HotSpot 中 java 对象布局
1.官方文档
| 源码、示例 | https://github.com/openjdk/jol |
| plugin for IntelliJ Idea | https://github.com/stokito/IdeaJol |
2.使用IntelliJ Idea 插件
2.1 线上安装
Settings/Preferences > --> Plugins --> Marketplace --> Search for "JOL" --> Install Plugin
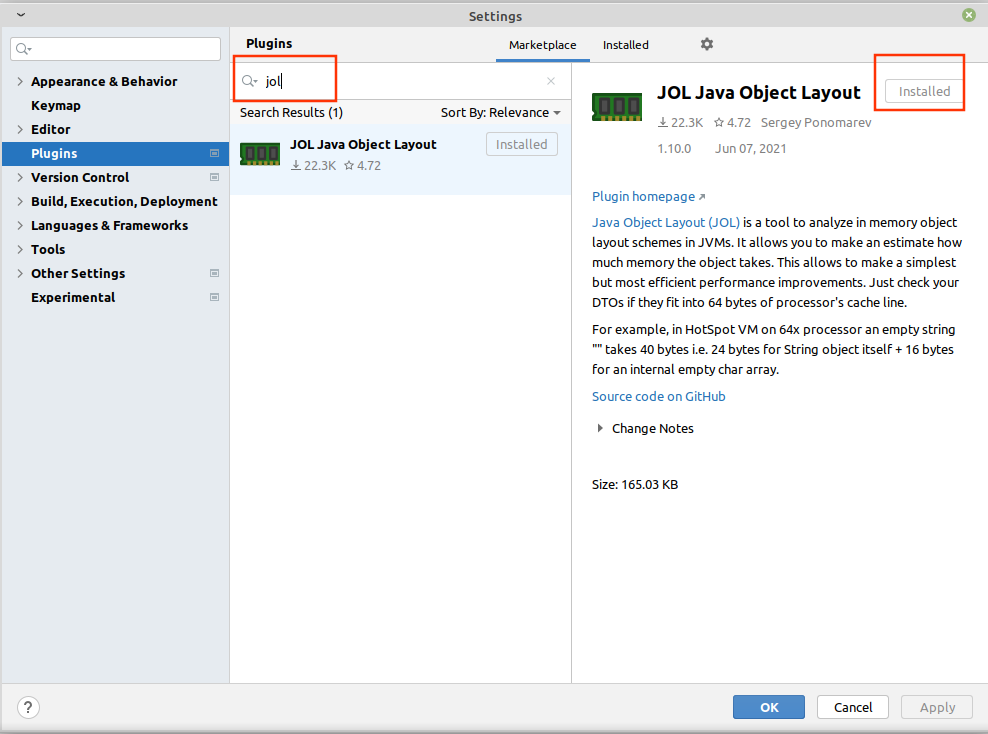
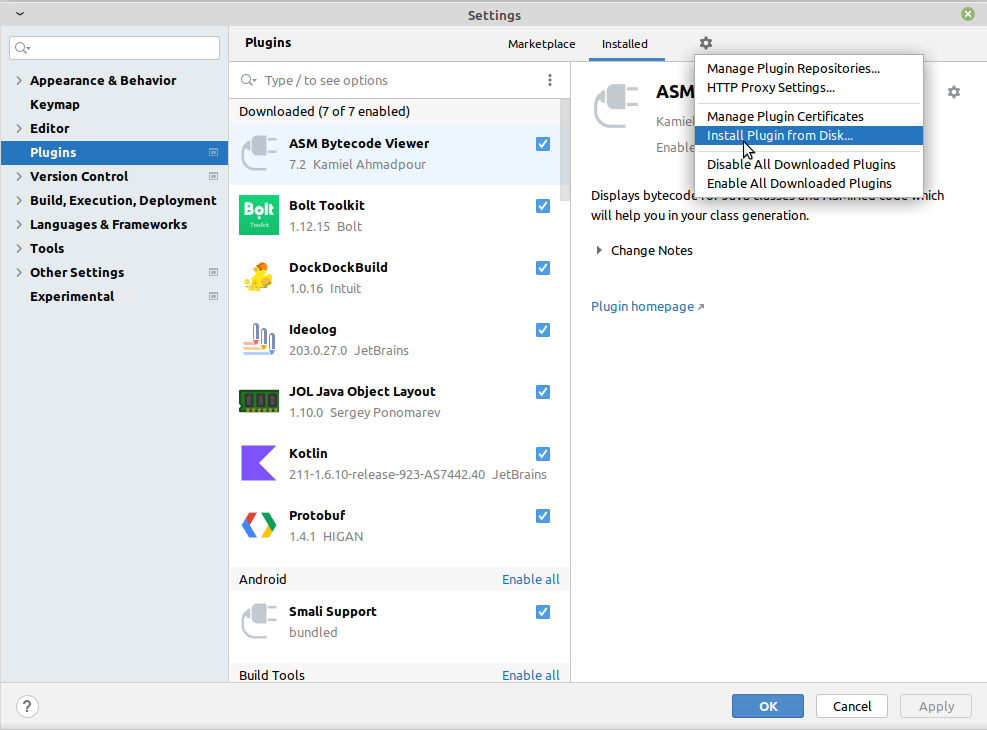
2.2 本地安装
第1步:下载安装文件
https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/10953-jol-java-object-layout/versions
