HotSpot 中 java 对象头
1.相关文档
|
官 方 文 档 |
Java HotSpot VM Options | https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/vmoptions-jsp.html |
|
open jdk 18 mark word源码 |
https://github.com/openjdk/jdk18/blob/master/src/hotspot/share/oops/markWord.hpp |
|
|
open jdk 18 klass word源码 |
https://github.com/openjdk/jdk18/blob/master/src/hotspot/share/oops/klass.hpp |
|
|
关于klass将被移除的草案 |
||
| open jdk 15 mark word源码 |
https://github.com/openjdk/jdk15/blob/e208d9aa1f185c11734a07 |
|
| Deprecate and Disable Biased Locking | https://openjdk.java.net/jeps/374 | |
|
其 它 文 档 |
baeldung | https://www.baeldung.com/java-memory-layout |
2.对象头
一个java对象在内存中除了有自身成员属性外,还有 锁信息、Hash码、对象年龄,class信息、数组长度等数据,它们称为对象头信息。
在HotSpot虚拟机中,对象头包含2个部分:
- mark word : 保存hashcode、锁信息、偏向锁状态、gc信息。
- class word :一个指针,指向本类元数据,它里面保存类的信息:类名、基类、修饰符等
- 数组长度 : 当变量为数组时,还要一个空间存放数组的长度。
3.查看jvm信息
@Test public void jvm() { out.println(VM.current().details()); }
结果:
# WARNING: Unable to get Instrumentation. Dynamic Attach failed. You may add this JAR as -javaagent manually, or supply -Djdk.attach.allowAttachSelf # WARNING: Unable to attach Serviceability Agent. You can try again with escalated privileges. Two options: a) use -Djol.tryWithSudo=true to try with sudo; b) echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM. # Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift. # Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift. # WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment! # WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE. # WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses. # Objects are 8 bytes aligned. # Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] # Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
其中后两行 (4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] )含义如下:
| \ | 引用 | booleans | byte | short | chars | int | float | long | double |
| 普通对象 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| 数组 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
HotSpot JVM 默认启用了指针压缩(-XX:+UseCompressedOops),所以引用的大小是4,未启用(-XX:-UseCompressedOops)时引用的大小是8。
4. mark word 信息
HotSpot 中对象按大端保存数据。保存hashcode、锁信息、偏向锁状态、gc信息。
4.1 open jdk 18 word
https://github.com/openjdk/jdk18/blob/master/src/hotspot/share/oops/markWord.hpp
// The markWord describes the header of an object. // // Bit-format of an object header (most significant first, big endian layout below): // // 32 bits: // -------- // hash:25 ------------>| age:4 unused_gap:1 lock:2 (normal object) // // 64 bits: // -------- // unused:25 hash:31 -->| unused_gap:1 age:4 unused_gap:1 lock:2 (normal object) // // - hash contains the identity hash value: largest value is // 31 bits, see os::random(). Also, 64-bit vm's require // a hash value no bigger than 32 bits because they will not // properly generate a mask larger than that: see library_call.cpp // // - the two lock bits are used to describe three states: locked/unlocked and monitor. // // [ptr | 00] locked ptr points to real header on stack // [header | 01] unlocked regular object header // [ptr | 10] monitor inflated lock (header is wapped out) // [ptr | 11] marked used to mark an object // [0 ............ 0| 00] inflating inflation in progress // // We assume that stack/thread pointers have the lowest two bits cleared. // // - INFLATING() is a distinguished markword value of all zeros that is // used when inflating an existing stack-lock into an ObjectMonitor. // See below for is_being_inflated() and INFLATING().
