加密
加密算法
对称加密:加密解密使用同一个密钥。常用的有:DES、3DES、AES。
非对称加密:加密解密使用一对密钥,称为公钥和私钥。发信方用收信方的公钥加密原文,收信方收到密文后,用自己的私钥解密密文。常用的有:RSA、DSA、ECC。
散列算法:又称哈希算法,是一种单向加密算法。由于是不可逆的,当然不能用它来加密解密。它对不同长度的输入,产生固定长度的输出。常用的有MD5、SHA1、HMAC。
其他算法:Base64,编码算法,通常用于把二进制数据编码为可写字符串形式,如对img编码用于传输。
URLEncoder,也是一种编码算法,通常对含有特殊字符的url进行编码,如中文乱码。
Https,安全版的http,即http下加入SSL证书层。详细参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wqhwe/p/5407468.html
3DES(DESede或TDES)
基于DES,对一块数据用三种不同的密钥进行三次加密,强度高,速度快,适用于大部分加密的场合。
引入pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.xmlbeans</groupId>
<artifactId>xmlbeans</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
3des+Base64加密
import org.apache.xmlbeans.impl.util.Base64; import javax.crypto.*; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; /** * 3des加密 */ public final class Crypt { /** * 采用的加密算法 */ private static final String Algorithm = "DESede"; /** * 加密解密的密钥 */ private static final String PASSWORD_CRYPT_KEY = "shenjp199940320"; /** * 密钥对象 */ private static SecretKey secretKey = null; /** * 加密对象 */ private static Cipher encryptCipher = null; /** * 解密对象 */ private static Cipher decryptCipher = null; /** * 完成工具类的初始化 */ static { try { secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(build3DesKey(PASSWORD_CRYPT_KEY), Algorithm); // 加密工具始化 encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance(Algorithm); encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey); // 解密工具初始化 decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance(Algorithm); decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvalidKeyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 根据密匙进行DES加密 * * @param info 要加密的信息 * @return String 加密后的信息 */ public static String encryptToDES(String info) { byte[] cipherByte = null; try { cipherByte = encryptCipher.doFinal(info.getBytes("UTF-8")); } catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BadPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return new String(Base64.encode(cipherByte)); } /** * 根据密匙进行DES解密 * * @param info 要解密的密文 * @return String 返回解密后信息 */ public static String decryptByDES(String info) { if (decryptCipher == null) { throw new RuntimeException(); } byte[] cipherByte = null; try { byte[] decryptBytes = Base64.decode(info.getBytes("UTF-8")); cipherByte = decryptCipher.doFinal(decryptBytes); } catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BadPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return new String(cipherByte); } /* * 根据字符串生成密钥字节数组 * @param keyStr 密钥字符串 * @return * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ private static byte[] build3DesKey(String keyStr) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { byte[] key = new byte[24]; //声明一个24位的字节数组,默认里面都是0 byte[] temp = keyStr.getBytes("UTF-8"); //将字符串转成字节数组 /* * 执行数组拷贝 * System.arraycopy(源数组,从源数组哪里开始拷贝,目标数组,拷贝多少位) */ if (key.length > temp.length) { // 如果temp不够24位,则拷贝temp数组整个长度的内容到key数组中 System.arraycopy(temp, 0, key, 0, temp.length); } else { // 如果temp大于24位,则拷贝temp数组24个长度的内容到key数组中 System.arraycopy(temp, 0, key, 0, key.length); } return key; } public static void main(String[] args) { //加密 System.out.println(Crypt.encryptToDES("eland")); //解密 System.out.println(Crypt.decryptByDES("WHWPnQFcw1U=")); } }
AES
高级加密标准,是下一代的加密算法标准,速度快,安全级别高。
引入pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.xmlbeans</groupId>
<artifactId>xmlbeans</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
aes+base64加密
