徐思201771010132《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十四周学习总结
一、理论知识部分
设计模式(Design pattern)是设计者一种流行的思考设计问题的方法,是一套被反复使用,多数人知晓的,经过分类编目的,代码设计经验的总结。使用设计模式是为了可重用代码、让代码更容易被他人理解、保证代码可靠性。每一个模式描述了一个不断重复发生的设计问题,以及该问题的核心解决方案
模型-视图-控制器设计模式(Model –ViewController )是Java EE平台下创建 Web 应用程序 的重要设计模式。
MVC设计模式 – Model(模型):是程序中用于处理程序数据逻辑的部分,通常模型负责在数据库中存取数据。– View(视图):是程序中处理数据显示的部分,通常视图依据模型存取的数据创建。 – Controller(控制器):是程序中处理用户交互的部分。通常控制器负责从视图读取数据,控制用户输入,并向模型发送数据。
MVC模式可应用于Java的GUI组件设计中。MVC模式GUI组件设计的唯一的模式,还有很多设计的模式(设计方法)。
Java组件有内容、外观、行为三个主要元素;这三个主要元素与模型—视图—控制器模式的 三部件的对应关系为:内容——控制器(作用:处理用户输入) 外观——视图(作用:显示内容)行为——模型(作用:存储内容)
布局管理器是一组类。实现 java.awt.LayoutManager 接口;决定容器中组件的位置和大小
Java.awt包中定义了5种布局管理类,每一种布局管理类对应一种布局策略。每个容器都有与之相关的默认布局管理器。当一个容器选定一种布局策略时,它应该创建该 策略对应的布局管理器对象,并将此对象设置为 自己的布局管理器。
5种布局管理器:(1)FlowLayout:流布局(Applet和Panel的默认布局管理器) (2)BorderLayout:边框布局( Window、Frame和Dialog的默认布局管理器)(3)GridLayout:网格布局(4)GridBagLayout: 网格组布局(5)CardLayout :卡片布局
FlowLayout Manager 组件采用从左到右,从上到下逐行摆放。
GridBagLayout不需要组件的尺寸一致,容许组件扩展到多行、多列。
每个容器对象在没有设置新的布局前,在容器中添加组件都按照该容器的缺省布局排列。通过setLayout( )方法为容器设置新的布局。格式 : 容器组件名.setLayout( 布局类对象名)
FlowLayout (流布局管理器):用于对组件逐行地定位,每完成一行,一个新行便又开始。与其他布局管理器不同的是,流布局管理器不限制它所管理组件的大小,允许它们有自己的最佳大小。
构造函数有:FlowLayout( ):生成一个默认的流式布局对象 ; FlowLayout(int align): 设定每一行组件的对齐方式(FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.CENTER, FlowLayout.RIGHT);FlowLayout(int align,int hgap,int vgap):可以设定组件间的水平和垂直距离(缺省时组件之间没有空隙)
流布局是面板的默认布局管理器
BorderLayout (边框布局管理器):边框布局管理器是每个JFrame的内容窗格的默认布局管理器;流布局管理器可将组件置于内容窗格的中部,北 部、南部、东部或西部位置。流布局管理器会扩展组件尺寸并填满指定方位区域。
BorderLayout的使用方法:设置容器的布局管理器为BorderLayout ;向容器中加入组件时,若使用两个参数的add() 方法,第二个参数必须说明加入组件在容器中的放置位置;位置参数是BorderLayout 类的常量:CENTER、 NORTH、SOUTH、EAST、WEST 例如: frame.add(component,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
BorderLayout( ) :创建新的BorderLayout,组件之间没有间距 ;setHgap(int hgap) :将组件间的水平间距设置为指定的值; setVgap(int vgap) :将组件间的垂直间距设置为指定的值
GridLayout (网格布局管理器):网格布局按行列排列所有的组件;在网格布局对象的构造器中,需要指定行数和列数: panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(6,10));放置组件的每个单元具有相同的尺寸。添加组件,从第一行和第一列开始,然后是第一行的第二列。以此类推。
GridLayout:指定网格中的行数和列数,创建网格布局
GridLayout的使用方法:GridLayout的构造函数如下:(1)GridLayout():生成一个单行单列的网格布局(2)GridLayout(int rows,int cols):生成一个设定行数和列数的网格布局 (3)GridLayout(int rows,int columns,int hgap,int vgap): 可以设置组件之间的水平和垂直间隔
由于网格中所有单元的宽度、高度是相同的,所以Grid布局管理器总是忽略组件的最佳大小。将组件添加到网格中的命令次序决定组件占有的单元。单元的列数是从左到右填充,而行是从上到下由行填充。
文本域(JTextField) : 用于获取单行文本输入。文本域的使用方法:JPanel panel = new JPanel(); JTextField textField = new JTextField("Default input", 20); panel.add(textField);第一个参数“Default input”:将文本域的缺省显示值为Default input ;第二个参数20:表示文本域显示宽度为20列。若要重新设置列数,可使用setColumns方法。
文本输入常用API:用于文本输入的组件继承于JTextComponent抽象类, java.swing.text.JTextComponent 1.2:String getText() ; void setText(String text) 获取或设置文本组件中的文本 。 boolean isEditable() ; void setEditable(boolean b) 获取或设置editable特性,这个特性决定了用户是否可以编辑文本组件中的内容。 Java.swing. JComponent : void revalidate( ) :重新计算容器内所有组件的大小和位置,并对它们重新布局。 如 panel.revalidate()
文本域JTextField常用API : Java.swing. JTextField: JTextField(int cols) 构造一个指定列数的空JTextField对象。 JTextField(String text,int cols) 构造一个指定列数、指定初始字符串的JTextField对象 。 int getColumns(int cols) ; void setColumns(int cols) 获取或设置文本域使用的列数
文本域初始化 :只要不为JTextField构造器提供字符串参数,就可以构造一个空白文本域。 JTextField textField=newJTextField(20);可在任何时候调用setText方法改变文本域内容。 textField.setText("Hello!"); 可调用getText方法获取键入的文本。要将返回的文本域内容的前后空格去掉,就需调用trim方法:String text=textField.getText().trim();若想改变显示文本的字体,则调用setFont方法。
文本区(JTextArea)组件可让用户输入多行文本。生成JTextArea组件对象时,可以指定文本区的行数和列数: textArea = new JTextArea(8, 40); // 8行40列。输入时,如果文本区的文本超出显示范围,则其余的文本会被剪裁;可以使用换行来避免过长的行被裁减: textArea.setLineWrap(true);在Swing中,文本区没有滚动条,需要手动安装 :JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea)
文本区与文本域的异同相同之处: 文本域和文本区组件都可用于获取文本输入。 不同之处:文本域只能接受单行文本的输入;文本区能够接受多行文本的输入。
文本区JTextArea的常用API:JTextArea(int rows, int cols) 构造一个rows行cols列的文本区对象 。JTextArea(String text,int rows, int cols) 用初始文本构造一个文本区对象。void setRows(int rows) 设置文本域使用的行数。 void append(String newText) 将给定文本附加到文本区中已有文本的后面。 void setLineWrap(boolean wrap) 打开或关闭换行。
标签是容纳文本的组件。它们没有任何修饰(如没有边界 ),也不响应用户输入。标签的常用用途之一就是标识组件,例如标识文本域。其使用步骤如下: 1. 创建一个JLabel组件。例: JLabel label = new JLabel(“hours”, SwingConstants.RIGHT); 或者 JLabel label = new JLabel(“hours”, JLabel.RIGHT);以上代码创建了一个label,并指定label的对齐方式为右对齐。 2. 将标签组件放置在距离被标识组件足够近的地方。
标签组件常用API:JLable(String text) JLable(Icon icon) JLable(String text,int align) JLable(String text,Icon icon,int align) 构造一个标签。 String getText() void setText(String text) 获取或设置标签的文本。 Icon getIcon() void setIcon(Icon icon) 获取或设置标签的图标
密码域是一种特殊类型的文本域。每个输入的字符都用回显字符实现,典型的回显字符为*。
复选框( JCheckBox ):如果想要接收的输入只是“是”或“非”,就可以使用复选框组件。用户通过单击某个复选框来选择相应的选项,再点击则取消选择。当复选框获得焦点时,用户也可以通过空格键来切换选择。
复选框构造器:1.bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); 复选框自动地带有表示标签。 2. JCheckBox(String label,Icon icon); 构造带有标签与图标的复选框,默认初始未被选择。 3.JCheckBox(String label,boolean state); 用指定的标签和初始化选择状态构造一个复选框
复选框常用API: 1.void setSelected(boolean state); 设置复选框的选择状态 2.boolean isSelected(); 获取复选框的选择状态
单选按钮:当需要用户只选择几个选项中的一个。即当用户选择另一项的时候,前一项就自动的取消选择。
单选按钮的构造器:1.JRadioButton(String label,Icon icon); 创建一个带标签和图标的单选按钮 2.JRadioButton(String label,boolean state); 用指定的标签和初始化状态构造单选按钮
按钮组:为单选按钮组构造一个ButtonGroup的对象。 然后,再将JRadioButton类型的对象添加到按钮组中。按钮组负责在新按钮被按下的时,取消前一个按钮的选择状态。 ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup() group.add(JRadioButton对象); 注意:按钮组仅仅控制按钮的行为,如果想把这些按钮组织在一起布局,还需要把它们添加到容器中 ,如JPanel.
边框:如果在一个窗口中有多组复选框或单选按 钮,就需要可视化的形式指明哪些按钮属于同 一组。Swing提供了一 组很有用的边框 ( borders)来解决这个问题。
边框的创建方法:可以调用BorderFactory类的静态方法创建。可选的风格有:凹斜面:BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder() 凸斜面:BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder() 蚀刻:BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder() 直线:BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color) 不光滑:BorderFactory.createMatteBorder()还可以给边框加标题 BorderFactory.createTitledBorder()
组合框:如果有多个选择项,使用单选按钮占据的屏幕空间太大时,就可以选择组合框。
组合框构造器与常用方法:faceCombo = new JComboBox(); faceCombo.setEditable(true); 让组合框可编辑 faceCombo.addItem("Serif"); faceCombo.insertItemAt("Monospace",0); 增加组合框选项 faceCombo.removeItem("Monospace"); faceCombo.removeItemAt(0); 删除组合框选项内容
滑动条( JSlider ):可以让用户从一组离散值中进行选择,并且它还允许进行连续值得选择。
滑动条的修饰可通过显示标尺(tricks)对滑动条进行修饰。 slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); 大标尺标记 slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); 小标尺标记要想显示以上标记,还需调用: slider.setPaintTicks(true);
