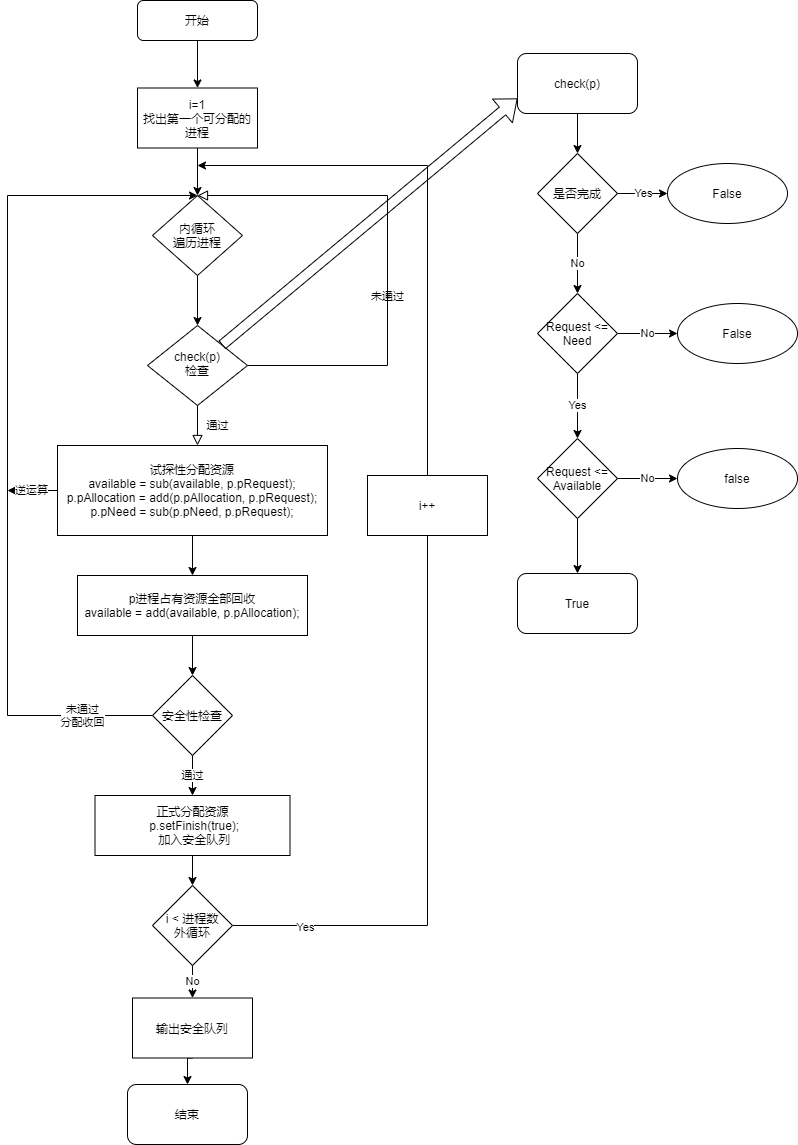
流程图
银行家算法核心流程图
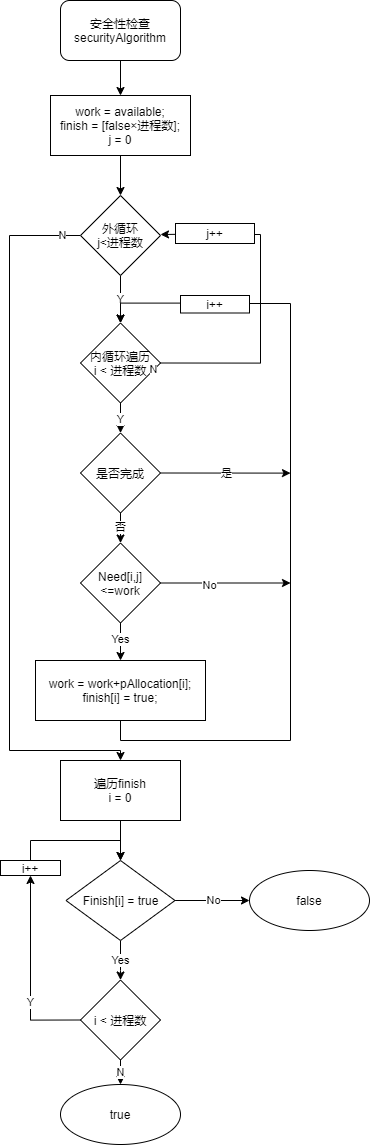
安全性检查流程图
数据结构及符号说明
Proces进程类
构造器设置为(String pName, int[] pMax, int[] pAllocation, int[] pNeed)。创建进程时必须有(进程名,最大资源需求向量,已分配资源向量,需要的资源向量)。
设置私有变量finish,表示完成状态,并附带你setter,getter方法实现状态查询与修改。
请求向量pRequest,默认为需求向量。
BlankerAlgorithm算法类
提供了向量加法add,向量减法sub,以及向量非负判断 nonNegative三个静态方法,无需创建实例即可使用。
check方法用于检测请求是否合法(不超过需求)以及是否能被满足(不超过可用资源)。传入进程p即可判断
securityAlgorithm方法即安全性检测。检测满足这个请求后资源是否还存在安全序列。需要传入进程队列以及当前可用资源
算法实现
java
进程类的定义
package com.process.banker;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author: SKPrimin
* @date: 2021/11/25 20:14
* @ClassName: Proces
* @Description: TODO 用于银行家算法中的进程定义
*/
public class Proces {
String pName;
int[] pMax;
int[] pAllocation;
int[] pNeed;
private boolean finish;
int[] pRequest;
public Proces(String pName, int[] pMax, int[] pAllocation, int[] pNeed) {
// 由于本次数据输入较多,容易出错,使用异常处理保证不会前功尽弃
if (pMax.length != pAllocation.length && pMax.length != pNeed.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入数据有误,三个数组必须长度一致");
}
if (!Arrays.equals(pNeed, BlankerAlgorithm.sub(pMax, pAllocation))) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入数据有误," + pName + "未满足Need" + Arrays.toString(pNeed) +
" = (Max - Allocation)" + Arrays.toString(BlankerAlgorithm.sub(pMax, pAllocation)));
}
this.pName = pName;
this.pMax = pMax;
this.pAllocation = pAllocation;
this.pNeed = pNeed;
this.pRequest = pNeed;
this.finish = false;
}
public boolean isFinish() {
return finish;
}
public void setFinish(boolean finish) {
this.finish = finish;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Proces{" +
"pName='" + pName + '\'' +
", pNeed=" + Arrays.toString(pNeed) +
", pAllocation=" + Arrays.toString(pAllocation) +
", pMax=" + Arrays.toString(pMax) +
", finish=" + finish +
", pRequest=" + Arrays.toString(pRequest) +
'}';
}
}
调度算法
package com.process.banker;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author: SKPrimin
* @date: 2021/11/25 19:13
* @ClassName: BlankerAlgorithm
* @Description: TODO 银行家算法,避免死锁 调度算法及其所使用的数组加减法,进程状态检测,试探调度后的安全性检测
*/
public class BlankerAlgorithm {
// 可用资源向量,
int[] available;
//创建一个银行家算法时必须有可用资源,禁止创建空实例
public BlankerAlgorithm(int[] available) {
this.available = available;
}
public void dispath(Proces[] pArr) {
// 先判断可用资源向量与进程的各向量长度是否一致
