STM32F103 移植UCOSIII LED例子测试 在GNU编译下实现
STM32F103 移植UCOSIII GNU编译实现
1、准备移植文件,从micrium官网下载在UCOSIII移植文件。
当前进入网站首页时,选择STM 法意半导体 芯片生产商查看全部型号。
下图,这里我们选择STM32F107 它使用的是UCOSIII V3.03.01 版本,IDE使用了
Atollic TrueSTUDIO V3.x 是市售增强C / C ++ IDE基于Eclipse ®,CDT ™,GCC和GDB。2017年以来已停止更新,ST已收购。
IAR (EWARM) V6.x 是IARSystems 公司为ARM 微处理器开发的一个集成开发环境。
Keil MDK V3.x 是美国Keil Software公司出品的单片机C语言软件开发系统。
以上三种IED 使用的编译链接器不相同,有GNU 、IAR、 RealView 、后面讲到选择uC-CPU文件夹里面的程序时,需要特别留意
自己IDE环境。
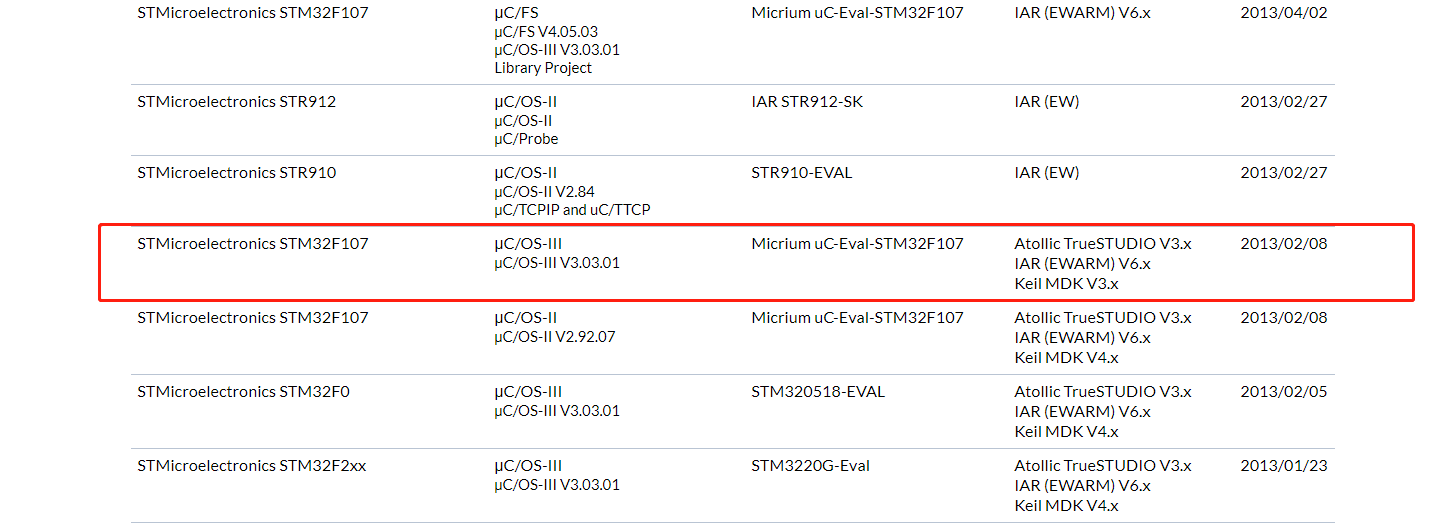
下载完毕后解压

2、整理和拷贝UCOSIII移植文件。
在程序目录下建立自定义文件夹如下:
在自定义的文件夹中,我们将官网下载的Ucosiii源码复制到文件中,详情见以下说明:
UCOSIII
├文件夹1:[UCOSIII_BSP] <-----------------------里面的bsp.c、bsp.h是自定义的程序。
│ ├(1)bsp.c
│ ├(2)bsp.h
│ └█
├文件夹2:[UCOSIII_CONFIG] <------------------Micrium\Software\EvalBoards\Micrium\uC-Eval-STM32F107\uCOS-III
│ ├(1)app_cfg.h
│ ├(2)cpu_cfg.h
│ ├(3)includes.h
│ ├(4)lib_cfg.h
│ ├(5)os_app_hooks.c
│ ├(6)os_app_hooks.h
│ ├(7)os_cfg.h
│ ├(8)os_cfg_app.h
│ └█
├文件夹3:[UCOSIII_CORE] <--------------------Micrium\Software\uCOS-III\Source
│ ├(1)os.h
│ ├(2)os_cfg_app.c
│ ├(3)os_core.c
│ ├(4)os_dbg.c
│ ├(5)os_flag.c
│ ├(6)os_int.c
│ ├(7)os_mem.c
│ ├(8)os_msg.c
│ ├(9)os_mutex.c
│ ├(10)os_pend_multi.c
│ ├(11)os_prio.c
│ ├(12)os_q.c
│ ├(13)os_sem.c
│ ├(14)os_stat.c
│ ├(15)os_task.c
│ ├(16)os_tick.c
│ ├(17)os_time.c
│ ├(18)os_tmr.c
│ ├(19)os_type.h
│ ├(20)os_var.c
│ └█
├文件夹4:[UCOSIII_CPU] <--------------------Micrium\Software\uC-CPU
│ ├(1)cpu.h
│ ├(2)cpu_a.s
│ ├(3)cpu_c.c
│ ├(4)cpu_core.c
│ ├(5)cpu_core.h
│ ├(6)cpu_def.h
│ └█
├文件夹5:[UCOSIII_LIB] <--------------------Micrium\Software\uC-LIB
│ ├(1)lib_ascii.c
│ ├(2)lib_ascii.h
│ ├(3)lib_def.h