可以调用下列方法为大标尺添加标尺标签: slider.setPaintLabels(true); 会根据构建标尺时的min,max,和大标尺的间距自动添加 还可以提供其他形式的标尺标记: Hashtable<integer,component> labelTable = new Hashtable<integer,component>(); 构造一个键为Integer类型且值为Component类型 的散列表。
菜单的创建:首先创建一个菜单栏菜单栏是一个可以添加到容器组件任何位置的组件。通常放置在框架的顶部。 JMenuBar menuBar=new JMenuBar();调用框架的setJMenuBar方法可将一个菜单栏对象添加到框架上 frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar); 创建菜单对象,并将菜单对象添加到菜单栏中 JMenu editMenu=new Jmenu("Edit"); menuBar.add(editMenu);向菜单对象添加一个菜单项。 JMenItem pasteItem=new JMenItem(); editMenu.add(pasteItem); 向菜单对象添加分隔符行。 editMenu.addSeperator();向菜单对象项添加子菜单。 JMenu optionsMenu=new Jmenu(“option”); editMenu.add(optionsMenu);
弹出菜单是不固定在菜单栏中随处浮动的菜单。
创建弹出菜单:创建一个弹出菜单与创建一个常规菜单的方法类似,但是弹出菜单没有标题: JPopupMenu popup = new JPopupMenu();然后用常规方法为弹出菜单添加菜单项: JMenuItem item = new JMenuItem("Cut"); item.addActionListener(listener); popup.add(item);弹出菜单调用show方法才能显示出来: popup.show(panel,x,y);
弹出式触发器(pop-up trigger):用户点击鼠标某个键时弹出菜单。在Windows或者Linux中,弹出式触发器是鼠标右键。要想在用户点击某一个组件的时候弹出菜单,该组件就要调用以下方法设置弹出式触发器:component.setComponentPopupMenu(popup);
快捷键:可以为菜单项设置快捷键。在当前菜单打开的情况下,可以按下某菜单项的快捷键,相当于鼠标单击了该菜单项。JMenuItem CutItem=new JMenuItem(" Index "); CutItem.setMnemonic(" I ");此快捷键就会自动显示在菜单项中,快捷键下面有一条下划线。
加速器:加速器可以在不打开菜单的情况下选中菜单项的快捷键。 例如,很多应用程序把CTRL + O和CTRL + S关 联到菜单中的Open和Save项。使用SetAccelerator方法可以将加速器关联到一个菜单项。该方法使用KeyStroke类型的对象作为参数。例如: openItem.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl o" ));当用户按下加速器组合键时,就自动选择了相应的菜单项,同时激活一个动作事件。加速器只能关联在菜单项,而不能关联菜单;加速器实际上并不打开菜单,而是直接激活菜单关联 的动作事件。
启用和禁用菜单项:在程序运行过程中,经常需要屏蔽某些暂时不适用的命令,待到条件允许时再使之重新可用。屏蔽 /启用菜单项的方法: aMenuItem.setEnabled(boolean):当参数值为false时,屏蔽该菜单项; 当参数值为true时,启用该菜单项; 如果需要动态启用 /屏蔽某菜单项,则需要为 “menu selected ”事件注册监听器。 javax.swing.event包定义了MenuListener接口,它有三个方法: void menuSelected(MenuEvent event) ; void menuDeselected(MenuEvent event) ; void menuCanceled(MenuEvent event) ;
工具栏(JToolBar):工具栏在程序中提供快速访问常用命令的按钮栏。工具栏的优点在于可以移动,脱离工具栏或拖拽到框架其他地方。关闭包含工具栏的框架后,工具栏回到原始的框架中。
工具提示:工具提示(tooltips)提示用户小按钮的含义。当光标停留在某个按钮上片刻是,工具提示就会激活。工具提示文本显示在一个有颜色的矩形里。当用户移开鼠标是,工具提示就会自动地消失;在Swing中,可以调用setToolTest方法将工具提示添加到JComponent上;exitButton.setToolTipText(" Exit ");另外一种方法是,如果使用Action对象,就可以用 SHORT-DESCRIPTION关联工具提示: exitButton.putValue(Action.SHORT-DESCRIPTION, " Exit ");
网格组布局 (GridBagLayout):GridBagLayout与GridLayout有点相似,它也是将组件排在格子里,但是GridBagLayout在网格的基础上提供更复杂的布局。GridBagLayout允许单个组件在一个单元中不填满整个单元,而只是占用最佳大小,也允许单个组件扩展成不止一个单元,并且可以用任意顺序加入组件。
GridBagLayout 的API:使用GridBagLayout,必须构造一个GridBagConstraints对象。GridBagConstraints 用于指定如何用GridBagLayout放置组件。 GridBagConstraints对象包含一些重要的约束,以指定组件的放置方式,这些约束的含义如下:
1.gridx 、gridy 、gridwidth 和gridheight参数。这四个参数用于指定组件在网格中的位置。gridx 和 gridy值用于指定组件左上角的坐标;gridwidth 和gridheight决定组件将占用多少行和列.
2.增量域(weightx和weighty)。 GridBagLayout内的每个区域都必须设置它的增量域,即weightx和weighty。如果将权值设置为0,那么这个区域就不会在那个方向上扩张或收缩,超出它的初始大小。 增量参数属于行和列的属性,而不属于某个单独的单元格。但却需在单元格上指定它们,这是因为 网格组布局并不暴露行和列。
3.fill 和anchor参数。fill参数用于指定组件在单元格 内进行伸缩时的填充方式,该参数可以有四种有效 值:GridBagConstraints.NONE(不伸缩 ) 、 GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL(水平伸缩 ) 、 GridBagConstraints.VERTICAL(垂直伸缩 ) 和 GridBagConstraints.BOTH 。 如果组件没有填充整个区域,可以通过设置 anchor域指定其对齐位置。有效值为 GridBagConstraints.CENTER, GridBagConstraints.NORTH, GridBagConstraints.NORTHEAST, GridBagConstraints.EAST 等
4 . 填 塞 : 填 充 参 数 insets , ipadx 和 ipady 。 insets参数用于设置沿单元格边界的外部填充空白区域。ipadx和ipady则用于指定在环绕组件四周的单元格内部填充空白区域。
对话框(JDialog):对话框是一种大小不能变化、不能有菜单的容器窗口;对话框不能作为一个应用程序的主框架,而必须包含在其他的容器中。Java提供多种对话框类来支持多种形式的对话框。JOptionPane类支持简单、标准的对话框;JDialog类支持定制用户自己的对话框; JFileChooser类支持文件打开、保存对话框;ProgressMonitor类支持操作进度条控制对话框等。
对话框依赖于框架。当框架撤销时,依赖该框架的对话框也撤销。当框架图标化时,依赖它的对话框也从屏幕上消失。当框架窗口恢复时,依赖框架的对话框又返回屏幕。对话框分为无模式和有模式两种。有模式的对话框处于激活状态时,程序只能响应对话框内部的事件,不能再激活它所依赖的窗口或组件,而且它将堵塞当前线程的执行,即堵塞使得对话框处于激活状态的线程,直到该对话框消失不可见。无模式对话框处于激活状态时,程序仍能激活它所依赖的窗口或组件,它也不堵塞线程的执行。
选项对话框(JOptionPane):JOptionPane提供的对话框是模式对话框。当模式对话框显示时,它不允许用户输入到程序的其他的窗口。使用JOptionPane,可以创建和自定义问题、信息、警告和错误等几种类型的对话框。
Swing提供了用于显示选项对话框(JOptionPane )的JOptionPane 类,定义了多个showXxxDialog形式的静态方法 :showMessageDialog —— 信息对话框,显示信息,告知用户发生了什么情况 。showConfirmDialog —— 确认对话框,显示问题,要求用户进行 确认(yes/no/cancel )。showOptionDialog —— 选项对话框,显示选项,要求用户进行选 择 。 showInputDialog —— 输入对话框,提示用户进行输入
创建对话框(JDialog):对话框的构造方法:JDialog(Frame owner) ——构造一个没有标题的非模式对话框。JDialog(Frame owner, boolean modal) ——构造一个没有标题的对话框,boolean型参数modal指定对话框是否为模式窗口。 JDialog(Frame owner, String title) ——构造一个有标题的非模式对话框. JDialog(Frame owner, String title, boolean modal) ——构造一个有标题的对话框。
showXxxDialog方法的参数:Component parentComponent对话框的父窗口对象,其屏幕坐标将决定对话框的显示位置;此参数也可以为null,表示采用缺省的Frame 作为父窗口,此时对话框将设置在屏幕的正中 。 String title 对话框的标题 。 Object message 显示在对话框中的描述信息。该参数通常是一个String对象,但也可以是一个图标、一个组件或者一个对象数组。int messageType – 对话框所传递的信息类型。int optionType对话框上按钮的类型,可以为以下常量:DEFAULT_OPTION YES_NO_OPTION YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION OK_CANCEL_OPTION 。Object[] options:对话框上的选项。在输入对话框中,通常以组合框形式显示,在选项对话框中,则指按钮的选项类型。该参数通常是一个String数组,但也可以是图标或组件数组。Icon icon 对话框上显示的装饰性图标,如果没有指定,则根据 messageType 参数显示缺省图标。 Object initialValue 初始选项或输入值
showXxxDialog()返回类型:showMessageDialog()没有返回值 。 showConfirmDialog() 和showOptionDialog()方法返 回int型数值,代表用户选择按钮的序号 。(JOptionPane中定义了YES_OPTION、 NO_OPTION、CANCEL_OPTION、OK_OPTION和 CLOSED_OPTION等常量,分别代表用户选择了 YES、NO、CANCEL、OK按钮以及未选择而直接关 闭了对话框)。 showInputDialog()方法的返回值为String或 Object,代表用户的输入或选项
数据交换:输入对话框含有供用户输入文本的文本框、一个确认和取消按钮,是有模式对话框。当输入对话框可见时,要求用户输入一个字符串。javax.swing包中的JOptionPane类的静态方法:public static String showInputDialog(Component parentComponent, Object message,String title,int messageType)。创建一个输入对话框,其中参数parentComponent指定消息对话框所依赖的组件,确认对话框会在该组件的正前方显示出来,参数message指定对话框上的提示信息,参数 title指定对话框上的标题,参数messageType可取的有效值是JoptionPane中的类常量
文件对话框(JFileChooser):专门用于对文件(或目录)进行浏览和选择的对话框,常用的构造方法: JFileChooser():根据用户的缺省目录创建文件对话框。JFileChooser(File currentDirectory):根据File型参数currentDirectory指定的目录创建文件对话框。JFileChooser(String currentDirectoryPath):根据 String型参数currentDirectoryPath指定的目录创建文件对话框。
二、实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握GUI布局管理器用法;
(2) 掌握各类Java Swing组件用途及常用API;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第12章示例程序,测试程序并进行组内讨论。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中运行教材479页程序12-1,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种布局管理器的用法;
l 理解GUI界面中事件处理技术的用途。
l 在布局管理应用代码处添加注释;