if (available.length != pArr[0].pAllocation.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("进程资源种类不适配");
}
ArrayList<String> securitySequence = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < pArr.length; i++) {
// 遍历整个队列
for (Proces p : pArr) {
// 先进行检查,通过后会试探性的分配资源
if (check(p)) {
// 打印当前进程调度信息
System.out.print(p.pName+ "检查通过" );
System.out.println("\t当前可用资源"+Arrays.toString(available));
System.out.println(p);
/*系统将资源调度给这个进程 从available分配给其 请求的资源
* 当前已分配的资源等于原分配的加上刚刚申请的
* 所需要的的资源减去已经申请到的
* */
available = sub(available, p.pRequest);
p.pAllocation = add(p.pAllocation, p.pRequest);
p.pNeed = sub(p.pNeed, p.pRequest);
// 该进程试探性调度完成,释放占有的所有资源
available = add(available, p.pAllocation);
// 如果通过安全性检查将正式分配资源,并将此进程设为完成态,添加到安全性队列中
if (securityAlgorithm(pArr, available)) {
System.out.println("试探分配"+p.pName+",通过安全性检查\n");
p.setFinish(true);
securitySequence.add(p.pName);
} else {
// 未通过安全性检查则试探分配作废,原样回退数据,进行下一个进程试调度
System.out.println("试探分配"+p.pName+",未通过安全性检查\n");
available = add(available, p.pRequest);
p.pAllocation = sub(p.pAllocation, p.pRequest);
p.pNeed = add(p.pNeed, p.pRequest);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("安全序列:{"+securitySequence+"}");
}
// 检查判断,检查p发出请求资源后Request <= Need 和 Request <= Available
public boolean check(Proces p) {
// 本进程未完成再继续检查
if (!p.isFinish()) {
// 如果 Request <= Need便继续检查,否则认为出错
if (nonNegative(sub(p.pNeed, p.pRequest))) {
// 如果Request <= Available ,即调度可行性检查通过,返回 true
return nonNegative(sub(available, p.pRequest));
}
return false;
}
return false;
}
// 安全性算法
public boolean securityAlgorithm(Proces[] pArr, int[] available) {
// 首先设置两个向量:工作向量work、Finish
// 工作向量work,表示系统可以提供给进程继续运行所需的各类资源数目,执行安全性算法开始时,work=available
int[] work = available;
/* Finish,表示系统是否有足够的资源分配给进程,使之运行完成,开始时Finish[i]=false;
* 布尔数组默认初始化恰好是false.当有足够资源分配给进程时,再令Finish[i] = true*/
boolean[] finish = new boolean[pArr.length];
//对所有进程进行一轮进行安全性检查,确保即使在最差的情况下也能遍历完全
for (int j = 0; j < pArr.length; j++) {
//在未试探的进程中先找到一个Need[i,j]<=work的进程,找到则进行分配,未找到做外出判断
for (int i = 0; i < pArr.length; i++) {
if (!finish[i] && nonNegative(sub(work, pArr[i].pNeed))) {
// 将释放的资源加入进work;本进行检查完成设为ture;退出本轮次循环,寻找下一个
work = add(work, pArr[i].pAllocation);
finish[i] = true;
}
}
}
// 如果有一个false,即不存在安全序列,返回false,全部通过检测才会返回true
for (boolean i : finish) {
if (!i) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 提供静态方法数组加法
public static int[] sub(int[] a, int[] b) {