│ ├(4)lib_math.c
│ ├(5)lib_math.h
│ ├(6)lib_mem.c
│ ├(7)lib_mem.h
│ ├(8)lib_mem_a.s
│ ├(9)lib_str.c
│ ├(10)lib_str.h
│ └█
├文件夹6:[UCOSIII_PORT] <--------------------uCOS-III\Ports\ARM-Cortex-M3\Generic\GNU
│ ├(1)os_cpu.h
│ ├(2)os_cpu_a.s
│ ├(3)os_cpu_c.c
│ └█
└█
这里需要特别说明文件夹6:确认自己的IDE 使用的编译器是GNU 、IAR、 RealView哪一种,对应着拷贝,使用不同的代码,移植会有
一些差异,具体可以参照其它教程,这里我们选择GNU编译的代码,即 ;uCOS-III\Ports\ARM-Cortex-M3\Generic\GNU\ 的 os_cpu.h 、 os_cpu_a.s 、 os_cpu_c.c 。
拷贝到UCOSIII文件夹到工程后,根据自己IDE设置方法将UCOSIII这个文件夹添加到IDE编译路径,不同的IDE是不同的,比如 我这边使用的是Clion 通过修改CMakelists.txt 增加代码的路径。
2.1修改 UCOSIII_BSP 的代码
官方的Bsp.c文件中,有很多代码是我们不需要用到的,我们只用到DWT的代码,应该参照官网源码,我们做以下修改。
Bsp.h
#ifndef BSP_PRESENT #define BSP_PRESENT #ifdef BSP_MODULE #define BSP_EXT #else #define BSP_EXT extern #endif #include <stdio.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <cpu.h> #include <cpu_core.h> #include <lib_def.h> #include <lib_ascii.h> //#include <stm32f10x_conf.h> //标准库方式的 #include "stm32f1xx_hal.h" //对应HAL库 主要目的是为了获取系统时钟源 #endif
Bsp.c
#define BSP_MODULE
#include <bsp.h>
#define BSP_REG_DEM_CR (*(CPU_REG32 *)0xE000EDFC) //DEMCR寄存器
#define BSP_REG_DWT_CR (*(CPU_REG32 *)0xE0001000) //DWT控制寄存器
#define BSP_REG_DWT_CYCCNT (*(CPU_REG32 *)0xE0001004) //DWT时钟计数寄存器
#define BSP_REG_DBGMCU_CR (*(CPU_REG32 *)0xE0042004)
//DEMCR寄存器的第24位,如果要使用DWT ETM ITM和TPIU的话DEMCR寄存器的第24位置1
#define BSP_BIT_DEM_CR_TRCENA DEF_BIT_24
//DWTCR寄存器的第0位,当为1的时候使能CYCCNT计数器,使用CYCCNT之前应当先初始化
#define BSP_BIT_DWT_CR_CYCCNTENA DEF_BIT_00
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* BSP_CPU_ClkFreq()
* Description : Read CPU registers to determine the CPU clock frequency of the chip.