import org.apache.xmlbeans.impl.util.Base64; import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException; import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.util.Arrays; public class Aes { private static final String CHARSET_NAME = "utf-8"; private static final String algorithm = "AES"; public static String encrypt(String content, String password) { String result = null; try { SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(getPaddingPwd(password), algorithm); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key); byte[] byteContent = content.getBytes(CHARSET_NAME); byte[] encryptContent = cipher.doFinal(byteContent); byte[] base64Content = Base64.encode(encryptContent); result = new String(base64Content); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvalidKeyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BadPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } public static String decrypt(String content, String password) { String result = null; try { SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(getPaddingPwd(password), algorithm); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key); byte[] base64Content = content.getBytes(CHARSET_NAME); byte[] encryptContent = Base64.decode(base64Content); byte[] byteResult = cipher.doFinal(encryptContent, 0, encryptContent.length); result = new String(byteResult, CHARSET_NAME); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvalidKeyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BadPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } private static byte[] getPaddingPwd(String password) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { // 密码必须是16byte的整數倍 byte[] src = password.getBytes(CHARSET_NAME); int left = src.length % 16; if (left != 0) { byte[] dest = new byte[src.length + 16 - left]; // 目标数组中所有元素的值置0 Arrays.fill(dest, (byte) 0); System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, src.length); return dest; } return src; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Aes.encrypt("eland","shenjp19940320")); System.out.println(Aes.decrypt("WFvNX/0Ll3F1Ru0Jv0DtSA==","shenjp19940320")); } }
RSA
Git就是采用的这种加密算法
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.security.Key; import java.security.KeyPair; import java.security.KeyPairGenerator; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; public class Rsa { //默认公钥的持久化文件存放位置 private static String PUBLIC_KEY_FILE = "PublicKey"; //默认私钥的持久化文件存放位置 private static String PRIVATE_KEY_FILE = "PrivateKey"; //设置公私钥持久化文件的存放位置 public static void setKeyPath(String path) { if (PUBLIC_KEY_FILE.equals("PublicKey")) { PUBLIC_KEY_FILE = path + (path.endsWith("//")?"PublicKey":"/PublicKey"); PRIVATE_KEY_FILE = path + (path.endsWith("//")?"PrivateKey":"/PrivateKey"); } } //创建公私钥对 private static void createKeyPair() throws Exception { //使用RSA算法获得密钥对生成器对象keyPairGenerator KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); //设置密钥长度为1024 keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024); //生成密钥对 KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); //获取公钥 Key publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); //获取私钥 Key privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); //保存公钥对象和私钥对象为持久化文件 ObjectOutputStream oos1 = null; ObjectOutputStream oos2 = null; try { oos1 = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(PUBLIC_KEY_FILE)); oos2 = new ObjectOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(PRIVATE_KEY_FILE)); oos1.writeObject(publicKey); oos2.writeObject(privateKey); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { oos1.close(); oos2.close(); } } //RSA加密 public static String encryptWithRSA(String str) throws Exception { createKeyPair(); Key publicKey = null; //读取持久化的公钥对象 ObjectInputStream ois = null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(PUBLIC_KEY_FILE)); publicKey = (Key) ois.readObject(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { ois.close(); } //获取一个加密算法为RSA的加解密器对象cipher。 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); //设置为加密模式,并将公钥给cipher。 cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); //获得密文 byte[] secret = cipher.doFinal(str.getBytes()); //进行Base64编码 return new BASE64Encoder().encode(secret); } //RSA解密 public static String decryptWithRSA(String secret) throws Exception { Key privateKey; ObjectInputStream ois = null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(PRIVATE_KEY_FILE)); privateKey = (Key) ois.readObject(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { ois.close(); } Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); //传递私钥,设置为解密模式。 cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); //解密器解密由Base64解码后的密文,获得明文字节数组 byte[] b = cipher.doFinal(new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer(secret)); //转换成字符串 return new String(b); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //设置公私钥对存放路径,可选,默认是工程目录 //RSAUtils.setKeyPath(str); System.out.println("请输入明文:"); Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); String str =sca.nextLine(); System.out.println("============================"); String secret = Rsa.encryptWithRSA(str); System.out.println("经过RSA加密后的密文为:"); System.out.println(secret); System.out.println("============================"); String original = Rsa.decryptWithRSA(secret); System.out.println("经过RSA解密后的原文为:"); System.out.println(original); } }
md5
应用场景
1.密码校验
对于用户密码加密最高境界就是:别人获得你数据库的用户资料也没有办法获知密码.要达到就要有一套复杂的加密规则,比如:MD5(MD5(用户名+用户密码)+MD5(KEY+项目名+公司名))
2.参数校验
用于拦截不合法的请求,传递参数的时候带上MD5值、随机数、时间戳,后端根据 MD5=MD5(随机数+时间戳+MD5(KEY+公司名+项目名))进行校验,通过了才可以继续访问。
3.文件校验
判断文件是否被修改,判断图片是否完整等
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; import java.security.MessageDigest; public class Md5 { public static String encrptByMD5(String str) { MessageDigest md5 = null; String newPassw = null; try { // 确定计算方法 md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); BASE64Encoder base = new BASE64Encoder(); newPassw = base.encode(md5.digest(str.getBytes("UTF-8"))); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 加密后的字符 return newPassw; } public static void main(String[] args) { /** *现在网上有很多MD5解密工具 ,可以对密文进行拼接拼接 */ System.out.println(1 + "." + encrptByMD5("eland")); } }
Base64
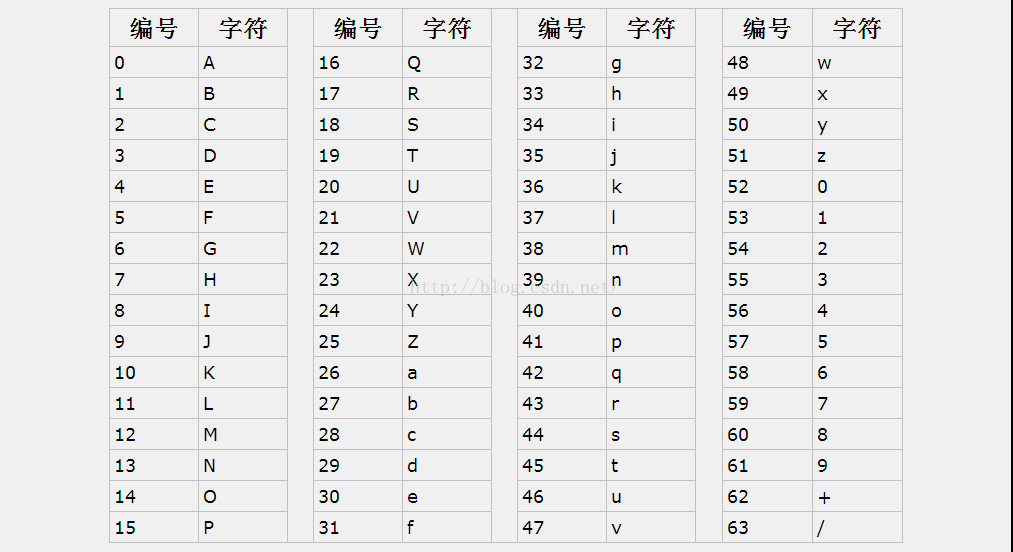
1.Base64每6个位元为一个单元,我们都知道一个字节8个位元,24=3*8=4*6,因此Base64编码后长度会比原来长1/3。
2.Base64的可用字符A-Z,a-z,0-9共62个字符,剩下的两个不同系统一般有所不同,经常为"+/"。
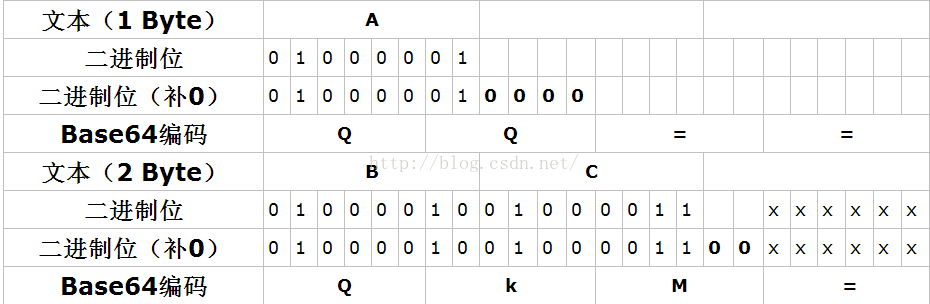
3.如果字节不是24的整数倍,Base64先加零凑够6位,剩下的用一个或两个=代替。为什么说一个或两个,因为多个8位转6位只会出现剩余2位和4位,,2位只需要一个表示6位的=即可变成24;4位需要两个表示6位的=即可变成24,如下图
Base64对图片编码解码
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; import java.io.*; public class Base64 { /** * @return * @Description: 根据图片地址转换为base64编码字符串 * @Author: * @CreateTime: */ public static String getImageStr(String imgFile) { InputStream inputStream = null; byte[] data = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(imgFile); data = new byte[inputStream.available()]; inputStream.read(data); inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 加密 BASE64Encoder encoder = new BASE64Encoder(); return encoder.encode(data); } /** * @param imgStr base64编码字符串 * @param path 图片路径-具体到文件 * @return * @Description: 将base64编码字符串转换为图片 * @Author: * @CreateTime: */ public static boolean generateImage(String imgStr, String path) { if (imgStr == null) return false; BASE64Decoder decoder = new BASE64Decoder(); try { byte[] b = decoder.decodeBuffer(imgStr); // 处理错误数据 for (int i = 0; i < b.length; ++i) { if (b[i] < 0) { b[i] += 256; } } OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(path); out.write(b); out.flush(); out.close(); return true; } catch (Exception e) { return false; } } /** * 示例 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String strImg = getImageStr("E:/3.jpg"); System.out.println(strImg); generateImage(strImg, "E:/4.jpg"); } }