package calculator; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Calculator { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { CalculatorFrame frame = new CalculatorFrame(); frame.setTitle("Calculator");// 设置窗口标题 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package calculator; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a calculator panel. */ public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame { public CalculatorFrame() { add(new CalculatorPanel()); pack(); } }

package calculator; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A panel with calculator buttons and a result display. */ public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel { private JButton display; private JPanel panel; private double result; private String lastCommand; private boolean start; public CalculatorPanel() { setLayout(new BorderLayout());// 构造一个边框布局管理器 result = 0; lastCommand = "="; start = true; // add the display display = new JButton("0");// 用来显示计算的计算结果 display.setEnabled(false);// 禁止使用按钮 add(display, BorderLayout.NORTH); ActionListener insert = new InsertAction(); ActionListener command = new CommandAction();// 设置两个监听器对象 // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4));// 设置4行4列的网格布局 addButton("7", insert); addButton("8", insert); addButton("9", insert); addButton("/", command); addButton("4", insert); addButton("5", insert); addButton("6", insert); addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert); addButton("2", insert); addButton("3", insert); addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert); addButton(".", insert); addButton("=", command); addButton("+", command); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);// 添加按钮到指定方位 } /** * Adds a button to the center panel. * * @param label the button label * @param listener the button listener */ private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(label); button.addActionListener(listener); panel.add(button); } /** * This action inserts the button action string to the end of the display text. */ private class InsertAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String input = event.getActionCommand(); if (start) { display.setText(""); start = false; } display.setText(display.getText() + input); } } /** * This action executes the command that the button action string denotes. */ private class CommandAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start) { if (command.equals("-")) { display.setText(command); start = false; } else lastCommand = command; } else { calculate(Double.parseDouble(display.getText())); lastCommand = command; start = true; } } } /** * Carries out the pending calculation. * * @param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result. */ public void calculate(double x) { if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x; else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x; display.setText("" + result); } }
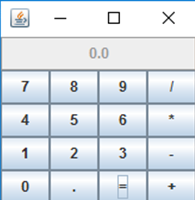
测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材486页程序12-2,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种文本组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package text; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.41 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class TextComponentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new TextComponentFrame(); frame.setTitle("TextComponentTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package text; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingConstants; /** * A frame with sample text components. */ public class TextComponentFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXTAREA_ROWS = 8; public static final int TEXTAREA_COLUMNS = 20; public TextComponentFrame() { JTextField textField = new JTextField(); JPasswordField passwordField = new JPasswordField(); JPanel northPanel = new JPanel(); northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); northPanel.add(new JLabel("User name: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT)); northPanel.add(textField); northPanel.add(new JLabel("Password: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT)); northPanel.add(passwordField);// 创建了两个个label,并指定label的对齐方式为右对齐 add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);// 北区域的边框布局约束(容器顶部)。 JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(TEXTAREA_ROWS, TEXTAREA_COLUMNS);// 构造具有指定行数和列数的新的空 TextArea JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea);// 创建一个显示指定组件内容的 JScrollPane,只要组件的内容超过视图大小就会显示水平和垂直滚动条。 add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER); // add button to append text into the text area JPanel southPanel = new JPanel(); JButton insertButton = new JButton("Insert"); southPanel.add(insertButton); insertButton.addActionListener(event -> textArea.append( "User name: " + textField.getText() + " Password: " + new String(passwordField.getPassword()) + "\n")); add(southPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }

测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材489页程序12-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握复选框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class CheckBoxTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new CheckBoxFrame(); frame.setTitle("CheckBoxTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and check boxes for selecting font * attributes. */ public class CheckBoxFrame extends JFrame { private JLabel label; private JCheckBox bold; private JCheckBox italic; private static final int FONTSIZE = 24; public CheckBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, FONTSIZE));// 设置组件的字体。 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);// 中间区域的布局约束(容器中央)。 // this listener sets the font attribute of // the label to the check box state ActionListener listener = event -> { int mode = 0; if (bold.isSelected()) mode += Font.BOLD; if (italic.isSelected()) mode += Font.ITALIC; label.setFont(new Font("Serif", mode, FONTSIZE)); }; // add the check boxes JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold");// 复选框自动地带有表示标签。 bold.addActionListener(listener); bold.setSelected(true);// 使用setSelected方法来选定或取消选定复选框 buttonPanel.add(bold); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic"); italic.addActionListener(listener); buttonPanel.add(italic); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }

测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材491页程序12-4,运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握单选按钮组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package radioButton; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class RadioButtonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new RadioButtonFrame(); frame.setTitle("RadioButtonTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package radioButton; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and radio buttons for selecting font sizes. */ public class RadioButtonFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; private JLabel label; private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 36; public RadioButtonFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));//设置组件的字体 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);//中间区域的布局约束(容器中央) // add the radio buttons buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Small", 8); addRadioButton("Medium", 12); addRadioButton("Large", 18); addRadioButton("Extra large", 36); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);//添加按钮到指定方位 pack(); } /** * Adds a radio button that sets the font size of the sample text. * * @param name the string to appear on the button * @param size the font size that this button sets */ public void addRadioButton(String name, int size) { boolean selected = size == DEFAULT_SIZE; JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(name, selected); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); // this listener sets the label font size ActionListener listener = event -> label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, size)); button.addActionListener(listener); } }
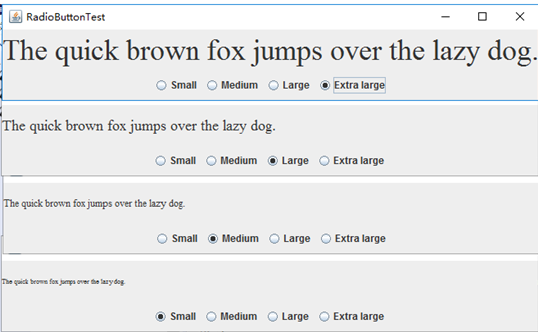
测试程序5
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材494页程序12-5,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握边框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-13 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BorderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BorderFrame(); frame.setTitle("BorderTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; /** * A frame with radio buttons to pick a border style. */ public class BorderFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel demoPanel; private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; public BorderFrame() { demoPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Lowered bevel", BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder());//创建一个具有凹入斜面边缘的边框,将组件当前背景色的较亮的色度用于高亮显示,较暗的色度用于阴影。(在凹入边框中,阴影位于顶部,高亮显示位于其下。) addRadioButton("Raised bevel", BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder()); //创建一个具有凸出斜面边缘的边框,将组件当前背景色的较亮的色度用于高亮显示,较暗的色度用于阴影。(在凸出边框中,高亮显示位于顶部,阴影位于其下。) addRadioButton("Etched", BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());//创建一个具有“浮雕化”外观效果的边框,将组件的当前背景色用于高亮显示和阴影显示。 addRadioButton("Line", BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.BLUE));//创建一个具有指定颜色的线边框。 addRadioButton("Matte", BorderFactory.createMatteBorder(10, 10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE));//使用纯色创建一个类似衬边的边框 addRadioButton("Empty", BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder());//创建一个不占用空间的空边框 Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(); Border titled = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched, "Border types"); buttonPanel.setBorder(titled); setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));//创建2行1列的网格布局 add(buttonPanel); add(demoPanel); pack(); } //单选按钮组件监听器 public void addRadioButton(String buttonName, Border b) { JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(buttonName); button.addActionListener(event -> demoPanel.setBorder(b)); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); } }
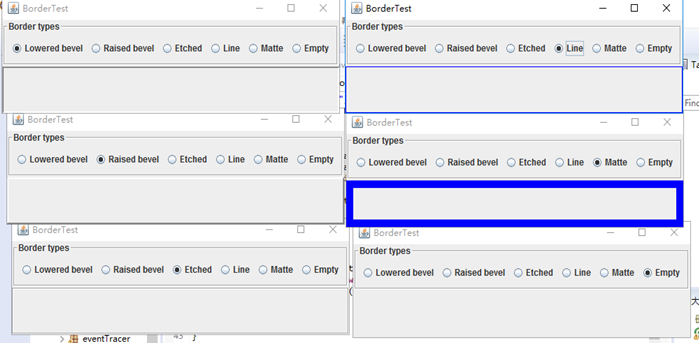
测试程序6
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材498页程序12-6,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握组合框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package comboBox; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.35 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ComboBoxTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ComboBoxFrame(); frame.setTitle("ComboBoxTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package comboBox; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Font; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A frame with a sample text label and a combo box for selecting font faces. */ public class ComboBoxFrame extends JFrame { private JComboBox<String> faceCombo; private JLabel label; private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 24; public ComboBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));//设置组件的字体 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // make a combo box and add face names faceCombo = new JComboBox<>(); faceCombo.addItem("Serif"); faceCombo.addItem("SansSerif"); faceCombo.addItem("Monospaced"); faceCombo.addItem("Dialog"); faceCombo.addItem("DialogInput"); // the combo box listener changes the label font to the selected face name faceCombo.addActionListener(event -> label .setFont(new Font(faceCombo.getItemAt(faceCombo.getSelectedIndex()), Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE))); // add combo box to a panel at the frame's southern border JPanel comboPanel = new JPanel(); comboPanel.add(faceCombo); add(comboPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }
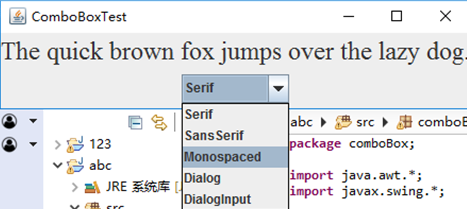
测试程序7
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材501页程序12-7,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握滑动条组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package slider; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.15 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SliderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { SliderFrame frame = new SliderFrame(); frame.setTitle("SliderTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package slider; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.event.*; /** * A frame with many sliders and a text field to show slider values. */ public class SliderFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel sliderPanel; private JTextField textField; private ChangeListener listener; public SliderFrame() { sliderPanel = new JPanel(); sliderPanel.setLayout(new GridBagLayout()); // common listener for all sliders listener = event -> { // update text field when the slider value changes JSlider source = (JSlider) event.getSource(); textField.setText("" + source.getValue()); }; // add a plain slider JSlider slider = new JSlider(); addSlider(slider, "Plain"); // add a slider with major and minor ticks slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); addSlider(slider, "Ticks"); // add a slider that snaps to ticks slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setSnapToTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); addSlider(slider, "Snap to ticks"); // add a slider with no track slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); slider.setPaintTrack(false); addSlider(slider, "No track"); // add an inverted slider slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); slider.setInverted(true); addSlider(slider, "Inverted"); // add a slider with numeric labels slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setPaintLabels(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); addSlider(slider, "Labels"); // add a slider with alphabetic labels slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintLabels(true); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); Dictionary<Integer, Component> labelTable = new Hashtable<>(); labelTable.put(0, new JLabel("A")); labelTable.put(20, new JLabel("B")); labelTable.put(40, new JLabel("C")); labelTable.put(60, new JLabel("D")); labelTable.put(80, new JLabel("E")); labelTable.put(100, new JLabel("F")); slider.setLabelTable(labelTable); addSlider(slider, "Custom labels"); // add a slider with icon labels slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true);// 显示标记 slider.setPaintLabels(true);// 确定是否在滑块上绘制标签 slider.setSnapToTicks(true);// 最靠近用户放置滑块处的刻度标记的值 slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20);// 大标尺标记 slider.setMinorTickSpacing(20);// 小标尺标记 labelTable = new Hashtable<Integer, Component>(); // add card images labelTable.put(0, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("nine.gif"))); labelTable.put(20, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("ten.gif"))); labelTable.put(40, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("jack.gif"))); labelTable.put(60, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("queen.gif"))); labelTable.put(80, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("king.gif"))); labelTable.put(100, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("ace.gif"))); slider.setLabelTable(labelTable); addSlider(slider, "Icon labels"); // add the text field that displays the slider value textField = new JTextField(); add(sliderPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER); add(textField, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * Adds a slider to the slider panel and hooks up the listener * * @param s the slider * @param description the slider description */ public void addSlider(JSlider s, String description) { s.addChangeListener(listener); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.add(s); panel.add(new JLabel(description)); panel.setAlignmentX(Component.LEFT_ALIGNMENT); GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints(); gbc.gridy = sliderPanel.getComponentCount(); gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.WEST; sliderPanel.add(panel, gbc); } }