* Argument(s) : none.
* Return(s) : The CPU clock frequency, in Hz.
* Caller(s) : Application.
* Note(s) : none.
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
CPU_INT32U BSP_CPU_ClkFreq (void)
{
// RCC_ClocksTypeDef rcc_clocks;
//
// RCC_GetClocksFreq(&rcc_clocks); //获取各个时钟频率
//
// return ((CPU_INT32U)rcc_clocks.HCLK_Frequency); //返回HCLK时钟频率
//RCC_ClkInitTypeDef rcc_clocks ;
//HAL_RCC_GetOscConfig();
//HAL_RCC_GetHCLKFreq(); //获取各个时钟频率
return ((CPU_INT32U)HAL_RCC_GetHCLKFreq()); //返回HCLK时钟频率
}
/*$PAGE*/
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* CPU_TS_TmrInit()
* Description : Initialize & start CPU timestamp timer.
* Argument(s) : none.
* Return(s) : none.
* Caller(s) : CPU_TS_Init().
* This function is an INTERNAL CPU module function & MUST be implemented by application/
* BSP function(s) [see Note #1] but MUST NOT be called by application function(s).
* Note(s) : (1) CPU_TS_TmrInit() is an application/BSP function that MUST be defined by the developer
* if either of the following CPU features is enabled :
* (a) CPU timestamps
* (b) CPU interrupts disabled time measurements
* See 'cpu_cfg.h CPU TIMESTAMP CONFIGURATION Note #1'
* & 'cpu_cfg.h CPU INTERRUPTS DISABLED TIME MEASUREMENT CONFIGURATION Note #1a'.
* (2) (a) Timer count values MUST be returned via word-size-configurable 'CPU_TS_TMR'
* data type.
* (1) If timer has more bits, truncate timer values' higher-order bits greater
* than the configured 'CPU_TS_TMR' timestamp timer data type word size.
* (2) Since the timer MUST NOT have less bits than the configured 'CPU_TS_TMR'
* timestamp timer data type word size; 'CPU_CFG_TS_TMR_SIZE' MUST be
* configured so that ALL bits in 'CPU_TS_TMR' data type are significant.
* In other words, if timer size is not a binary-multiple of 8-bit octets
* (e.g. 20-bits or even 24-bits), then the next lower, binary-multiple
* octet word size SHOULD be configured (e.g. to 16-bits). However, the
* minimum supported word size for CPU timestamp timers is 8-bits.
* See also 'cpu_cfg.h CPU TIMESTAMP CONFIGURATION Note #2'
* & 'cpu_core.h CPU TIMESTAMP DATA TYPES Note #1'.
* (b) Timer SHOULD be an 'up' counter whose values increase with each time count.
* (c) When applicable, timer period SHOULD be less than the typical measured time
* but MUST be less than the maximum measured time; otherwise, timer resolution
* inadequate to measure desired times.
* See also 'CPU_TS_TmrRd() Note #2'.
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
#if (CPU_CFG_TS_TMR_EN == DEF_ENABLED)
void CPU_TS_TmrInit (void)
{
CPU_INT32U fclk_freq;
fclk_freq = BSP_CPU_ClkFreq();
BSP_REG_DEM_CR |= (CPU_INT32U)BSP_BIT_DEM_CR_TRCENA; //使用DWT /* Enable Cortex-M4's DWT CYCCNT reg. */
BSP_REG_DWT_CYCCNT = (CPU_INT32U)0u; //初始化CYCCNT寄存器
BSP_REG_DWT_CR |= (CPU_INT32U)BSP_BIT_DWT_CR_CYCCNTENA;//开启CYCCNT
CPU_TS_TmrFreqSet((CPU_TS_TMR_FREQ)fclk_freq);
}
#endif
/*$PAGE*/
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* CPU_TS_TmrRd()
* Description : Get current CPU timestamp timer count value.