32 位机器:(大端)
| 00000101 00000000 00000000 0 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| hash(25位) | gc age(4位) | unused_gap(1位) | lock(2位) |
64位机器:(大端)
| 00000000 00000000 00000000 0 | 00000000 00000000 00000000 0000000 | 0 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| unused:25 | hash:31 | unused_gap:1 | age:4 | unused_gap:1 | lock(2位) |
其中 :
- hash :位保存hash值,无论32位机器还是64位机器,最大到31位。
- age : 如果对象在Survivor区复制一次,年龄增加1。当对象达到设定的阈值时,将会晋升到老年代。默认情况下,并行GC的年龄阈值为15,并发GC的年龄阈值为6。
- gap : 空白位
- lock :锁状态标记位
- unused:未使用位
| [ptr | 00] | locked | ptr points to real header on stack |
| [header | 01] | unlocked | regular object header |
| [ptr | 10] | monitor | inflated lock (header is wapped out) |
| [ptr | 11] | marked | used to mark an object |
| [0 ............ 0| 00] | inflating | inflation in progress |
4.2 open jdk 15 word
// The markWord describes the header of an object. // // Bit-format of an object header (most significant first, big endian layout below): // // 32 bits: // -------- // hash:25 ------------>| age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object) // JavaThread*:23 epoch:2 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object) // // 64 bits: // -------- // unused:25 hash:31 -->| unused_gap:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object) // JavaThread*:54 epoch:2 unused_gap:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object) // // - hash contains the identity hash value: largest value is // 31 bits, see os::random(). Also, 64-bit vm's require // a hash value no bigger than 32 bits because they will not // properly generate a mask larger than that: see library_call.cpp // and c1_CodePatterns_sparc.cpp. // // - the biased lock pattern is used to bias a lock toward a given // thread. When this pattern is set in the low three bits, the lock // is either biased toward a given thread or "anonymously" biased, // indicating that it is possible for it to be biased. When the // lock is biased toward a given thread, locking and unlocking can // be performed by that thread without using atomic operations. // When a lock's bias is revoked, it reverts back to the normal // locking scheme described below. // // Note that we are overloading the meaning of the "unlocked" state // of the header. Because we steal a bit from the age we can // guarantee that the bias pattern will never be seen for a truly // unlocked object. // // Note also that the biased state contains the age bits normally // contained in the object header. Large increases in scavenge // times were seen when these bits were absent and an arbitrary age // assigned to all biased objects, because they tended to consume a // significant fraction of the eden semispaces and were not // promoted promptly, causing an increase in the amount of copying // performed. The runtime system aligns all JavaThread* pointers to // a very large value (currently 128 bytes (32bVM) or 256 bytes (64bVM)) // to make room for the age bits & the epoch bits (used in support of // biased locking). // // [JavaThread* | epoch | age | 1 | 01] lock is biased toward given thread // [0 | epoch | age | 1 | 01] lock is anonymously biased // // - the two lock bits are used to describe three states: locked/unlocked and monitor. // // [ptr | 00] locked ptr points to real header on stack // [header | 0 | 01] unlocked regular object header // [ptr | 10] monitor inflated lock (header is wapped out) // [ptr | 11] marked used to mark an object // // We assume that stack/thread pointers have the lowest two bits cleared.