int num = a.length;
int[] c = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
c[i] = a[i] - b[i];
}
return c;
}
// 加法静态方法数组减法
public static int[] add(int[] a, int[] b) {
int num = a.length;
int[] c = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
return c;
}
// 检测本向量是否非负,即用于检测两个矩阵相减结果是否符合,避免非法
public static boolean nonNegative(int[] array) {
for (int i : array) {
if (i < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试类
package com.process.banker;
/**
* @author: SKPrimin
* @date: 2021/11/25 19:29
* @ClassName: Test
* @Description: TODO 测试类 调用银行家算法
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Proces[] pArr = new Proces[5];
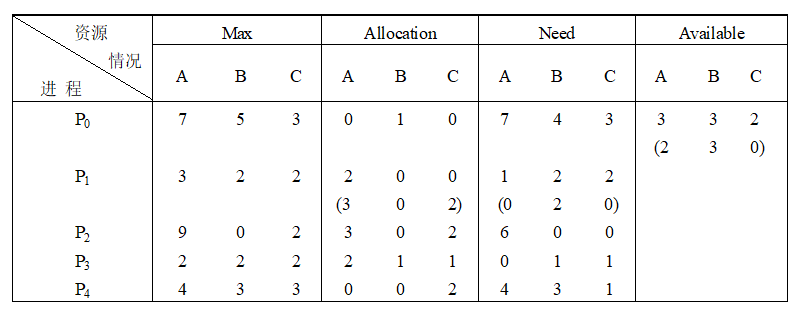
pArr[0] = new Proces("P0", new int[]{7, 5, 3}, new int[]{0, 1, 0}, new int[]{7, 4, 3});
pArr[1] = new Proces("P1", new int[]{3, 2, 2}, new int[]{2, 0, 0}, new int[]{1, 2, 2});
pArr[2] = new Proces("P2", new int[]{9, 0, 2}, new int[]{3, 0, 2}, new int[]{6, 0, 0});
pArr[3] = new Proces("P3", new int[]{2, 2, 2}, new int[]{2, 1, 1}, new int[]{0, 1, 1});
pArr[4] = new Proces("P4", new int[]{4, 3, 3}, new int[]{0, 0, 2}, new int[]{4, 3, 1});
BlankerAlgorithm ba = new BlankerAlgorithm(new int[]{3, 3,2});
ba.dispatch(pArr);
}
}
python
import copy
# 需要的是否小于可分配的
def NeedLessWork(nd, wk):
for i in range(len(wk)):
if nd[i] > wk[i]:
return False # 只要要一个资源不满足则返回False
return True
# 判断是否已经分配结束
def isFinish(finish):
for fns in finish:
if not fns:
return False # 只要有一个还未分配则表示未分配结束
return True
# 读取资源分配表文件的信息
def getinf(filename):
allocation = [] # 分配矩阵
need = [] # 需求矩阵
Max = [] # 最大需求矩阵
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
lines = fp.readlines()
num=lines[0].strip()
pronum=int(num[0])
rscnum=int(num[2])
for i in range(1, pronum + 1):
p = lines[i].strip() # 去掉换行符
p = list(map(lambda x: int(x), p.split()))
allocation.append(p[:rscnum])
need.append(p[rscnum:]) # 前半部分是已分配资源,后半部分是还需资源
maxi = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, p[:rscnum], p[rscnum:]))
Max.append(maxi)
available = lines[len(lines) - 1].strip() # 去掉换行符
available = list(map(lambda x: int(x), available.split())) # 可用资源
return Max, allocation, need, available
# 输出当前的资源分配情况
def printrsc(Max, allocation, need, available):
print('-------------当前的资源分配情况如下:----------------')
print('\t\t\tMax\t\t\tAllocation\t\t\tNeed\t\tAvailable')
