双向链表C语言实现
双向链表实现(带头结点版)
双向链表的实现与单链表类似,在这里使用C语言实现,主要包括头插法插入节点,删除节点以及创建空链表
抽象数据结构ADT定义
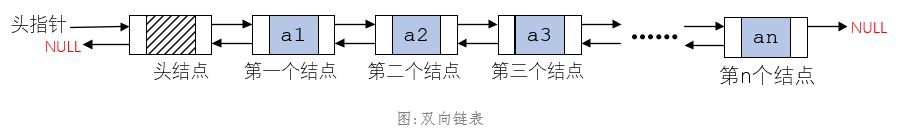
双向链表与单链表的区别在于多了一个指向上一个节点的指针prev
typedef struct _Node {
int data;
struct _Node* next;
struct _Node* prev;
}Node;
typedef Node* Link;
创建空链表
基于上次单链表的demo中碰到的问题,为了避免使用二级指针,使用带头结点的头指针方式实现,因此创建一个新的空链表代码如下:
Link CreateLink() {
//使用malloc函数返回一个不存放内容的头结点head
Link head = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("Link create error\n");
exit(1);
}
head->next = NULL;
head->prev = NULL;
return head;
}
插入新节点--头插法
带头结点的链表的实现逻辑与单链表略有不同,首先是函数的参数,只需传入指向头结点的指针Link head和值int value。最主要的还是插入新节点的逻辑,假设原链表顺序为head->A,我们需要插入新节点B:
(1) 首先是设置B的next和prev指针,next指向A,prev指向头结点
(2) 接着依次断开head与A之间的next和prev指针,并插入新节点B。在这里需要考虑两种情况:
- 如果链表是空的,也就是只有一个头结点,这时A=NULL,如果想改变节点A的指针prev指向新节点B显然不现实,此时则不需要对A节点的prev指针设置
- 如果链表非空也就是head->A->...->NULL的情况,此时头插法设置A的prev指向新节点B
- 最后设置头结点head的next指向新节点B,头插法结束
/*新增节点--头插法*/
int Insert(Link head, int value) {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node* cur = head;
temp->data = value;
if(head == NULL) {
return -1;
}
//设置新节点的首尾指针
temp->next = cur->next;
temp->prev = cur;
//断开原链表的链接,并链接新节点
if(cur->next != NULL)
{
cur->next->prev = temp;
}
cur->next = temp;
return 1;
}
删除指定下标的节点
删除节点的逻辑都是相同的,先遍历至该节点处或该节点的前一个节点,由于是双向链表,因此两种都可以,这里是直接遍历到要删除的节点处
(1) 链表判空
(2) 遍历到要删除的节点处
(3) 修改前一个节点的next指向下一个节点,下一个节点的prev指向前一个节点
(4) 最后将当前节点的指针回收即可完成删除
/*删除指定下标节点*/
int Delete(Link head, int index) {
int i = 0;
//从第一个节点开始,注意不是头结点,而是head->next
Node* cur = head->next;
if(head == NULL || cur == NULL)
return -1;
//遍历到要删除的节点,因此条件为(i < index - 1)
while(cur && i < index - 1)
{
cur = cur->next;
i++;
}
cur->prev->next = cur->next;
if(cur->next != NULL)
cur->next->prev = cur->prev;
cur->next = NULL;
cur->prev = NULL;
return 1;
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct _Node {
int data;
struct _Node* next;
struct _Node* prev;
}Node;
typedef Node* Link;
Link CreateLink() {
Link head = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("Link create error\n");
exit(1);
}
head->next = NULL;
head->prev = NULL;
return head;
}
/*新增节点--头插法*/
int Insert(Link head, int value) {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node* cur = head;
temp->data = value;
if(head == NULL) {
return -1;
}
//设置新节点的首尾指针
temp->next = cur->next;
temp->prev = cur;
//断开原链表的链接,并链接新节点
if(cur->next != NULL)
{
cur->next->prev = temp;
}
cur->next = temp;
return 1;
}
/*删除指定下标节点*/
int Delete(Link head, int index) {
int i = 0;
Node* cur = head->next;
if(head == NULL || cur == NULL)
return -1;
while(cur && i < index - 1)
{
cur = cur->next;
i++;
}
cur->prev->next = cur->next;
if(cur->next != NULL)
cur->next->prev = cur->prev;
cur->next = NULL;
cur->prev = NULL;
return 1;
}
/*打印链表*/
void Print(Link head) {
Node* node = head->next;
if(head == NULL) {
printf("head is null\n");
return;
}
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
return;
}
int main() {
int flag = 0;
Node* head = CreateLink();
Insert(head, 1);
Insert(head, 2);
Insert(head, 3);
Insert(head, 4);
Print(head);
flag = Delete(head, 2);
if(flag < 0) printf("delete error\n");
Print(head);
return 0;
}
莫愁前路无知己,天下谁人不识君
本文作者:Arthur-Morgan
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/six-years/p/17966818
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步