测试程序8
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材512页程序12-8,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握菜单的创建、菜单事件监听器、复选框和单选按钮菜单项、弹出菜单以及快捷键和加速器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package menu; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.24 2012-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class MenuTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new MenuFrame(); frame.setTitle("MenuTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package menu; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample menu bar. */ public class MenuFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private Action saveAction; private Action saveAsAction; private JCheckBoxMenuItem readonlyItem; private JPopupMenu popup; /** * A sample action that prints the action name to System.out */ class TestAction extends AbstractAction { public TestAction(String name) { super(name); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.out.println(getValue(Action.NAME) + " selected."); } } public MenuFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); fileMenu.add(new TestAction("New")); // demonstrate accelerators JMenuItem openItem = fileMenu.add(new TestAction("Open")); openItem.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl O")); fileMenu.addSeparator(); saveAction = new TestAction("Save"); JMenuItem saveItem = fileMenu.add(saveAction); saveItem.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl S")); saveAsAction = new TestAction("Save As"); fileMenu.add(saveAsAction); fileMenu.addSeparator(); fileMenu.add(new AbstractAction("Exit") { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.exit(0); } }); // demonstrate checkbox and radio button menus readonlyItem = new JCheckBoxMenuItem("Read-only"); readonlyItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { boolean saveOk = !readonlyItem.isSelected(); saveAction.setEnabled(saveOk); saveAsAction.setEnabled(saveOk); } }); ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButtonMenuItem insertItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Insert"); insertItem.setSelected(true); JRadioButtonMenuItem overtypeItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Overtype"); group.add(insertItem); group.add(overtypeItem); // demonstrate icons Action cutAction = new TestAction("Cut"); cutAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("cut.gif")); Action copyAction = new TestAction("Copy"); copyAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("copy.gif")); Action pasteAction = new TestAction("Paste"); pasteAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("paste.gif")); JMenu editMenu = new JMenu("Edit"); editMenu.add(cutAction); editMenu.add(copyAction); editMenu.add(pasteAction); // demonstrate nested menus JMenu optionMenu = new JMenu("Options"); optionMenu.add(readonlyItem); optionMenu.addSeparator(); optionMenu.add(insertItem); optionMenu.add(overtypeItem); editMenu.addSeparator(); editMenu.add(optionMenu); // demonstrate mnemonics JMenu helpMenu = new JMenu("Help"); helpMenu.setMnemonic('H'); JMenuItem indexItem = new JMenuItem("Index"); indexItem.setMnemonic('I'); helpMenu.add(indexItem); // you can also add the mnemonic key to an action Action aboutAction = new TestAction("About"); aboutAction.putValue(Action.MNEMONIC_KEY, new Integer('A')); helpMenu.add(aboutAction); // add all top-level menus to menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); menuBar.add(fileMenu); menuBar.add(editMenu); menuBar.add(helpMenu); // demonstrate pop-ups popup = new JPopupMenu(); popup.add(cutAction); popup.add(copyAction); popup.add(pasteAction); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setComponentPopupMenu(popup); add(panel); } }

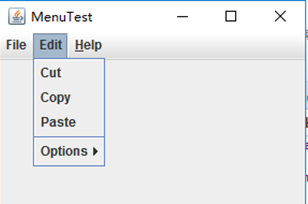
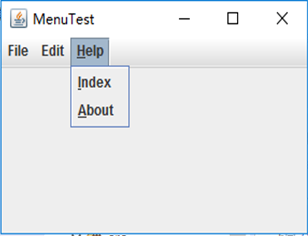
测试程序9
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材517页程序12-9,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握工具栏和工具提示的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package toolBar; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.14 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ToolBarsTet { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { ToolBarFrame frame = new ToolBarFrame(); frame.setTitle("ToolBarTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package toolBar; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a toolbar and menu for color changes. */ public class ToolBarFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private JPanel panel; public ToolBarFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // add a panel for color change panel = new JPanel(); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // set up actions Action blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE); Action yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"), Color.YELLOW); Action redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED); Action exitAction = new AbstractAction("Exit", new ImageIcon("exit.gif")) { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.exit(0); } }; exitAction.putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Exit"); // populate toolbar JToolBar bar = new JToolBar(); bar.add(blueAction); bar.add(yellowAction); bar.add(redAction); bar.addSeparator(); bar.add(exitAction); add(bar, BorderLayout.NORTH); // populate menu JMenu menu = new JMenu("Color"); menu.add(yellowAction); menu.add(blueAction); menu.add(redAction); menu.add(exitAction); JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); menuBar.add(menu); setJMenuBar(menuBar); } /** * The color action sets the background of the frame to a given color. */ class ColorAction extends AbstractAction { public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c) { putValue(Action.NAME, name); putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon); putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, name + " background"); putValue("Color", c); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { Color c = (Color) getValue("Color"); panel.setBackground(c); } } }
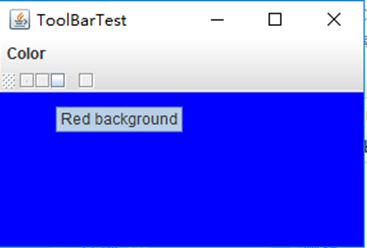
测试程序10
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材524页程序12-10、12-11,结合运行结果理解程序,了解GridbagLayout的用法。
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材533页程序12-12,结合程序运行结果理解程序,了解GroupLayout的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package gridbag; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; /** * @version 1.35 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class GridBagLayoutTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new FontFrame(); frame.setTitle("GridBagLayoutTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package gridbag; import java.awt.*; /** * This class simplifies the use of the GridBagConstraints class. * * @version 1.01 2004-05-06 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class GBC extends GridBagConstraints { /** * Constructs a GBC with a given gridx and gridy position and all other grid bag * constraint values set to the default. * * @param gridx the gridx position * @param gridy the gridy position */ public GBC(int gridx, int gridy) { this.gridx = gridx; this.gridy = gridy; } /** * Constructs a GBC with given gridx, gridy, gridwidth, gridheight and all other * grid bag constraint values set to the default. * * @param gridx the gridx position * @param gridy the gridy position * @param gridwidth the cell span in x-direction * @param gridheight the cell span in y-direction */ public GBC(int gridx, int gridy, int gridwidth, int gridheight) { this.gridx = gridx; this.gridy = gridy; this.gridwidth = gridwidth; this.gridheight = gridheight; } /** * Sets the anchor. * * @param anchor the anchor value * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setAnchor(int anchor) { this.anchor = anchor; return this; } /** * Sets the fill direction. * * @param fill the fill direction * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setFill(int fill) { this.fill = fill; return this; } /** * Sets the cell weights. * * @param weightx the cell weight in x-direction * @param weighty the cell weight in y-direction * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setWeight(double weightx, double weighty) { this.weightx = weightx; this.weighty = weighty; return this; } /** * Sets the insets of this cell. * * @param distance the spacing to use in all directions * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setInsets(int distance) { this.insets = new Insets(distance, distance, distance, distance); return this; } /** * Sets the insets of this cell. * * @param top the spacing to use on top * @param left the spacing to use to the left * @param bottom the spacing to use on the bottom * @param right the spacing to use to the right * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setInsets(int top, int left, int bottom, int right) { this.insets = new Insets(top, left, bottom, right); return this; } /** * Sets the internal padding * * @param ipadx the internal padding in x-direction * @param ipady the internal padding in y-direction * @return this object for further modification */ public GBC setIpad(int ipadx, int ipady) { this.ipadx = ipadx; this.ipady = ipady; return this; } }

