2016CCPC东北地区大学生程序设计竞赛 Auxiliary Set (BFSt预处理+ 思维)
Auxiliary Set
Time Limit: 9000/4500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1976 Accepted Submission(s): 576
Problem Description
Given a rooted tree with n vertices, some of the vertices are important.
An auxiliary set is a set containing vertices satisfying at least one of the two conditions:
∙It is an important vertex
∙It is the least common ancestor of two different important vertices.
You are given a tree with n vertices (1 is the root) and q queries.
Each query is a set of nodes which indicates the unimportant vertices in the tree. Answer the size (i.e. number of vertices) of the auxiliary set for each query.
An auxiliary set is a set containing vertices satisfying at least one of the two conditions:
∙It is an important vertex
∙It is the least common ancestor of two different important vertices.
You are given a tree with n vertices (1 is the root) and q queries.
Each query is a set of nodes which indicates the unimportant vertices in the tree. Answer the size (i.e. number of vertices) of the auxiliary set for each query.
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T≤1000),
which indicates the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains two integers n (1≤n≤100000), q (0≤q≤100000).
In the following n -1 lines, the i-th line contains two integers ui,vi(1≤ui,vi≤n) indicating there is an edge between uii and vi in the tree.
In the next q lines, the i-th line first comes with an integer mi(1≤mi≤100000) indicating the number of vertices in the query set.Then comes with mi different integers, indicating the nodes in the query set.
It is guaranteed that ∑qi=1mi≤100000.
It is also guaranteed that the number of test cases in which n≥1000 or ∑qi=1mi≥1000 is no more than 10.
For each test case, the first line contains two integers n (1≤n≤100000), q (0≤q≤100000).
In the following n -1 lines, the i-th line contains two integers ui,vi(1≤ui,vi≤n) indicating there is an edge between uii and vi in the tree.
In the next q lines, the i-th line first comes with an integer mi(1≤mi≤100000) indicating the number of vertices in the query set.Then comes with mi different integers, indicating the nodes in the query set.
It is guaranteed that ∑qi=1mi≤100000.
It is also guaranteed that the number of test cases in which n≥1000 or ∑qi=1mi≥1000 is no more than 10.
Output
For each test case, first output one line "Case #x:", where x is the case number (starting from 1).
Then q lines follow, i-th line contains an integer indicating the size of the auxiliary set for each query.
Then q lines follow, i-th line contains an integer indicating the size of the auxiliary set for each query.
Sample Input
1
6 3
6 4
2 5
5 4
1 5
5 3
3 1 2 3
1 5
3 3 1 4
Sample Output
Case #1:
3
6
3
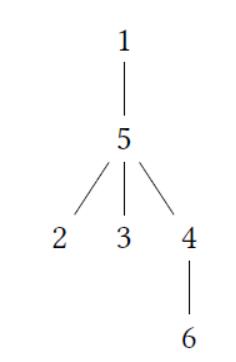 For the query {1,2, 3}:
•node 4, 5, 6 are important nodes For the query {5}:
•node 1,2, 3, 4, 6 are important nodes
•node 5 is the lea of node 4 and node 3 For the query {3, 1,4}:
• node 2, 5, 6 are important nodes
For the query {1,2, 3}:
•node 4, 5, 6 are important nodes For the query {5}:
•node 1,2, 3, 4, 6 are important nodes
•node 5 is the lea of node 4 and node 3 For the query {3, 1,4}:
• node 2, 5, 6 are important nodes
Hint
 For the query {1,2, 3}:
•node 4, 5, 6 are important nodes For the query {5}:
•node 1,2, 3, 4, 6 are important nodes
•node 5 is the lea of node 4 and node 3 For the query {3, 1,4}:
• node 2, 5, 6 are important nodes
For the query {1,2, 3}:
•node 4, 5, 6 are important nodes For the query {5}:
•node 1,2, 3, 4, 6 are important nodes
