[Abp vNext微服务实践] - 业务开发
前几篇分别介绍了abp vNext微服务框架、开发环境搭建和vue element admin前端框架接入,在vue element admin中实现用户角色管理基本功能后就可以开始进行业务开发了,本篇会详细的介绍如何在abp vNext中开发业务接口和前端页面实现。
业务接口开发#
业务接口就是针对业务api接口,通过abp vNext微服务中实现并发布业务接口后,前端获取接口并进行界面开发,如此就实现了abp vNext微服务的前后端分离开发。
step1:创建实体(model)#
abp vNext微服务框架中的业务开发同样采用了经典的ddd架构风格和ef core 的code first模式,所以一切的业务都从领域模型(domain)开始。创建数据字典模型如下:
public class DataDictionary : AuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>,ISoftDelete
{
[NotNull]
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Code { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public string FullName { get; set; }
public Guid? CategoryID { get; set; }
public string Notes { get; set; }
public Guid? PID { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public int SEQ { get; set; }
public bool IsEdit { get; set; }
public bool IsDeleted { get; set; }
}
step2:加入AbpDbContext:#
public DbSet<DataDictionary> Dictionary { get; set; }
step3:构建ef实体:#
builder.Entity<DataDictionary>(b =>
{
b.ToTable("Dictionary");
b.ConfigureConcurrencyStamp();
b.ConfigureExtraProperties();
b.ConfigureAudited();
b.Property(x => x.Name).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(ProductConsts.MaxNameLength);
b.Property(x => x.Code).HasMaxLength(ProductConsts.MaxCodeLength);
b.Property(x => x.FullName).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(ProductConsts.MaxFullNameLength);
b.Property(x => x.Notes).HasMaxLength(ProductConsts.MaxNotesLength);
b.Property(x => x.SEQ).IsRequired();
b.HasIndex(q => q.Code);
b.HasIndex(q => q.Name);
b.HasIndex(q => q.CategoryID);
});
step4:使用ef迁移数据库:#
Add-Migration Update-Database
查看输出日志是否成功迁移。
创建数据字典应用服务接口
step5:创建数据字典接口和dto如下:#
public interface IDictionaryAppService : IApplicationService
{
Task<PagedResultDto<DictionaryDto>> GetAll(GetDictionaryInputDto input);
Task<DictionaryDto> Get(Guid id);
Task<DictionaryDto> Create(CreateDictionaryDto input);
Task<DictionaryDto> Update(Guid id, UpdateDictionary input);
Task Delete(List<Guid> ids);
}
public class CreateDictionaryDto
{
[Required]
[StringLength(ProductConsts.MaxNameLength)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[StringLength(ProductConsts.MaxCodeLength)]
public string Code { get; set; }
public Guid? CategoryID { get; set; }
[StringLength(ProductConsts.MaxNotesLength)]
public string Notes { get; set; }
public Guid? PID { get; set; }
public int SEQ { get; set; }
public bool IsEdit { get; set; }
}
public class DictionaryDto : AuditedEntityDto<Guid>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Code { get; set; }
public string FullName { get; set; }
public Guid? CategoryID { get; set; }
public string Notes { get; set; }
public Guid? PID { get; set; }
public int SEQ { get; set; }
public bool IsEdit { get; set; }
}
public class GetDictionaryInputDto: PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto
{
public string Filter { get; set; }
public Guid CategoryID { get; set; }
}
public class UpdateDictionary
{
[StringLength(ProductConsts.MaxNotesLength)]
public string Notes { get; set; }
public Guid? PID { get; set; }
public int SEQ { get; set; }
}
实现数据字典应用服务
step6:应用层实现如下:#
继承基类:
public class DictionaryAppService : ApplicationService, IDictionaryAppService
注入仓储:
private readonly IRepository<DataDictionary, Guid> _repository;
public DictionaryAppService( IRepository<DataDictionary, Guid> repository) { _repository = repository; }
实现接口
新增:
public async Task<DictionaryDto> Create(CreateDictionaryDto input)
{
var existingDic = await _repository.FirstOrDefaultAsync(d => d.Name == input.Name);
if (existingDic != null)
{
throw new BusinessException("名称: "+input.Name+"已存在");
}var result = await _repository.InsertAsync(new DataDictionary
{
Id = GuidGenerator.Create(),
Name = input.Name,
Code = input.Code,
FullName = input.Name,
CategoryID = input.CategoryID,
Notes = input.Notes,
PID = input.PID,
SEQ = input.SEQ,
IsEdit=input.IsEdit
});