* Argument(s) : none.
* Return(s) : Timestamp timer count (see Notes #2a & #2b).
* Caller(s) : CPU_TS_Init(),
* CPU_TS_Get32(),
* CPU_TS_Get64(),
* CPU_IntDisMeasStart(),
* CPU_IntDisMeasStop().
* This function is an INTERNAL CPU module function & MUST be implemented by application/
* BSP function(s) [see Note #1] but SHOULD NOT be called by application function(s).
* Note(s) : (1) CPU_TS_TmrRd() is an application/BSP function that MUST be defined by the developer
* if either of the following CPU features is enabled :
* (a) CPU timestamps
* (b) CPU interrupts disabled time measurements
* See 'cpu_cfg.h CPU TIMESTAMP CONFIGURATION Note #1'
* & 'cpu_cfg.h CPU INTERRUPTS DISABLED TIME MEASUREMENT CONFIGURATION Note #1a'.
* (2) (a) Timer count values MUST be returned via word-size-configurable 'CPU_TS_TMR'
* data type.
* (1) If timer has more bits, truncate timer values' higher-order bits greater
* than the configured 'CPU_TS_TMR' timestamp timer data type word size.
* (2) Since the timer MUST NOT have less bits than the configured 'CPU_TS_TMR'
* timestamp timer data type word size; 'CPU_CFG_TS_TMR_SIZE' MUST be
* configured so that ALL bits in 'CPU_TS_TMR' data type are significant.
* In other words, if timer size is not a binary-multiple of 8-bit octets
* (e.g. 20-bits or even 24-bits), then the next lower, binary-multiple
* octet word size SHOULD be configured (e.g. to 16-bits). However, the
* minimum supported word size for CPU timestamp timers is 8-bits.
* See also 'cpu_cfg.h CPU TIMESTAMP CONFIGURATION Note #2'
* & 'cpu_core.h CPU TIMESTAMP DATA TYPES Note #1'.
* (b) Timer SHOULD be an 'up' counter whose values increase with each time count.
* (1) If timer is a 'down' counter whose values decrease with each time count,
* then the returned timer value MUST be ones-complemented.
* (c) (1) When applicable, the amount of time measured by CPU timestamps is
* calculated by either of the following equations :
* (A) Time measured = Number timer counts * Timer period
* where
*
* Number timer counts Number of timer counts measured
* Timer period Timer's period in some units of
* (fractional) seconds
* Time measured Amount of time measured, in same
* units of (fractional) seconds
* as the Timer period
*
* Number timer counts
* (B) Time measured = ---------------------
* Timer frequency
*
* where
*
* Number timer counts Number of timer counts measured
* Timer frequency Timer's frequency in some units
* of counts per second
* Time measured Amount of time measured, in seconds
*
* (2) Timer period SHOULD be less than the typical measured time but MUST be less
* than the maximum measured time; otherwise, timer resolution inadequate to
* measure desired times.
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
#if (CPU_CFG_TS_TMR_EN == DEF_ENABLED)
CPU_TS_TMR CPU_TS_TmrRd (void)
{
CPU_TS_TMR ts_tmr_cnts;
ts_tmr_cnts = (CPU_TS_TMR)BSP_REG_DWT_CYCCNT;
return (ts_tmr_cnts);
}
#endif
/*$PAGE*/
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* CPU_TSxx_to_uSec()
* Description : Convert a 32-/64-bit CPU timestamp from timer counts to microseconds.
* Argument(s) : ts_cnts CPU timestamp (in timestamp timer counts [see Note #2aA]).
* Return(s) : Converted CPU timestamp (in microseconds [see Note #2aD]).
* Caller(s) : Application.
* This function is an (optional) CPU module application programming interface (API)
* function which MAY be implemented by application/BSP function(s) [see Note #1] &
* MAY be called by application function(s).
