机器学习-Sequential(pytorch环境)
一个例子
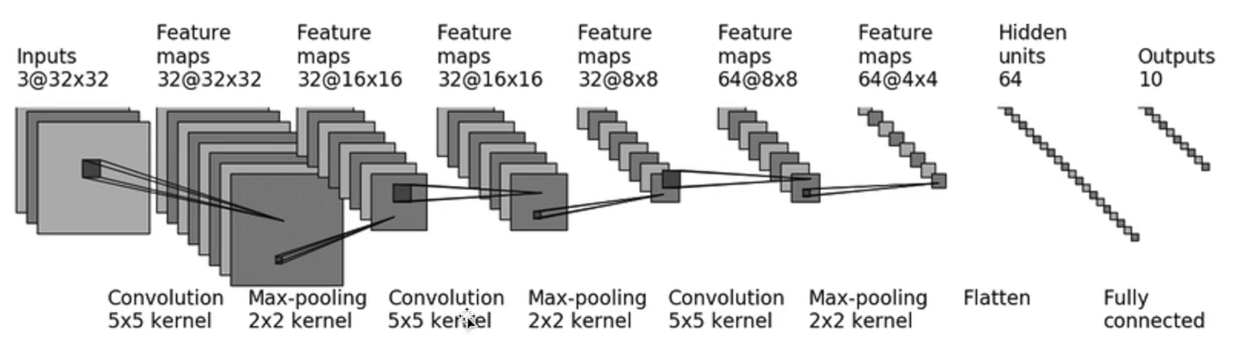
padding算法

代码
import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter class TuDui(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(TuDui, self).__init__() self.mod1 = Sequential( Conv2d(3,32,5,padding=2), MaxPool2d(2), Conv2d(32,32,5,padding=2), MaxPool2d(2), Conv2d(32,64,5,padding=2), MaxPool2d(2), Flatten(), # 如果不知道参数,可以通过print(output.shape)来获取 # 仅保留不知到参数的那行,后面的暂时注释 Linear(1024,64), Linear(64,10) ) def forward(self,x): x = self.mod1(x) return x tudui = TuDui() input = torch.ones((64,3,32,32)) output = tudui(input) writer = SummaryWriter("Seq") writer.add_graph(tudui,input) writer.close()
结果
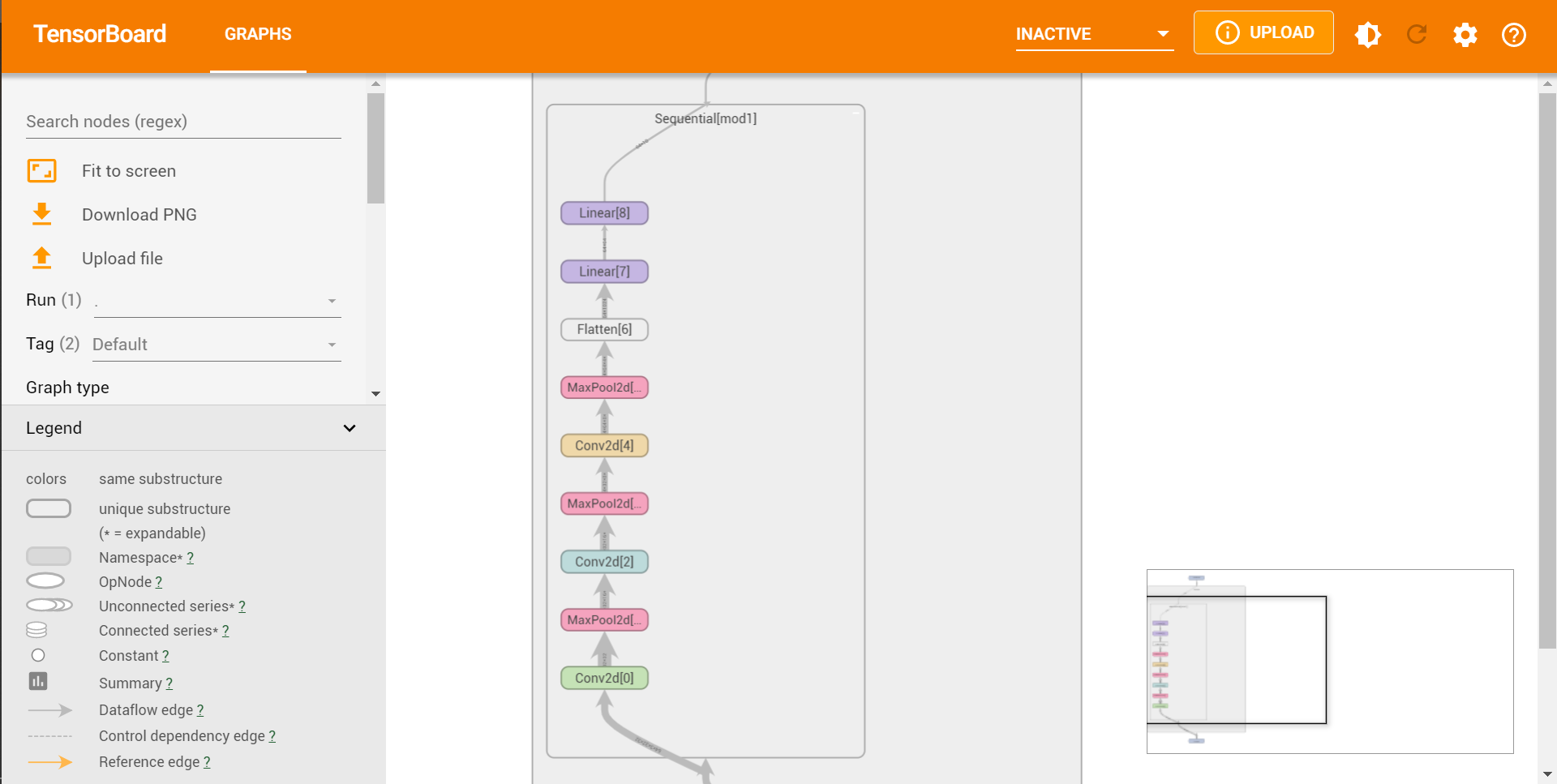
Sequential