或者
https://github.com/stokito/IdeaJol/releases/latest
第2步:安装
Settings/Preferences -> Plugins -> Installed 右边的 按钮 ![]() -> Install plugin from disk...
-> Install plugin from disk...
2.3 使用
类的名字 --> 右键 --> Show Object Layout
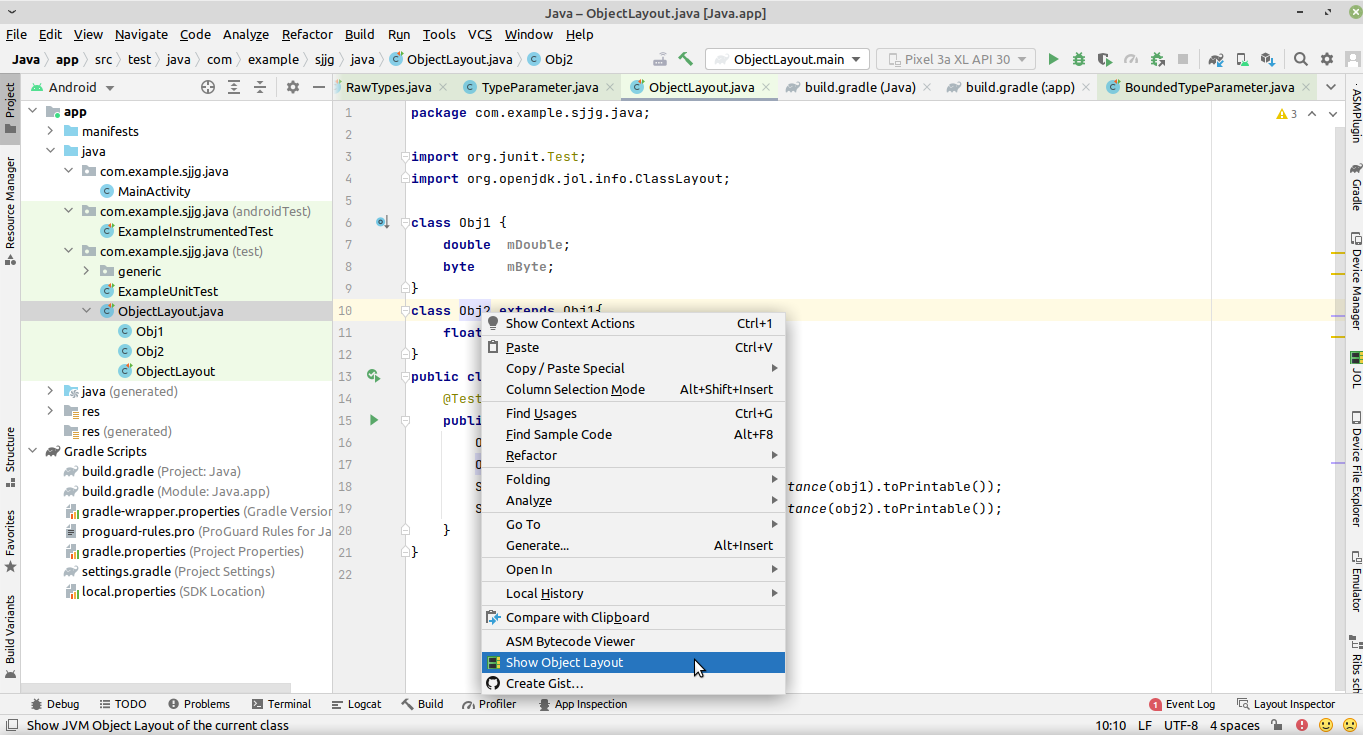
结果如下:
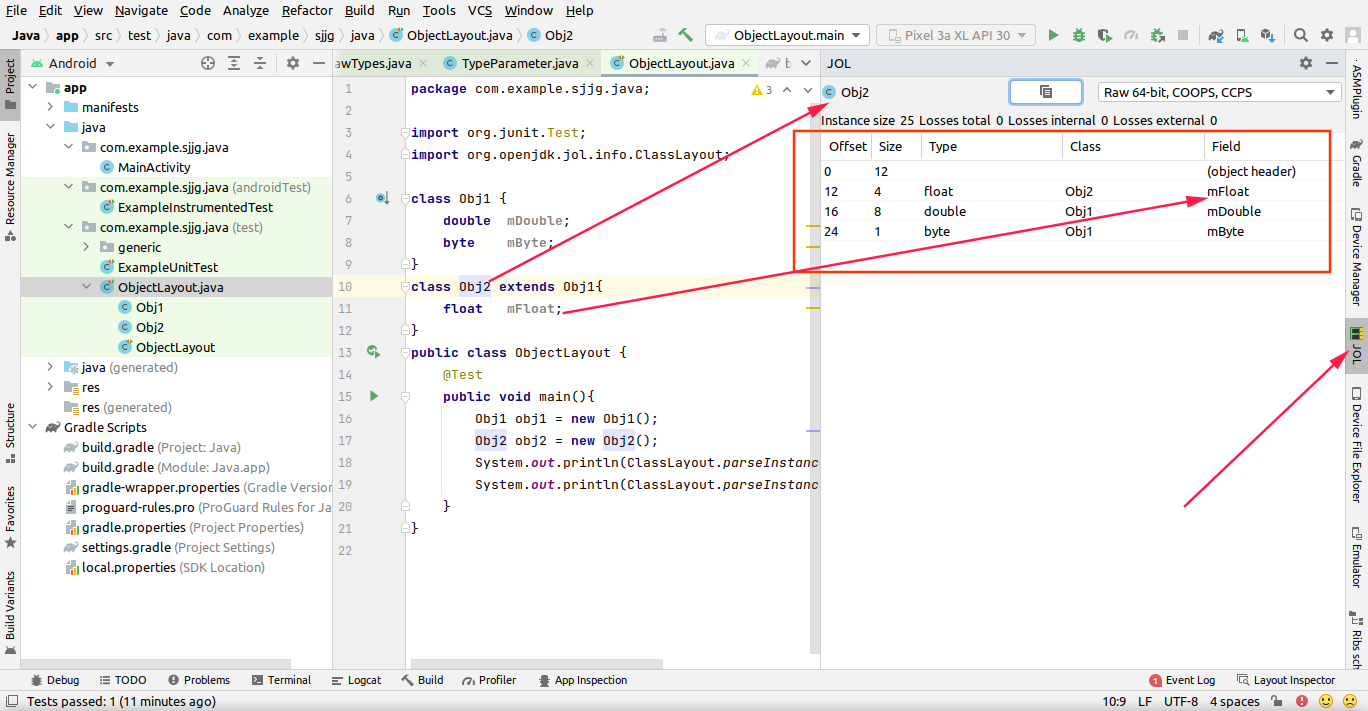
3.在代码中使用jol库打印对象布局
3.1 引入jol库
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId>
<artifactId>jol-core</artifactId>
<version>0.9</version>
</dependency>复制上面代码,在android studio 中粘贴会自动生成
implementation 'org.openjdk.jol:jol-core:0.9'可在这里相看版本发布记录
https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/openjdk/jol/jol-cli/
3.2 简单示例
class Obj1 {
double mDouble;
byte mByte;
}
public class ObjectLayout {
/*
* This sample showcases the basic field layout.