32位:(大端)
| 00000000 00000000 00000000 0 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| hash:25 | age:4 | biased_lock:1 | lock:2 |
| 00000000 00000000 0000000 | 00 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| JavaThread*:23 | epoch:2 | age:4 | biased_lock:1 | lock:2 |
64位:(大端)
| 00000000 00000000 00000000 0 | 00000000 00000000 00000000 0000000 | 0 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| unused:25 | hash:31 | unused_gap:1 | age:4 | biased_lock:1 | lock:2 |
| 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 000000 | 00 | 0 | 0000 | 0 | 00 |
| JavaThread*:54 | epoch:2 | unused_gap:1 | age:4 | biased_lock:1 | lock:2 |
其中:
- hash :位保存hash值,无论32位机器还是64位机器,最大到31位。
- age : 如果对象在Survivor区复制一次,年龄增加1。当对象达到设定的阈值时,将会晋升到老年代。默认情况下,并行GC的年龄阈值为15,并发GC的年龄阈值为6。
- gap : 空白位
- biased_lock:偏向锁标记,为1时表示对象启用偏向锁,为0时表示对象没有偏向锁
- lock :锁状态标记位
- JavaThread*:持有偏向锁的线程指针。
- epoch:偏向时间戳
4.3 open jdk 18 与 15 区别
对比发现:
- open jdk18 中不在对象头里区分biased_object还是normal object,默认不打开biased locking.可通过XX:+UseBiasedLocking打开。
- 没有了 biased_lock、epoch、JavaThread*
- 具体参见 源码:https://github.com/openjdk/jdk18
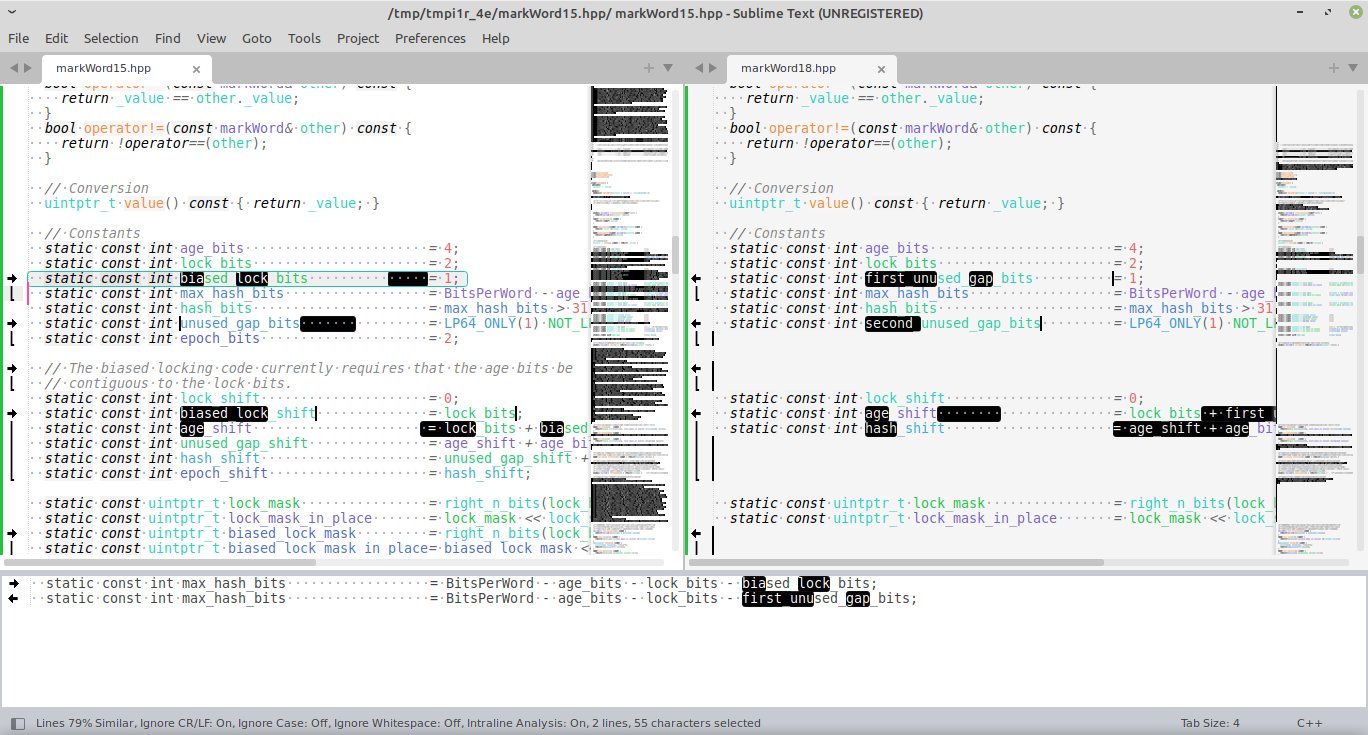
详细可参看官方文档:
https://openjdk.java.net/jeps/374
4.4 hash值示例
@Test public void hash(){ class A {} final A a = new A(); ClassLayout layout = ClassLayout.parseInstance(a); out.println(VM.current().details()); out.println("**** Fresh object"); out.println(layout.toPrintable()); out.println("hashCode: " + Integer.toHexString(a.hashCode())); out.println(); out.println("**** After identityHashCode()"); out.println(layout.toPrintable()); }
结果
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM. # Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift. # Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift. # WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment! # WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE. # WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses. # Objects are 8 bytes aligned. # Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] # Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] **** Fresh object com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$8A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) a3 63 03 20 (10100011 01100011 00000011 00100000) (537093027) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$8A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total hashCode: 455b6df1 **** After identityHashCode() com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$8A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 01 f1 6d 5b (00000001 11110001 01101101 01011011) (1533931777) 4 4 (object header) 45 00 00 00 (01000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (69) 8 4 (object header) a3 63 03 20 (10100011 01100011 00000011 00100000) (537093027) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$8A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
当调用对象的hashCode()或者System.identityHashCode(obj) 函数时,才生成hash值,保存在相应的hash位中。
- 上述代码第9行,第1次打印对象头,这时并没有调用hashCode()函数,并没有生成相应的值,
- 第11行调用了hashCode(),其值为:0x45456df1
- 第14行再次打印对象布局时,发现在对象头中已经保存了对应的值。
4.5 锁信息示例
/* * This is another dive into the mark word. * * This one is the example of thin (displaced) lock. The data * in mark word when lock is acquired is the reference to the * displaced object header, allocated on stack. Once we leave * the lock, the displaced header is discarded, and mark word * is reverted to the default value. * * This example relies on biased locking not biasing the object * at the first lock acquisition. Since JDKs up to 8 have biased * locking startup delay, this example works out of the box there. * On modern JDKs, starting with 9, this example should be run * with with -XX:-UseBiasedLocking. */ @Test public void thin_locking(){ class A { /* no fields */ } final A a = new A(); ClassLayout layout = ClassLayout.parseInstance(a); out.println(VM.current().details()); out.println("**** Fresh object"); out.println(layout.toPrintable()); synchronized (a) { out.println("**** With the lock"); out.println(layout.toPrintable()); } out.println("**** After the lock"); out.println(layout.toPrintable()); }
结果