class Sequential(Module): r"""A sequential container. Modules will be added to it in the order they are passed in the constructor. Alternatively, an ``OrderedDict`` of modules can be passed in. The ``forward()`` method of ``Sequential`` accepts any input and forwards it to the first module it contains. It then "chains" outputs to inputs sequentially for each subsequent module, finally returning the output of the last module. The value a ``Sequential`` provides over manually calling a sequence of modules is that it allows treating the whole container as a single module, such that performing a transformation on the ``Sequential`` applies to each of the modules it stores (which are each a registered submodule of the ``Sequential``). What's the difference between a ``Sequential`` and a :class:`torch.nn.ModuleList`? A ``ModuleList`` is exactly what it sounds like--a list for storing ``Module`` s! On the other hand, the layers in a ``Sequential`` are connected in a cascading way. Example:: # Using Sequential to create a small model. When `model` is run, # input will first be passed to `Conv2d(1,20,5)`. The output of # `Conv2d(1,20,5)` will be used as the input to the first # `ReLU`; the output of the first `ReLU` will become the input # for `Conv2d(20,64,5)`. Finally, the output of # `Conv2d(20,64,5)` will be used as input to the second `ReLU` model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1,20,5), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(20,64,5), nn.ReLU() ) # Using Sequential with OrderedDict. This is functionally the # same as the above code model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([ ('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1,20,5)), ('relu1', nn.ReLU()), ('conv2', nn.Conv2d(20,64,5)), ('relu2', nn.ReLU()) ])) """
writer.add_grahp()

def add_graph(self, model, input_to_model=None, verbose=False): # prohibit second call? # no, let tensorboard handle it and show its warning message. """Add graph data to summary. Args: model (torch.nn.Module): Model to draw. input_to_model (torch.Tensor or list of torch.Tensor): A variable or a tuple of variables to be fed. verbose (bool): Whether to print graph structure in console. """





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)