* You can see a few notable things here:
* a) how much the object header consumes;
* b) how fields are laid out;
* c) how the external alignment beefs up the object size
*/
static class B { /* none */ }
@Test //1
public void basic() {
class A { boolean f; }
out.println("--------------jvm-------------------");
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println("--------------instance--------------");
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new Obj1()).toPrintable());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new A()).toPrintable());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new B()).toPrintable());
out.println("--------------class-----------------");
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(Object.class).toPrintable());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(B.class).toPrintable());
}
}- ObjectA 是全局类,B是内部静态类,A是普通内部类。A持有对其外部类的引用ObjectLayout$1A.this$0.
- parseInstance解析对象,parseClass解析类,运行结果:
--------------jvm-------------------
# WARNING: Unable to get Instrumentation. Dynamic Attach failed. You may add this JAR as -javaagent manually, or supply -Djdk.attach.allowAttachSelf
# WARNING: Unable to attach Serviceability Agent. You can try again with escalated privileges. Two options: a) use -Djol.tryWithSudo=true to try with sudo; b) echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
--------------instance--------------
com.example.sjjg.java.Obj1 object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 15 63 03 20 (00010101 01100011 00000011 00100000) (537092885)
12 1 byte Obj1.mByte 0
13 3 (alignment/padding gap)
16 8 double Obj1.mDouble 0.0
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 3 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 3 bytes total
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$1A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 8f 65 03 20 (10001111 01100101 00000011 00100000) (537093519)
12 1 boolean ObjectLayout$1A.f false
13 3 (alignment/padding gap)
16 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$1A.this$0 (object)
20 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 3 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 7 bytes total
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) d1 65 03 20 (11010001 01100101 00000011 00100000) (537093585)
12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
--------------class-----------------
java.lang.Object object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$1A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 1 boolean ObjectLayout$1A.f N/A
13 3 (alignment/padding gap)
16 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$1A.this$0 N/A
20 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 3 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 7 bytes total
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total4.常用对象布局打印示例
https://github.com/openjdk/jol/tree/master/jol-samples/src/main/java/org/openjdk/jol/samples
4.1 JVM信息
@Test
public void jvm() {
out.println(VM.current().details());
}结果如下:
# WARNING: Unable to get Instrumentation. Dynamic Attach failed. You may add this JAR as -javaagent manually, or supply -Djdk.attach.allowAttachSelf
# WARNING: Unable to attach Serviceability Agent. You can try again with escalated privileges. Two options: a) use -Djol.tryWithSudo=true to try with sudo; b) echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]其中后两行含义如下:
| \ | 引用 | booleans | byte | short | chars | int | float | long | double |
| 普通对象 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| 数组 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
在测试机器(64位)上JVM 启用了指针压缩,所以引用的大小是4,未启用时引用的大小是8。可通过jvm选项 -XX:-UseCompressedOops 控制。
4.2 JVM对象对齐方式
@Test //2
public void aligned() {
/*
* This is the more advanced field layout example.
*
* Because the underlying hardware platform often requires aligned accesses
* to maintain the performance and correctness, it is expected the fields
* are aligned by their size. For booleans it does not mean anything, but
* for longs it's different. In this example, we can see the long field
* is indeed aligned for 8 bytes, sometimes making the gap after the
* object header.
*/
class A { long f; }
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
}结果
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$2A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$2A.this$0 N/A
16 8 long ObjectLayout$2A.f N/A
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total4.3 JVM中对象属性的压缩方式
@Test //3
public void packing() {
/*
* This is the example how VM packs the fields.