package gridbag; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.GridBagLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.BorderFactory; import javax.swing.JCheckBox; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JTextArea; /** * A frame that uses a grid bag layout to arrange font selection components. */ public class FontFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXT_ROWS = 10; public static final int TEXT_COLUMNS = 20; private JComboBox<String> face; private JComboBox<Integer> size; private JCheckBox bold; private JCheckBox italic; private JTextArea sample; public FontFrame() { GridBagLayout layout = new GridBagLayout(); setLayout(layout); ActionListener listener = event -> updateSample(); // construct components JLabel faceLabel = new JLabel("Face: "); face = new JComboBox<>(new String[] { "Serif", "SansSerif", "Monospaced", "Dialog", "DialogInput" }); face.addActionListener(listener); JLabel sizeLabel = new JLabel("Size: "); size = new JComboBox<>(new Integer[] { 8, 10, 12, 15, 18, 24, 36, 48 }); size.addActionListener(listener); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); bold.addActionListener(listener); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic"); italic.addActionListener(listener); sample = new JTextArea(TEXT_ROWS, TEXT_COLUMNS); sample.setText("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"); sample.setEditable(false); sample.setLineWrap(true); sample.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder()); // add components to grid, using GBC convenience class add(faceLabel, new GBC(0, 0).setAnchor(GBC.EAST)); add(face, new GBC(1, 0).setFill(GBC.HORIZONTAL).setWeight(100, 0).setInsets(1)); add(sizeLabel, new GBC(0, 1).setAnchor(GBC.EAST)); add(size, new GBC(1, 1).setFill(GBC.HORIZONTAL).setWeight(100, 0).setInsets(1)); add(bold, new GBC(0, 2, 2, 1).setAnchor(GBC.CENTER).setWeight(100, 100)); add(italic, new GBC(0, 3, 2, 1).setAnchor(GBC.CENTER).setWeight(100, 100)); add(sample, new GBC(2, 0, 1, 4).setFill(GBC.BOTH).setWeight(100, 100)); pack(); updateSample(); } public void updateSample() { String fontFace = (String) face.getSelectedItem(); int fontStyle = (bold.isSelected() ? Font.BOLD : 0) + (italic.isSelected() ? Font.ITALIC : 0); int fontSize = size.getItemAt(size.getSelectedIndex()); Font font = new Font(fontFace, fontStyle, fontSize); sample.setFont(font); sample.repaint(); } }
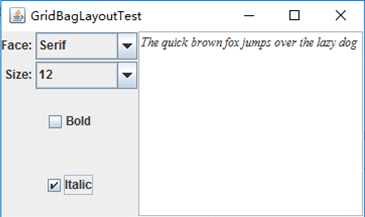

package groupLayout; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; /** * @version 1.01 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class GroupLayoutTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new FontFrame(); frame.setTitle("GroupLayoutTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package groupLayout; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.BorderFactory; import javax.swing.GroupLayout; import javax.swing.JCheckBox; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.LayoutStyle; import javax.swing.SwingConstants; /** * A frame that uses a group layout to arrange font selection components. */ public class FontFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXT_ROWS = 10; public static final int TEXT_COLUMNS = 20; private JComboBox<String> face; private JComboBox<Integer> size; private JCheckBox bold; private JCheckBox italic; private JScrollPane pane; private JTextArea sample; public FontFrame() { ActionListener listener = event -> updateSample(); // construct components JLabel faceLabel = new JLabel("Face: "); face = new JComboBox<>(new String[] { "Serif", "SansSerif", "Monospaced", "Dialog", "DialogInput" }); face.addActionListener(listener); JLabel sizeLabel = new JLabel("Size: "); size = new JComboBox<>(new Integer[] { 8, 10, 12, 15, 18, 24, 36, 48 }); size.addActionListener(listener); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); bold.addActionListener(listener); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic"); italic.addActionListener(listener); sample = new JTextArea(TEXT_ROWS, TEXT_COLUMNS); sample.setText("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"); sample.setEditable(false); sample.setLineWrap(true); sample.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder()); pane = new JScrollPane(sample); GroupLayout layout = new GroupLayout(getContentPane()); setLayout(layout); layout.setHorizontalGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING) .addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup().addContainerGap() .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING) .addGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.TRAILING, layout.createSequentialGroup() .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.TRAILING) .addComponent(faceLabel).addComponent(sizeLabel)) .addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED) .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING, false) .addComponent(size).addComponent(face))) .addComponent(italic).addComponent(bold)) .addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED).addComponent(pane).addContainerGap())); layout.linkSize(SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL, new java.awt.Component[] { face, size }); layout.setVerticalGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING) .addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup().addContainerGap() .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING) .addComponent(pane, GroupLayout.Alignment.TRAILING) .addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup() .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.BASELINE) .addComponent(face).addComponent(faceLabel)) .addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED) .addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(GroupLayout.Alignment.BASELINE) .addComponent(size).addComponent(sizeLabel)) .addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED) .addComponent(italic, GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, Short.MAX_VALUE) .addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED).addComponent(bold, GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, Short.MAX_VALUE))) .addContainerGap())); pack(); } public void updateSample() { String fontFace = (String) face.getSelectedItem(); int fontStyle = (bold.isSelected() ? Font.BOLD : 0) + (italic.isSelected() ? Font.ITALIC : 0); int fontSize = size.getItemAt(size.getSelectedIndex()); Font font = new Font(fontFace, fontStyle, fontSize); sample.setFont(font); sample.repaint(); } }
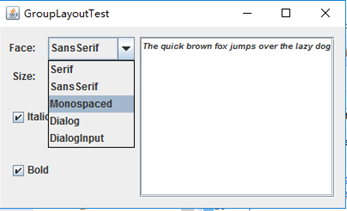
测试程序11
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材539页程序12-13、12-14,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握定制布局管理器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package circleLayout; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.33 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class CircleLayoutTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new CircleLayoutFrame(); frame.setTitle("CircleLayoutTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package circleLayout; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame that shows buttons arranged along a circle. */ public class CircleLayoutFrame extends JFrame { public CircleLayoutFrame() { setLayout(new CircleLayout()); add(new JButton("Yellow")); add(new JButton("Blue")); add(new JButton("Red")); add(new JButton("Green")); add(new JButton("Orange")); add(new JButton("Fuchsia")); add(new JButton("Indigo")); pack(); } }

package circleLayout; import java.awt.*; /** * A layout manager that lays out components along a circle. */ public class CircleLayout implements LayoutManager { private int minWidth = 0; private int minHeight = 0; private int preferredWidth = 0; private int preferredHeight = 0; private boolean sizesSet = false; private int maxComponentWidth = 0; private int maxComponentHeight = 0; public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp) { } public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp) { } public void setSizes(Container parent) { if (sizesSet) return; int n = parent.getComponentCount(); preferredWidth = 0; preferredHeight = 0; minWidth = 0; minHeight = 0; maxComponentWidth = 0; maxComponentHeight = 0; // compute the maximum component widths and heights // and set the preferred size to the sum of the component sizes. for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Component c = parent.getComponent(i); if (c.isVisible()) { Dimension d = c.getPreferredSize(); maxComponentWidth = Math.max(maxComponentWidth, d.width); maxComponentHeight = Math.max(maxComponentHeight, d.height); preferredWidth += d.width; preferredHeight += d.height; } } minWidth = preferredWidth / 2; minHeight = preferredHeight / 2; sizesSet = true; } public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent) { setSizes(parent); Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int width = preferredWidth + insets.left + insets.right; int height = preferredHeight + insets.top + insets.bottom; return new Dimension(width, height); } public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent) { setSizes(parent); Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int width = minWidth + insets.left + insets.right; int height = minHeight + insets.top + insets.bottom; return new Dimension(width, height); } public void layoutContainer(Container parent) { setSizes(parent); // compute center of the circle Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int containerWidth = parent.getSize().width - insets.left - insets.right; int containerHeight = parent.getSize().height - insets.top - insets.bottom; int xcenter = insets.left + containerWidth / 2; int ycenter = insets.top + containerHeight / 2; // compute radius of the circle int xradius = (containerWidth - maxComponentWidth) / 2; int yradius = (containerHeight - maxComponentHeight) / 2; int radius = Math.min(xradius, yradius); // lay out components along the circle int n = parent.getComponentCount(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Component c = parent.getComponent(i); if (c.isVisible()) { double angle = 2 * Math.PI * i / n; // center point of component int x = xcenter + (int) (Math.cos(angle) * radius); int y = ycenter + (int) (Math.sin(angle) * radius); // move component so that its center is (x, y) // and its size is its preferred size Dimension d = c.getPreferredSize(); c.setBounds(x - d.width / 2, y - d.height / 2, d.width, d.height); } } } }
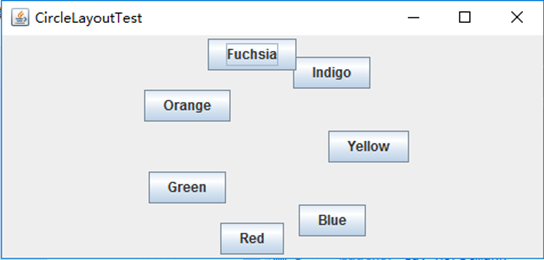
测试程序12
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材544页程序12-15、12-16,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握选项对话框的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package optionDialog; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class OptionDialogTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new OptionDialogFrame(); frame.setTitle("OptionDialogTest");//设置窗体标题 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//设置用户在窗体上发起 "close" 时默认执行的操作 frame.setVisible(true);//设置窗口可见 }); } }