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM. # Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift. # Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift. # WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment! # WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE. # WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses. # Objects are 8 bytes aligned. # Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] # Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] **** Fresh object com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$10A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 0d 00 00 00 (00001101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (13) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 0a d6 02 20 (00001010 11010110 00000010 00100000) (537056778) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$10A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total **** With the lock com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$10A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 0d 98 01 b0 (00001101 10011000 00000001 10110000) (-1342072819) 4 4 (object header) ed 7f 00 00 (11101101 01111111 00000000 00000000) (32749) 8 4 (object header) 0a d6 02 20 (00001010 11010110 00000010 00100000) (537056778) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$10A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total **** After the lock com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$10A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 0d 98 01 b0 (00001101 10011000 00000001 10110000) (-1342072819) 4 4 (object header) ed 7f 00 00 (11101101 01111111 00000000 00000000) (32749) 8 4 (object header) 0a d6 02 20 (00001010 11010110 00000010 00100000) (537056778) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$10A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
4.6 对象age信息
volatile Object consumer; @Test public void gc_age(){ Object instance = new Object(); long lastAddr = VM.current().addressOf(instance); ClassLayout layout = ClassLayout.parseInstance(instance); for (int i = 0; i < 10_000; i++) { long currentAddr = VM.current().addressOf(instance); if (currentAddr != lastAddr) { System.out.println(layout.toPrintable()); } for (int j = 0; j < 10_000; j++) { consumer = new Object(); } lastAddr = currentAddr; } }
结果:
java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 11 00 00 00 (00010001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (17) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 19 00 00 00 (00011001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (25) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 21 00 00 00 (00100001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (33) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 29 00 00 00 (00101001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (41) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 31 00 00 00 (00110001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (49) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 39 00 00 00 (00111001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (57) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 41 00 00 00 (01000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (65) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 49 00 00 00 (01001001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (73) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 51 00 00 00 (01010001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (81) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 59 00 00 00 (01011001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (89) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total java.lang.Object object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 61 00 00 00 (01100001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (97) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 00 02 00 20 (00000000 00000010 00000000 00100000) (536871424) 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
注意结果中age位中值的变化
11 00 00 00 (00010001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (17) ^^^^ 19 00 00 00 (00011001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (25) ^^^^ 21 00 00 00 (00100001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (33) ^^^^ 29 00 00 00 (00101001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (41) ^^^^ 31 00 00 00 (00110001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (49) ^^^^ 39 00 00 00 (00111001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (57) ^^^^ 41 00 00 00 (01000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (65) ^^^^ 49 00 00 00 (01001001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (73) ^^^^ 51 00 00 00 (01010001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (81) ^^^^ 59 00 00 00 (01011001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (89) ^^^^ 61 00 00 00 (01100001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (97) ^^^^
5. class word 信息
5.1 作用
一个指针,指向本类元数据,它里面保存类的信息:类名、基类、修饰符等。在64位机器上如果可压缩,那么为32位。