* Note(s) : (1) CPU_TS32_to_uSec()/CPU_TS64_to_uSec() are application/BSP functions that MAY be
* optionally defined by the developer when either of the following CPU features is
* enabled :
* (a) CPU timestamps
* (b) CPU interrupts disabled time measurements
* See 'cpu_cfg.h CPU TIMESTAMP CONFIGURATION Note #1'
* & 'cpu_cfg.h CPU INTERRUPTS DISABLED TIME MEASUREMENT CONFIGURATION Note #1a'.
* (2) (a) The amount of time measured by CPU timestamps is calculated by either of
* the following equations :
*
* 10^6 microseconds
* (1) Time measured = Number timer counts * ------------------- * Timer period
* 1 second
*
* Number timer counts 10^6 microseconds
* (2) Time measured = --------------------- * -------------------
* Timer frequency 1 second
*
* where
*
* (A) Number timer counts Number of timer counts measured
* (B) Timer frequency Timer's frequency in some units
* of counts per second
* (C) Timer period Timer's period in some units of
* (fractional) seconds
* (D) Time measured Amount of time measured,
* in microseconds
*
* (b) Timer period SHOULD be less than the typical measured time but MUST be less
* than the maximum measured time; otherwise, timer resolution inadequate to
* measure desired times.
*
* (c) Specific implementations may convert any number of CPU_TS32 or CPU_TS64 bits
* -- up to 32 or 64, respectively -- into microseconds.
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
#if (CPU_CFG_TS_32_EN == DEF_ENABLED)
CPU_INT64U CPU_TS32_to_uSec (CPU_TS32 ts_cnts)
{
CPU_INT64U ts_us;
CPU_INT64U fclk_freq;
fclk_freq = BSP_CPU_ClkFreq();
ts_us = ts_cnts / (fclk_freq / DEF_TIME_NBR_uS_PER_SEC);
return (ts_us);
}
#endif
#if (CPU_CFG_TS_64_EN == DEF_ENABLED)
CPU_INT64U CPU_TS64_to_uSec (CPU_TS64 ts_cnts)
{
CPU_INT64U ts_us;
CPU_INT64U fclk_freq;
fclk_freq = BSP_CPU_ClkFreq();
ts_us = ts_cnts / (fclk_freq / DEF_TIME_NBR_uS_PER_SEC);
return (ts_us);
}
#endif
3、修改UCOSiii关联的代码。
完成第2大点的步骤,UCOSiii的文件算是全部准备好了,下来我们将相关代码来匹配当前的环境。
3.1 UCOSIII/UCOSIII_CONFIG/includes.h 修改
将#include <stm32f10x_lib.h> 注释掉,我们不需要使用。