package optionDialog; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.awt.geom.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame that contains settings for selecting various option dialogs. */ public class OptionDialogFrame extends JFrame { private ButtonPanel typePanel; private ButtonPanel messagePanel; private ButtonPanel messageTypePanel; private ButtonPanel optionTypePanel; private ButtonPanel optionsPanel; private ButtonPanel inputPanel; private String messageString = "Message"; private Icon messageIcon = new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"); private Object messageObject = new Date(); private Component messageComponent = new SampleComponent(); public OptionDialogFrame() { JPanel gridPanel = new JPanel(); gridPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 3));//创建2行3列的网格布局 typePanel = new ButtonPanel("Type", "Message", "Confirm", "Option", "Input"); messageTypePanel = new ButtonPanel("Message Type", "ERROR_MESSAGE", "INFORMATION_MESSAGE", "WARNING_MESSAGE", "QUESTION_MESSAGE", "PLAIN_MESSAGE"); messagePanel = new ButtonPanel("Message", "String", "Icon", "Component", "Other", "Object[]"); optionTypePanel = new ButtonPanel("Confirm", "DEFAULT_OPTION", "YES_NO_OPTION", "YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION", "OK_CANCEL_OPTION"); optionsPanel = new ButtonPanel("Option", "String[]", "Icon[]", "Object[]"); inputPanel = new ButtonPanel("Input", "Text field", "Combo box"); gridPanel.add(typePanel); gridPanel.add(messageTypePanel); gridPanel.add(messagePanel); gridPanel.add(optionTypePanel); gridPanel.add(optionsPanel); gridPanel.add(inputPanel);//添加按钮 // add a panel with a Show button JPanel showPanel = new JPanel(); JButton showButton = new JButton("Show");//创建一个带"Show"的按钮。 showButton.addActionListener(new ShowAction()); showPanel.add(showButton); add(gridPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);//中间区域的布局约束(容器中央)。 add(showPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);//南区域的布局约束(容器底部)。 pack(); } /** * Gets the currently selected message. * * @return a string, icon, component, or object array, depending on the Message * panel selection */ public Object getMessage() { String s = messagePanel.getSelection(); if (s.equals("String"))//将此字符串与指定的对象比较 return messageString; else if (s.equals("Icon")) return messageIcon; else if (s.equals("Component")) return messageComponent; else if (s.equals("Object[]")) return new Object[] { messageString, messageIcon, messageComponent, messageObject }; else if (s.equals("Other")) return messageObject; else return null; } /** * Gets the currently selected options. * * @return an array of strings, icons, or objects, depending on the Option panel * selection */ public Object[] getOptions() { String s = optionsPanel.getSelection(); if (s.equals("String[]")) return new String[] { "Yellow", "Blue", "Red" }; else if (s.equals("Icon[]")) return new Icon[] { new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"), new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif") }; else if (s.equals("Object[]")) return new Object[] { messageString, messageIcon, messageComponent, messageObject }; else return null; } /** * Gets the selected message or option type * * @param panel the Message Type or Confirm panel * @return the selected XXX_MESSAGE or XXX_OPTION constant from the JOptionPane * class */ public int getType(ButtonPanel panel) { String s = panel.getSelection(); try { return JOptionPane.class.getField(s).getInt(null); } catch (Exception e) { return -1; } } /** * The action listener for the Show button shows a Confirm, Input, Message, or * Option dialog depending on the Type panel selection. */ private class ShowAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Confirm")) JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(optionTypePanel), getType(messageTypePanel)); else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Input")) { if (inputPanel.getSelection().equals("Text field")) JOptionPane.showInputDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel)); else JOptionPane.showInputDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel), null, new String[] { "Yellow", "Blue", "Red" }, "Blue"); } else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Message")) JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel)); else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Option")) JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(optionTypePanel), getType(messageTypePanel), null, getOptions(), getOptions()[0]); } } } /** * A component with a painted surface */ class SampleComponent extends JComponent { public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(0, 0, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);//根据指定的 double 坐标构造和初始化 Rectangle2D g2.setPaint(Color.YELLOW); g2.fill(rect); g2.setPaint(Color.BLUE); g2.draw(rect); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(10, 10);//构造一个 Dimension,并将其初始化为指定宽度和高度。 } }

package optionDialog; import javax.swing.*; /** * A panel with radio buttons inside a titled border. */ public class ButtonPanel extends JPanel { private ButtonGroup group; /** * Constructs a button panel. * * @param title the title shown in the border * @param options an array of radio button labels */ public ButtonPanel(String title, String... options) { setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(), title));//设置组件的边框,向现有边框添加一个标题 setLayout(new BoxLayout(this, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));//从上到下垂直布置组件 group = new ButtonGroup(); // make one radio button for each option for (String option : options) { JRadioButton b = new JRadioButton(option);//创建一个具有指定文本的状态为未选择的单选按钮 b.setActionCommand(option);//设置此按钮的动作命令 add(b); group.add(b);//将按钮添加到组中 b.setSelected(option == options[0]);//设置按钮的状态 } } /** * Gets the currently selected option. * * @return the label of the currently selected radio button. */ public String getSelection() { return group.getSelection().getActionCommand();//返回该按钮的动作命令字符串 } }
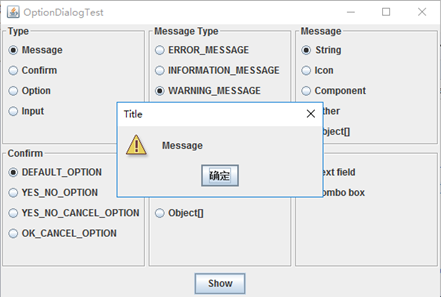
测试程序13
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材552页程序12-17、12-18,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的创建方法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package dialog; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2012-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class DialogTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new DialogFrame(); frame.setTitle("DialogTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package dialog; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JMenu; import javax.swing.JMenuBar; import javax.swing.JMenuItem; /** * A frame with a menu whose File->About action shows a dialog. */ public class DialogFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private AboutDialog dialog; public DialogFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // Construct a File menu. JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(fileMenu); // Add About and Exit menu items. // The About item shows the About dialog. JMenuItem aboutItem = new JMenuItem("About"); aboutItem.addActionListener(event -> { if (dialog == null) // first time dialog = new AboutDialog(DialogFrame.this); dialog.setVisible(true); // pop up dialog }); fileMenu.add(aboutItem); // The Exit item exits the program. JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); fileMenu.add(exitItem); } }

package dialog; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A sample modal dialog that displays a message and waits for the user to click * the OK button. */ public class AboutDialog extends JDialog { public AboutDialog(JFrame owner) { super(owner, "About DialogTest", true); // add HTML label to center add(new JLabel("<html><h1><i>Core Java</i></h1><hr>By Cay Horstmann</html>"), BorderLayout.CENTER); // OK button closes the dialog JButton ok = new JButton("OK"); ok.addActionListener(event -> setVisible(false)); // add OK button to southern border JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.add(ok); add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }
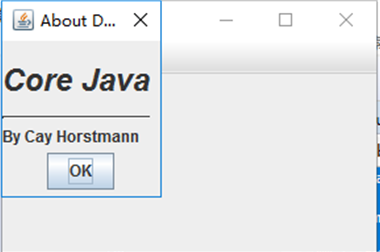
测试程序14
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材556页程序12-19、12-20,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的数据交换用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