print('P0\t\t{}\t\t{}\t\t{}\t\t{}'.format(Max[0], allocation[0], need[0], available))
for i in range(1, len(Max)):
print('P{}\t\t{}\t\t{}\t\t{}'.format(i, Max[i], allocation[i], need[i]))
print('----------------------------------------------------')
# 安全性算法
def safe_alg(need, allocation, available):
work = copy.deepcopy(available)
finish = [False] * len(need)
safe = [] # 存放安全序列
while not isFinish(finish):
i = 0
for i in range(len(need)):
if not finish[i] and NeedLessWork(need[i], work):
work = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, allocation[i], work)) # 分配资源后回收资源
finish[i] = True
safe.append(i)
i = 0 # 从头开始找可以分配资源的进程
break
if i == len(need):
break # 已经找不到可以分配资源的进程了
if isFinish(finish):
return safe
else:
return False # 未找到安全序列
# 银行家算法
def banker_alg(p, rqst, need, allocation, available):
if not NeedLessWork(rqst, need[p]) or not NeedLessWork(rqst, available):
return False
tempneed = copy.deepcopy(need)
tempalloc = copy.deepcopy(allocation)
# 假定给进程分配资源
work = list(map(lambda x, y: x - y, available, rqst))
tempneed[p] = list(map(lambda x, y: x - y, tempneed[p], rqst))
tempalloc[p] = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, tempalloc[p], rqst))
seq = safe_alg(tempneed, tempalloc, work)
if not seq:
return False
else:
return seq
# 主函数
def main():
filename = 'RAT.txt'
Max, allocation, need, available = getinf(filename)
printrsc(Max, allocation, need, available)
seq = safe_alg(need, allocation, available)
if seq:
print('当前状态的安全序列为:', end='')
for i in seq:
print('P' + str(i), end=' ')
else:
print('该状态不安全!')
return
while True:
print()
p = input('\n请输入申请资源的进程序号(输入的不是自然数则退出):')
if p.isdigit():
p = int(p)
else:
print('已退出!')
return
request = input('请输入该进程的请求资源向量(空格分隔):')
request = list(map(lambda x: int(x), request.split()))
seq = banker_alg(p, request, need, allocation, available)
if seq:
print('可将资源分配给该进程,分配后:')
need[p] = list(map(lambda x, y: x - y, need[p], request))
allocation[p] = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, allocation[p], request))
available = list(map(lambda x, y: x - y, available, request))
M = []
for i in range(len(need)):
maxi = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, need[i], allocation[i]))
M.append(maxi)
printrsc(M, allocation, need, available)
print('当前状态的安全序列为:', end='')
for i in seq:
print('P' + str(i), end=' ')
else:
print('不能将资源分配给该进程!')