3.2 UCOSIII/UCOSIII_PORT/os_cpu_a.s 及 Core/Src/stm32f1xx_it.c 修改
os_cpu_a.s
OS_CPU_PendSVHandler 改为 PendSV_Handler

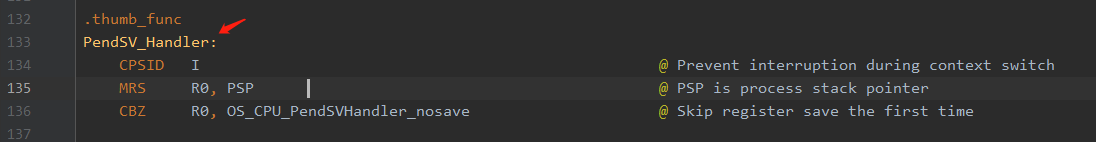
在ucos的源码都定义好了名称是OS_CPU_PendSVHandler,在文件os_cpu_a.s中如3.2上图所示。但是stm32中也定义了异常中断,在stm32的启动文件startup_stm32xxx.s中
可以看到如下图所示,其名称为PendSVHandler(或PendSV_Handler)与前者的名字不同而已。由于stm32是先从启动文件开始运行,中断异常自然是按启动文件中定义的为准,所以后面
ucos在进行任务切换的时候触发了异常中断,而ucos异常中断函数相当于是没用的,所以如果将OS_CPU_PendSVHandler 改为 PendSV_Handler 出现了卡死情况。

stm32f1xx_it.c
将 void PendSV_Handler(void) 注释掉如下图,原因是:stm32f1xx_it.c 和 os_cpu_a.s 中重复定义了 PendSV_Handler 这个函数。

3.3 延时delay.c 程序的修改。
delay.c是用于时间延时控制的,STM32 delay.c的网上有很多教程,这里就不另外展开了。
3.3.1 SysTick_Handler (void) 重名修改。
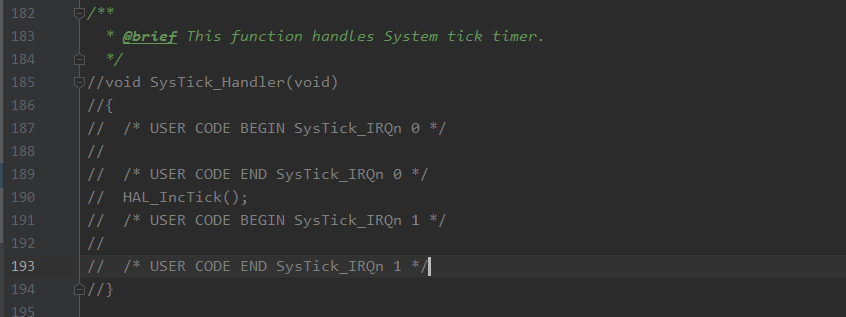
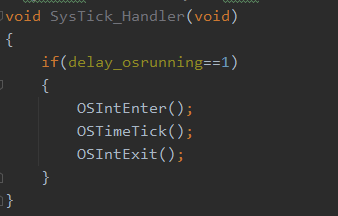
自定义的Delay.c 延时程序中使用了void SysTick_Handler(void) 函数系统滴答计时器如右图。因为自定义的Delay.c 和 stm32f1xx_it.c 中存在同名冲突, 所以需要屏蔽掉stm32f1xx_it.c 中的函数如左图。
屏蔽掉stm32f1xx_it.c的函数后,HAL的时钟也不启用,其它程序不能使用HAL的Delay() 函数功能。
3.3.2 Delay.c 支持 Ucosiii 功能启用。
自定义的 sys.h 的 SYSTEM_SUPPORT_OS = 1 支持Ucosiii

3、Main.c创建任务运行Ucosiii
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "sys.h" // 时钟配置、GPIO位带 【时钟配置不用这里的】
#include "delay.h"
#include "includes.h"
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
void flesh_LED(int Delay);
void flesh_LEDB8(int Delay);
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define START_TASK_PRIO 3 //任务优先级
#define START_STK_SIZE 512 //任务堆栈大小
OS_TCB StartTaskTCB; //任务控制块
CPU_STK START_TASK_STK[START_STK_SIZE]; //任务堆栈
void start_task(void *p_arg); //任务函数
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define LED0_TASK_PRIO 4 //任务优先级
#define LED0_STK_SIZE 128 //任务堆栈大小
OS_TCB Led0TaskTCB; //任务控制块
CPU_STK LED0_TASK_STK[LED0_STK_SIZE]; //任务堆栈
void led0_task(void *p_arg); //任务函数
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define LED1_TASK_PRIO 5 //任务优先级
#define LED1_STK_SIZE 128 //任务堆栈大小
OS_TCB Led1TaskTCB; //任务控制块
CPU_STK LED1_TASK_STK[LED1_STK_SIZE]; //任务堆栈
void led1_task(void *p_arg); //任务函数
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick.