The klass word in the object header points to the internal type metadata for the object. This word can be 64 bits, or if compressed, 32 bits.
5.2 示例
/* * This is the example to have insight into object headers. * * In HotSpot, object header consists of two parts: mark word, * and class word. We can clearly see the class word by analysing * two empty instances of two distinct classes. See the difference * in class word, that difference is the reference to class. */ @Test //10 ClassWord public void class_word(){ class A { /* no fields */ } class B { /* no fields */ } out.println(VM.current().details()); out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new A()).toPrintable()); out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new A()).toPrintable()); out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new B()).toPrintable()); }
结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM. # Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift. # Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift. # WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment! # WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE. # WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses. # Objects are 8 bytes aligned. # Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] # Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$7A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 15 63 03 20 (00010101 01100011 00000011 00100000) (537092885) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$7A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$7A object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 15 63 03 20 (00010101 01100011 00000011 00100000) (537092885) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$7A.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$5B object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 90 65 03 20 (10010000 01100101 00000011 00100000) (537093520) 12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$5B.this$0 (object) Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
其中:
- 代码中new了两个A类对象,一个B类对象。
- 两个A对象指向相同的类元数据。
- A与B指向不同的类元数据。
5.3 注意事项:klass word 将被移除的草案

具体见:
https://openjdk.java.net/jeps/8198332
6.对象头中数组的长度
除了mark word 和 klass word 外,数组的对象头中还需要4个字节保存数组元素的个数。
/* * The example for array length. * * Array length is not the part of array type, so VMs need another * slot in header to store the array length. This can be demonstrated * by this example. */ @Test //11 public void array_length(){ out.println(VM.current().details()); for (int c = 0; c < 8; c++) { out.println("**** int[" + c + "]"); out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new int[c]).toPrintable()); } }
结果
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM. # Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift. # Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift. # WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment! # WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE. # WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses. # Objects are 8 bytes aligned. # Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] # Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes] **** int[0] [I object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298) 12 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 16 0 int [I.<elements> N/A Instance size: 16 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total **** int[1] [I object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298) 12 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 16 4 int [I.<elements> N/A 20 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 24 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total **** int[2] [I object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298) 12 4 (object header) 02 00 00 00 (00000010 00000000 00000000 00000000) (2) 16 8 int [I.<elements> N/A Instance size: 24 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total **** int[3] [I object internals: OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298) 12 4 (object header) 03 00 00 00 (00000011 00000000 00000000 00000000) (3) 16 12 int [I.<elements> N/A 28 4 (loss due to the next object alignment) Instance size: 32 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
其中的
12 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0) 12 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1) 12 4 (object header) 02 00 00 00 (00000010 00000000 00000000 00000000) (2) 12 4 (object header) 03 00 00 00 (00000011 00000000 00000000 00000000) (3)
就是4个数组的长度。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 【杂谈】分布式事务——高大上的无用知识?