return ObjectMapper.Map<DataDictionary, DictionaryDto>(result);
}
删除:
public async Task Delete(List<Guid> ids)
{
foreach (var id in ids)
{
await _repository.DeleteAsync(id);
}
}
查询
public async Task<DictionaryDto> Get(Guid id)
{
var query = await _repository.GetAsync(id);
var dto = ObjectMapper.Map<DataDictionary, DictionaryDto>(query);return dto;
}
public async Task<PagedResultDto<DictionaryDto>> GetAll(GetDictionaryInputDto input)
{
var query = _repository
.Where(d => d.CategoryID == input.CategoryID)
.WhereIf(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(input.Filter), d => d.Name.Contains(input.Filter) ||
d.Code.Contains(input.Filter));
var items = await query.OrderBy(input.Sorting ?? "SEQ")
.Skip(input.SkipCount)
.Take(input.MaxResultCount).ToListAsync();
var totalCount = await query.CountAsync();
var dtos = ObjectMapper.Map<List<DataDictionary>, List<DictionaryDto>>(items);return new PagedResultDto<DictionaryDto>(totalCount, dtos);
}
修改:
public async Task<DictionaryDto> Update(Guid id, UpdateDictionary input)
{var dic = await _repository.GetAsync(id);
dic.Notes = input.Notes;
dic.SEQ = input.SEQ;
return ObjectMapper.Map<DataDictionary, DictionaryDto>(dic);
}
增加数据字典权限
step7:权限#
ProductManagementPermissions中增加静态类DataDictionary:
public static class DataDictionary
{
public const string Default = BasicDataManagement + ".DataDictionary";
public const string Delete = Default + ".Delete";
public const string Update = Default + ".Update";
public const string Create = Default + ".Create";
}
step8:构造权限#
ProductManagementPermissionDefinitionProvider中增加dataDictionary:
var dataDictionary = basicDataManagementGroup.AddPermission(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Default, L("DataDictionary"));
dataDictionary.AddChild(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Create, L("Permission:Create"));
dataDictionary.AddChild(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Delete, L("Permission:Delete"));
dataDictionary.AddChild(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Update, L("Permission:Edit"));
增加完成后在数据字典应用服务中分别加上权限过滤器
[Authorize(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Default)] [Authorize(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Create)] [Authorize(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Delete)] [Authorize(ProductManagementPermissions.DataDictionary.Update)]
数据字典DTO映射
step9:ProductManagementApplicationAutoMapperProfile中增加数据字典模型-Dto映射:#
CreateMap<DataDictionary, DictionaryDto>();
数据字典web api实现
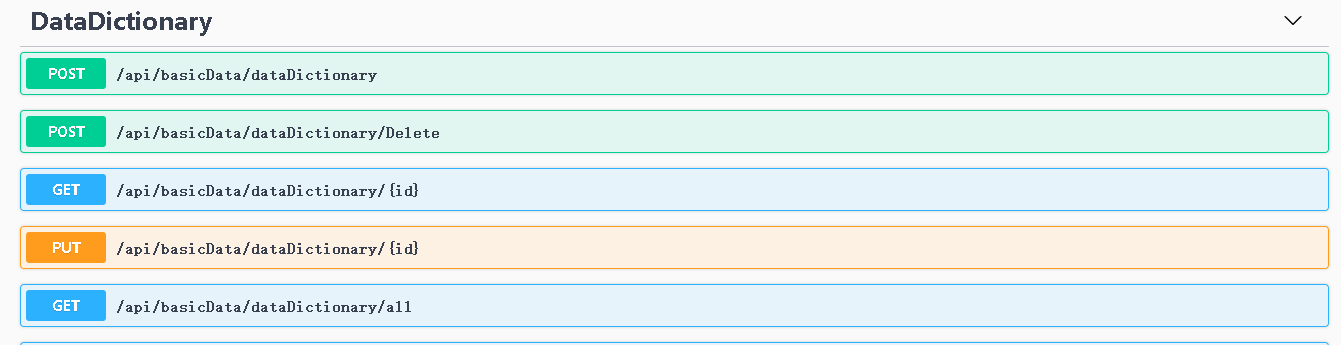
step10:abp vNext中没有使用原先的应用服务动态api,现在api需要在控制器中实现#
[RemoteService]
[Area("basicData")]
[Route("api/basicData/dataDictionary")]
public class DataDictionaryController : AbpController, IDictionaryAppService
{
private readonly IDictionaryAppService _dictionaryAppService;
public DataDictionaryController(IDictionaryAppService dictionaryAppService)
{
_dictionaryAppService = dictionaryAppService;
}
[HttpPost]
public Task<DictionaryDto> Create(CreateDictionaryDto input)
{
return _dictionaryAppService.Create(input);
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("Delete")]
public Task Delete(List<Guid> ids)
{
return _dictionaryAppService.Delete(ids);
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("{id}")]
public Task<DictionaryDto> Get(Guid id)
{
return _dictionaryAppService.Get(id);
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("all")]
public Task<PagedResultDto<DictionaryDto>> GetAll(GetDictionaryInputDto input)
{
return _dictionaryAppService.GetAll(input);
}
[HttpPut]
[Route("{id}")]
public Task<DictionaryDto> Update(Guid id, UpdateDictionary input)
{
return _dictionaryAppService.Update(id, input);
}
}
swagger文档
总结#
abp vNext的业务开发模式并没有做太多改动,虽然接口开发的过程有些繁琐,但是对于业务拆分和模型解耦来说是非常有必要的。ddd的架构风格让开发人员无需依赖于sql语法,可以使用抽象的仓储进行轻松高效的查询,这对于代码维护和项目交接来说是十分幸运的。此外,abp vNext还将身份、权限、模型验证、异常处理等进行了完美封装,使得开发人员可以专注于业务开发。










【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律