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行结果
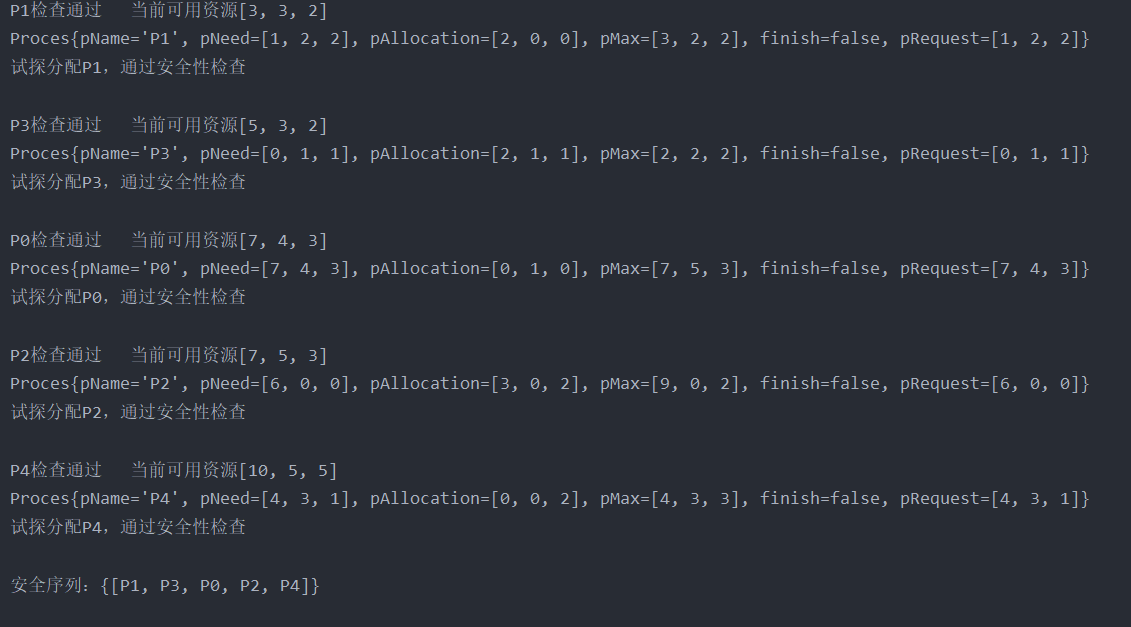
初值
(String pName, int[] pMax, int[] pAllocation, int[] pNeed)
("P0", new int[]{7, 5, 3}, new int[]{0, 1, 0}, new int[]{7, 4, 3});
("P1", new int[]{3, 2, 2}, new int[]{2, 0, 0}, new int[]{1, 2, 2});
("P2", new int[]{9, 0, 2}, new int[]{3, 0, 2}, new int[]{6, 0, 0});
("P3", new int[]{2, 2, 2}, new int[]{2, 1, 1}, new int[]{0, 1, 1});
("P4", new int[]{4, 3, 3}, new int[]{0, 0, 2}, new int[]{4, 3, 1});
P1检查通过 当前可用资源[3, 3, 2]
Proces{pName='P1', pNeed=[1, 2, 2], pAllocation=[2, 0, 0], pMax=[3, 2, 2], finish=false, pRequest=[1, 2, 2]}
试探分配P1,通过安全性检查
P3检查通过 当前可用资源[5, 3, 2]
Proces{pName='P3', pNeed=[0, 1, 1], pAllocation=[2, 1, 1], pMax=[2, 2, 2], finish=false, pRequest=[0, 1, 1]}
试探分配P3,通过安全性检查
P0检查通过 当前可用资源[7, 4, 3]
Proces{pName='P0', pNeed=[7, 4, 3], pAllocation=[0, 1, 0], pMax=[7, 5, 3], finish=false, pRequest=[7, 4, 3]}
试探分配P0,通过安全性检查
P2检查通过 当前可用资源[7, 5, 3]
Proces{pName='P2', pNeed=[6, 0, 0], pAllocation=[3, 0, 2], pMax=[9, 0, 2], finish=false, pRequest=[6, 0, 0]}
试探分配P2,通过安全性检查
P4检查通过 当前可用资源[10, 5, 5]
Proces{pName='P4', pNeed=[4, 3, 1], pAllocation=[0, 0, 2], pMax=[4, 3, 3], finish=false, pRequest=[4, 3, 1]}
试探分配P4,通过安全性检查
安全序列:{[P1, P3, P0, P2, P4]}