*
* JVMs pack the fields to minimize the memory footprint. Run
* this example and see the fields are densely packed, and gaps
* are minimal. It is achieved by aligning fields in 8->4->2->1
* order, because it can not break the initial alignment, once we
* align the 8-byte field. The gap resulted in the initial 8-byte
* align can be taken by one or few smaller-sized fields.
*
* Note that the actual field order is very different from the
* declared order. Nothing in the JVM spec requires otherwise.
*/
class A {
boolean bo1, bo2;
byte b1 , b2 ;
char c1 , c2 ;
double d1 , d2 ;
float f1 , f2 ;
int i1 , i2 ;
long l1 , l2 ;
short s1 , s2 ;
}
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$3A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 float ObjectLayout$3A.f1 N/A
16 8 double ObjectLayout$3A.d1 N/A
24 8 double ObjectLayout$3A.d2 N/A
32 8 long ObjectLayout$3A.l1 N/A
40 8 long ObjectLayout$3A.l2 N/A
48 4 float ObjectLayout$3A.f2 N/A
52 4 int ObjectLayout$3A.i1 N/A
56 4 int ObjectLayout$3A.i2 N/A
60 2 char ObjectLayout$3A.c1 N/A
62 2 char ObjectLayout$3A.c2 N/A
64 2 short ObjectLayout$3A.s1 N/A
66 2 short ObjectLayout$3A.s2 N/A
68 1 boolean ObjectLayout$3A.bo1 N/A
69 1 boolean ObjectLayout$3A.bo2 N/A
70 1 byte ObjectLayout$3A.b1 N/A
71 1 byte ObjectLayout$3A.b2 N/A
72 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$3A.this$0 N/A
76 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 80 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total4.4 继承与对象属性的布局
测试1:
@Test //4
public void inheritance(){
/*
* This is the example how VM lays out the fields in the hierarchy.
*
* The important invariant for JVM to maintain is laying out the
* accessible fields at the same offsets regardless of the class
* the field is being accessed through. That is, for classes B and C
* below the field A.a should reside on the same offset. This prompts
* VM to lay out the superclass fields first.
*/
class A { int a; }
class B extends A { int b; }
class C extends B { int c; }
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}测试1结果:
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$1C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 int ObjectLayout$4A.a N/A
16 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$4A.this$0 N/A
20 4 int ObjectLayout$1B.b N/A
24 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$1B.this$0 N/A
28 4 int ObjectLayout$1C.c N/A
32 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$1C.this$0 N/A
36 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 40 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total测试2:
@Test //5
public void super_gaps(){
class A { long a; }
class B extends A { long b; }
class C extends B { long c; int d;}
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}
测试2结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$2C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$5A.this$0 N/A
16 8 long ObjectLayout$5A.a N/A
24 8 long ObjectLayout$3B.b N/A
32 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$3B.this$0 N/A
36 4 int ObjectLayout$2C.d N/A
40 8 long ObjectLayout$2C.c N/A
48 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$2C.this$0 N/A
52 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 56 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total测试3:
@Test //6
public void hierarchy_gaps(){
class A { boolean a; }
class B extends A { boolean b; }
class C extends B { boolean c; }
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}测试3结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout$3C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 1 boolean ObjectLayout$6A.a N/A
13 3 (alignment/padding gap)
16 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$6A.this$0 N/A
20 1 boolean ObjectLayout$4B.b N/A
21 3 (alignment/padding gap)
24 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$4B.this$0 N/A
28 1 boolean ObjectLayout$3C.c N/A
29 3 (alignment/padding gap)
32 4 com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout ObjectLayout$3C.this$0 N/A
36 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 40 bytes
Space losses: 9 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 13 bytes total
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 2s
19 actionable tasks: 2 executed, 17 up-to-date
Build Analyzer results available
10:48:29 PM: Task execution finished ':app:testDebugUnitTest --tests "com.example.sjjg.java.ObjectLayout.hierarchy_gaps"'.4.5 exception、class
exception:
@Test //7
public void exception(){
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(Throwable.class).toPrintable());
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
java.lang.Throwable object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 java.lang.Object Throwable.backtrace N/A
16 4 java.lang.String Throwable.detailMessage N/A
20 4 java.lang.Throwable Throwable.cause N/A
24 4 java.lang.StackTraceElement[] Throwable.stackTrace N/A
28 4 java.util.List Throwable.suppressedExceptions N/A
32 4 int Throwable.depth N/A
36 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 40 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes totalclass:
@Test //8
public void classes(){
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(Class.class).toPrintable());
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
java.lang.Class object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 java.lang.reflect.Constructor Class.cachedConstructor N/A
16 4 java.lang.Class Class.newInstanceCallerCache N/A
20 4 java.lang.String Class.name N/A
24 4 java.lang.Module Class.module N/A
28 4 (alignment/padding gap)
32 4 java.lang.String Class.packageName N/A
36 4 java.lang.Class Class.componentType N/A
40 4 java.lang.ref.SoftReference Class.reflectionData N/A
44 4 sun.reflect.generics.repository.ClassRepository Class.genericInfo N/A