•node 5 is the lea of node 4 and node 3 For the query {3, 1,4}:
• node 2, 5, 6 are important nodes
【题意】
给 n-1 个 关系 m 个查询
问 每次查询 给 出 不重要的 点, 问 有多少重要的点, 重要的点 如果一个点 是不重要的点, 但是与 两个以上重要的点有关系 那么这个点也算是重要的点;
【思路】
m 和n 的数据量 非常大 很容易超时
但是 我们可以 从 一个不重要的点 若他有两个以上的孩子是重要的话 就可以算作重要的点, 而 他没有孩子时 那么他对他的父亲贡献 就为0
所以 我们可以先预处理 这些关系,
然后 m 次查询的时候 统计
【感悟】
这个时间控制的是真好 开数组 1e6+10; 数组清理, 多一个 memset 就超时。 change 数组 去掉后 接着就A 了
【代码实现】
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define findx(x) lower_bound(b+1,b+1+bn,x)-b
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin)
#define FOUT freopen("output.txt","w",stdout)
#define S1(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define SL1(n) scanf("%I64d",&n)
#define S2(n,m) scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)
#define SL2(n,m) scanf("%I64d%I64d",&n,&m)
#define Pr(n) printf("%d\n",n)
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1|1, mid + 1, r
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp=1e-6;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int MAXN=1e6+5;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[5][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
ll inv[maxn*2];
inline void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){ x=1; y=0; d=a; }else{ ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b);};}
inline ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
inline ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}ll ans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);ll temp=x;x=y;y=temp-a/b*y;return ans;}
inline ll lcm(ll a,ll b){ return b/gcd(a,b)*a;}
inline ll qpow(ll x,ll n){ll res=1;for(;n;n>>=1){if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD;x=(x*x)%MOD;}return res;}
inline ll inv_exgcd(ll a,ll n){ll d,x,y;ex_gcd(a,n,d,x,y);return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1;}
inline ll inv1(ll b){return b==1?1:(MOD-MOD/b)*inv1(MOD%b)%MOD;}
inline ll inv2(ll b){return qpow(b,MOD-2);}
int cot;
int head[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN];
int son[MAXN];
int fa[MAXN];
int deq[MAXN];
int sat[MAXN];
int change[maxn];
struct node{
int v,next;
}edge[MAXN];
int cmp( int a,int b)
{
return deq[a]>deq[b];
}
void init()
{
cot=0;
mem(head,-1);
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
edge[++cot].v=v;
edge[cot].next=head[u];
head[u]=cot;
}
void bfs(int rt)
{
queue<int>Q;
mem(vis,0);
vis[rt]=1;
Q.push(rt);
while(!Q.empty())
{
int u=Q.front();
Q.pop();
// vis[u]=0;
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].v;
if(!vis[v])
{
deq[v]=deq[u]+1;
son[u]++;
fa[v]=u;
Q.push(v);
vis[v]=1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
int cont=0;
int ans;
while(t--)
{
int n,m;
int x,y;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
init();
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
add(y,x);
}
mem(deq,0);
mem(son,0);
mem(fa,0);
bfs(1);
printf("Case #%d:\n",++cont);
while(m--)
{
int num;
ans=0;
scanf("%d",&num);
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
scanf("%d",&sat[i]);
sort(sat+1,sat+num+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
{
if(son[sat[i]]==0)// 对父亲 没有贡献
{
son[fa[sat[i]]]--;
change[fa[sat[i]]]++; //记录 减去 等会要还原sat
}
if(son[sat[i]]>=2)// 如果非重要点 由两个重要的点组成 也是重要点
ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",n-num+ans);
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)// 还原son
{
if(change[fa[sat[i]]])// 父亲变化
{
son[fa[sat[i]]]+=change[fa[sat[i]]];
change[fa[sat[i]]]=0;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
123
岂曰无衣?与子同袍。王于兴师,修我戈矛。与子同仇!
岂曰无衣?与子同泽。王于兴师,修我矛戟。与子偕作!
岂曰无衣?与子同裳。王于兴师,修我甲兵。与子偕行!