* 重置所有外围设备,初始化Flash接口和Systick*/
HAL_Init();
/* 系统时钟初始化 */
SystemClock_Config();
/* 系统初始化*/
delay_init(72);//初始化延时函数
/*初始化设置外围设备---------------------------------------------------------*/
MX_GPIO_Init();
/*任务开启------------------------------------------------------------------*/
OS_ERR err;
CPU_SR_ALLOC();
HAL_NVIC_SetPriorityGrouping(NVIC_PRIORITYGROUP_2); //中断分组配置
OSInit(&err); //初始化UCOSIII
OS_CRITICAL_ENTER(); //进入临界区
//创建开始任务
OSTaskCreate((OS_TCB * )&StartTaskTCB, //任务控制块
(CPU_CHAR * )"start task", //任务名字
(OS_TASK_PTR )start_task, //任务函数
(void * )0, //传递给任务函数的参数
(OS_PRIO )START_TASK_PRIO, //任务优先级
(CPU_STK * )&START_TASK_STK[0],//任务堆栈基地址
(CPU_STK_SIZE)START_STK_SIZE/10, //任务堆栈深度限位
(CPU_STK_SIZE)START_STK_SIZE, //任务堆栈大小
(OS_MSG_QTY )0, //任务内部消息队列能够接收的最大消息数目,为0时禁止接收消息
(OS_TICK )0, //当使能时间片轮转时的时间片长度,为0时为默认长度,
(void * )0, //用户补充的存储区
(OS_OPT )OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CHK|OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CLR, //任务选项
(OS_ERR * )&err); //存放该函数错误时的返回值
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT(); //退出临界区
OSStart(&err); //开启UCOSIII
while (1)
{
}
}
//开始任务
void start_task(void *p_arg)
{
OS_ERR err;
CPU_SR_ALLOC();
p_arg = p_arg;
CPU_Init();
#if OS_CFG_STAT_TASK_EN > 0u
OSStatTaskCPUUsageInit(&err); //统计任务
#endif
#ifdef CPU_CFG_INT_DIS_MEAS_EN //如果使能了测量中断关闭时间
CPU_IntDisMeasMaxCurReset();
#endif
#if OS_CFG_SCHED_ROUND_ROBIN_EN //当使用时间片轮转的时候
//使能时间片轮转调度功能,时间片长度为1个系统时钟节拍,既1*5=5ms
OSSchedRoundRobinCfg(DEF_ENABLED,1,&err);
#endif
OS_CRITICAL_ENTER(); //进入临界区
//创建LED0任务
OSTaskCreate((OS_TCB * )&Led0TaskTCB,
(CPU_CHAR * )"led0 task",
(OS_TASK_PTR )led0_task,
(void * )0,
(OS_PRIO )LED0_TASK_PRIO,
(CPU_STK * )&LED0_TASK_STK[0],
(CPU_STK_SIZE)LED0_STK_SIZE/10,
(CPU_STK_SIZE)LED0_STK_SIZE,
(OS_MSG_QTY )0,
(OS_TICK )0,
(void * )0,
(OS_OPT )OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CHK|OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CLR,
(OS_ERR * )&err);
//创建LED1任务
OSTaskCreate((OS_TCB * )&Led1TaskTCB,
(CPU_CHAR * )"led1 task",
(OS_TASK_PTR )led1_task,
(void * )0,
(OS_PRIO )LED1_TASK_PRIO,
(CPU_STK * )&LED1_TASK_STK[0],
(CPU_STK_SIZE)LED1_STK_SIZE/10,
(CPU_STK_SIZE)LED1_STK_SIZE,
(OS_MSG_QTY )0,
(OS_TICK )0,
(void * )0,
(OS_OPT )OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CHK|OS_OPT_TASK_STK_CLR,
(OS_ERR * )&err);
OS_TaskSuspend((OS_TCB*)&StartTaskTCB,&err); //挂起开始任务
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT(); //进入临界区
}
/**
* @brief 任务0 PB8 LED闪烁
*/
void led0_task(void *p_arg)
{
OS_ERR err;
p_arg = p_arg;
while(1)
{
flesh_LEDB8(100);
}
}
/**
* @brief 任务1 PC13 LED闪烁
*/
void led1_task(void *p_arg)
{
OS_ERR err;
p_arg = p_arg;
while(1)
{
flesh_LED(500);
}
}
/**
* @brief LED闪烁PC13
* @param Delay 延时ms
* @retval None
*/
void flesh_LED(int Delay)
{ //闪烁一个LED PC13 自定义函数
PCout(13) =0;
delay_ms(Delay);
PCout(13) =1;
delay_ms(Delay);
}
void flesh_LEDB8(int Delay)
{ //闪烁一个LED PC13 自定义函数
PBout(8) =0;
delay_ms(Delay);
PBout(8) =1;
delay_ms(Delay);
}
运行程序后可以发现PC13 和PB8 通过位带操作以不同的频率进行闪烁。
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42660303/article/details/107931915
https://blog.csdn.net/chuancey_cc/article/details/84844740