48 4 java.lang.Object[] Class.enumConstants N/A
52 4 java.util.Map Class.enumConstantDirectory N/A
56 4 java.lang.Class.AnnotationData Class.annotationData N/A
60 4 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationType Class.annotationType N/A
64 4 java.lang.ClassValue.ClassValueMap Class.classValueMap N/A
68 28 (alignment/padding gap)
96 4 int Class.classRedefinedCount N/A
100 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 104 bytes
Space losses: 32 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 36 bytes total4.6 对象头信息
https://www.cnblogs.com/sjjg/p/4572779.html
4.7 数组相关
4.7.1 数组长度
@Test //11
public void array_length(){
out.println(VM.current().details());
for (int c = 0; c < 8; c++) {
out.println("**** int[" + c + "]");
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new int[c]).toPrintable());
}
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
**** int[0]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
16 0 int [I.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
**** int[1]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
16 4 int [I.<elements> N/A
20 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
**** int[2]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 02 00 00 00 (00000010 00000000 00000000 00000000) (2)
16 8 int [I.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
**** int[3]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 03 00 00 00 (00000011 00000000 00000000 00000000) (3)
16 12 int [I.<elements> N/A
28 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 32 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
**** int[4]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 04 00 00 00 (00000100 00000000 00000000 00000000) (4)
16 16 int [I.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 32 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
**** int[5]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5)
16 20 int [I.<elements> N/A
36 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 40 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
**** int[6]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 06 00 00 00 (00000110 00000000 00000000 00000000) (6)
16 24 int [I.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 40 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
**** int[7]
[I object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 82 01 00 20 (10000010 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871298)
12 4 (object header) 07 00 00 00 (00000111 00000000 00000000 00000000) (7)
16 28 int [I.<elements> N/A
44 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 48 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total4.7.2 数组中元素的对齐方式
/*
* This sample showcases that the alignment requirements are also
* affecting arrays. This test introspects the byte[] arrays of different
* small sizes. It may be seen that many arrays are actually consuming the
* same space, since they are also required to be externally aligned.
*
* The internal alignment can be demonstrated in some specific VM modes, e.g.
* on long[] arrays with 32-bit modes. There, the zero-th element of long[]
* array should be aligned by 8.
*
* Or, even on byte[] arrays in 64-bit mode with compressed references disabled,
* on some VMs:
* https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-8139457
*/
@Test
public void array_alignment() {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new long[0]).toPrintable());
for (int size = 0; size <= 8; size++) {
out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new byte[size]).toPrintable());
}
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
[J object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) c1 01 00 20 (11000001 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871361)
12 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
16 0 long [J.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
16 0 byte [B.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
16 1 byte [B.<elements> N/A
17 7 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 7 bytes external = 7 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 02 00 00 00 (00000010 00000000 00000000 00000000) (2)
16 2 byte [B.<elements> N/A
18 6 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 6 bytes external = 6 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 03 00 00 00 (00000011 00000000 00000000 00000000) (3)
16 3 byte [B.<elements> N/A
19 5 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 5 bytes external = 5 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 04 00 00 00 (00000100 00000000 00000000 00000000) (4)
16 4 byte [B.<elements> N/A
20 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 05 00 00 00 (00000101 00000000 00000000 00000000) (5)
16 5 byte [B.<elements> N/A
21 3 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 3 bytes external = 3 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 06 00 00 00 (00000110 00000000 00000000 00000000) (6)
16 6 byte [B.<elements> N/A
22 2 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 2 bytes external = 2 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 07 00 00 00 (00000111 00000000 00000000 00000000) (7)
16 7 byte [B.<elements> N/A
23 1 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 1 bytes external = 1 bytes total
[B object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
8 4 (object header) 04 01 00 20 (00000100 00000001 00000000 00100000) (536871172)
12 4 (object header) 08 00 00 00 (00001000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (8)
16 8 byte [B.<elements> N/A
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total4.8 ArrayList与LinkedList内在布局对比
/*
* The example of traversing the reachability graphs.
*
* In addition to introspecting the object internals, we can also
* see the object externals, that is, the objects referenced from the
* object in question. There are multiple ways to illustrate this,
* the summary table seems to work well.
*
* In this example, you can clearly see the difference between
* the shadow heap (i.e. space taken by the reachable objects)
* for ArrayList and LinkedList.
*
* When several roots are handed over to JOL, it tracks the objects reachable
* from either root, and also avoids double-counting.
*/
@Test
public void arrayList_linkedList() {
out.println(VM.current().details());
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> ll = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Integer io = i; // box once
al.add(io);
ll.add(io);
}
al.trimToSize();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out);
pw.println(GraphLayout.parseInstance(al).toFootprint());
pw.println(GraphLayout.parseInstance(ll).toFootprint());
pw.println(GraphLayout.parseInstance(al, ll).toFootprint());
pw.close();
}结果:
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
java.util.ArrayList@6e005dc9d footprint:
COUNT AVG SUM DESCRIPTION
1 4016 4016 [Ljava.lang.Object;
1000 16 16000 java.lang.Integer
1 24 24 java.util.ArrayList
1002 20040 (total)
java.util.LinkedList@6e6d5d29d footprint:
COUNT AVG SUM DESCRIPTION
1000 16 16000 java.lang.Integer
1 32 32 java.util.LinkedList
1000 24 24000 java.util.LinkedList$Node
2001 40032 (total)
java.util.ArrayList@6e005dc9d, java.util.LinkedList@6e6d5d29d footprint:
COUNT AVG SUM DESCRIPTION
1 4016 4016 [Ljava.lang.Object;
1000 16 16000 java.lang.Integer
1 24 24 java.util.ArrayList
1 32 32 java.util.LinkedList
1000 24 24000 java.util.LinkedList$Node
2003 44072 (total)
4.9 对象分配
/*
* The example of allocation addresses.
*
* This example shows the addresses of newly allocated objects
* grow linearly in HotSpot. This is because the allocation in
* parallel collectors is linear. We can also see it rewinds back
* to the same offsets -- that's the start of some GC generation.
*
* For Parallel-like GCs, while GC adjusts for the allocation rate.
* For G1-like GCs, the allocation address changes by region size,
* as collector switches to another region for allocation.
*
* Run with test with smaller heap (about 1 GB) for best results.
*/
@Test
public void allocation() {
out.println(VM.current().details());
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out, true);
long last = VM.current().addressOf(new Object());
for (int l = 0; l < 1000 * 1000 * 1000; l++) {
long current = VM.current().addressOf(new Object());
long distance = Math.abs(current - last);
if (distance > 4096) {
pw.printf("Jumping from %x to %x (distance = %d bytes, %dK, %dM)%n",
last,
current,
distance,
distance / 1024,
distance / 1024 / 1024);
}
last = current;
}
pw.close();
}结果
# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
Jumping from 73d16f4c0 to 73d175180 (distance = 23744 bytes, 23K, 0M)
Jumping from 73d175180 to 73d17ae40 (distance = 23744 bytes, 23K, 0M)
Jumping from 73d17ae40 to 73d180b00 (distance = 23744 bytes, 23K, 0M)
Jumping from 73d180b00 to 73d1867c0 (distance = 23744 bytes, 23K, 0M)
...


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号