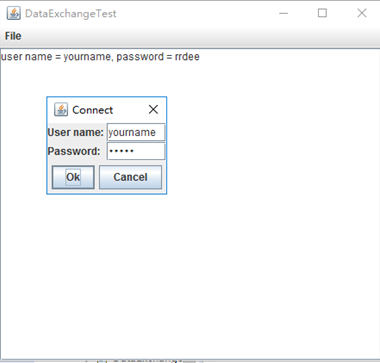
package dataExchange; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class DataExchangeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new DataExchangeFrame(); frame.setTitle("DataExchangeTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package dataExchange; /** * A user has a name and password. For security reasons, the password is stored * as a char[], not a String. */ public class User { private String name; private char[] password; public User(String aName, char[] aPassword) { name = aName; password = aPassword; } public String getName() { return name; } public char[] getPassword() { return password; } public void setName(String aName) { name = aName; } public void setPassword(char[] aPassword) { password = aPassword; } }

package dataExchange; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a menu whose File->Connect action shows a password dialog. */ public class DataExchangeFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXT_ROWS = 20; public static final int TEXT_COLUMNS = 40; private PasswordChooser dialog = null; private JTextArea textArea; public DataExchangeFrame() { // construct a File menu JMenuBar mbar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(mbar); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); mbar.add(fileMenu); // add Connect and Exit menu items JMenuItem connectItem = new JMenuItem("Connect"); connectItem.addActionListener(new ConnectAction()); fileMenu.add(connectItem); // The Exit item exits the program JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); fileMenu.add(exitItem); textArea = new JTextArea(TEXT_ROWS, TEXT_COLUMNS); add(new JScrollPane(textArea), BorderLayout.CENTER); pack(); } /** * The Connect action pops up the password dialog. */ private class ConnectAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { // if first time, construct dialog if (dialog == null) dialog = new PasswordChooser(); // set default values dialog.setUser(new User("yourname", null)); // pop up dialog if (dialog.showDialog(DataExchangeFrame.this, "Connect")) { // if accepted, retrieve user input User u = dialog.getUser(); textArea.append("user name = " + u.getName() + ", password = " + (new String(u.getPassword())) + "\n"); } } } }

package dataExchange; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Component; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingUtilities; /** * A password chooser that is shown inside a dialog */ public class PasswordChooser extends JPanel { private JTextField username; private JPasswordField password; private JButton okButton; private boolean ok; private JDialog dialog; public PasswordChooser() { setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // construct a panel with user name and password fields JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); panel.add(new JLabel("User name:")); panel.add(username = new JTextField("")); panel.add(new JLabel("Password:")); panel.add(password = new JPasswordField("")); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // create Ok and Cancel buttons that terminate the dialog okButton = new JButton("Ok"); okButton.addActionListener(event -> { ok = true; dialog.setVisible(false); }); JButton cancelButton = new JButton("Cancel"); cancelButton.addActionListener(event -> dialog.setVisible(false)); // add buttons to southern border JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.add(okButton); buttonPanel.add(cancelButton); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); } /** * Sets the dialog defaults. * * @param u the default user information */ public void setUser(User u) { username.setText(u.getName()); } /** * Gets the dialog entries. * * @return a User object whose state represents the dialog entries */ public User getUser() { return new User(username.getText(), password.getPassword()); } /** * Show the chooser panel in a dialog * * @param parent a component in the owner frame or null * @param title the dialog window title */ public boolean showDialog(Component parent, String title) { ok = false; // locate the owner frame Frame owner = null; if (parent instanceof Frame) owner = (Frame) parent; else owner = (Frame) SwingUtilities.getAncestorOfClass(Frame.class, parent); // if first time, or if owner has changed, make new dialog if (dialog == null || dialog.getOwner() != owner) { dialog = new JDialog(owner, true); dialog.add(this); dialog.getRootPane().setDefaultButton(okButton); dialog.pack(); } // set title and show dialog dialog.setTitle(title); dialog.setVisible(true); return ok; } }
测试程序15
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材556页程序12-21、12-2212-23,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握文件对话框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

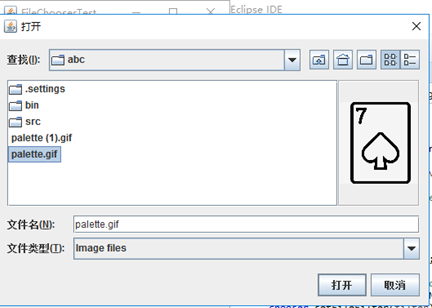
package fileChooser; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.25 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class FileChooserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); frame.setTitle("FileChooserTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package fileChooser; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter; /** * A file view that displays an icon for all files that match a file filter. */ public class FileIconView extends FileView { private FileFilter filter; private Icon icon; /** * Constructs a FileIconView. * * @param aFilter a file filter--all files that this filter accepts will be * shown with the icon. * @param anIcon--the icon shown with all accepted files. */ public FileIconView(FileFilter aFilter, Icon anIcon) { filter = aFilter; icon = anIcon; } public Icon getIcon(File f) { if (!f.isDirectory() && filter.accept(f)) return icon; else return null; } }

package fileChooser; import java.awt.*; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A file chooser accessory that previews images. */ public class ImagePreviewer extends JLabel { /** * Constructs an ImagePreviewer. * * @param chooser the file chooser whose property changes trigger an image * change in this previewer */ public ImagePreviewer(JFileChooser chooser) { setPreferredSize(new Dimension(100, 100)); setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder()); chooser.addPropertyChangeListener(event -> { if (event.getPropertyName() == JFileChooser.SELECTED_FILE_CHANGED_PROPERTY) { // the user has selected a new file File f = (File) event.getNewValue(); if (f == null) { setIcon(null); return; } // read the image into an icon ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(f.getPath()); // if the icon is too large to fit, scale it if (icon.getIconWidth() > getWidth()) icon = new ImageIcon(icon.getImage().getScaledInstance(getWidth(), -1, Image.SCALE_DEFAULT)); setIcon(icon); } }); } }

package fileChooser; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter; /** * A frame that has a menu for loading an image and a display area for the * loaded image. */ public class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; private JLabel label; private JFileChooser chooser; public ImageViewerFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // set up menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); menu.add(openItem); openItem.addActionListener(event -> { chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); // show file chooser dialog int result = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); // if image file accepted, set it as icon of the label if (result == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); pack(); } }); JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); menu.add(exitItem); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); // use a label to display the images label = new JLabel(); add(label); // set up file chooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); // accept all image files ending with .jpg, .jpeg, .gif FileFilter filter = new FileNameExtensionFilter("Image files", "jpg", "jpeg", "gif"); chooser.setFileFilter(filter); chooser.setAccessory(new ImagePreviewer(chooser)); chooser.setFileView(new FileIconView(filter, new ImageIcon("palette.gif"))); } }
测试程序16
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材570页程序12-24,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 了解颜色选择器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

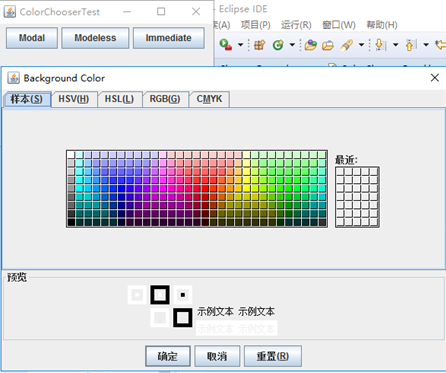
package colorChooser; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.04 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ColorChooserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ColorChooserFrame(); frame.setTitle("ColorChooserTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

package colorChooser; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a color chooser panel */ public class ColorChooserFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public ColorChooserFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // add color chooser panel to frame ColorChooserPanel panel = new ColorChooserPanel(); add(panel); } }

package colorChooser; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JColorChooser; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A panel with buttons to pop up three types of color choosers */ public class ColorChooserPanel extends JPanel { public ColorChooserPanel() { JButton modalButton = new JButton("Modal"); modalButton.addActionListener(new ModalListener()); add(modalButton); JButton modelessButton = new JButton("Modeless"); modelessButton.addActionListener(new ModelessListener()); add(modelessButton); JButton immediateButton = new JButton("Immediate"); immediateButton.addActionListener(new ImmediateListener()); add(immediateButton); } /** * This listener pops up a modal color chooser */ private class ModalListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { Color defaultColor = getBackground(); Color selected = JColorChooser.showDialog(ColorChooserPanel.this, "Set background", defaultColor); if (selected != null) setBackground(selected); } } /** * This listener pops up a modeless color chooser. The panel color is changed * when the user clicks the OK button. */ private class ModelessListener implements ActionListener { private JDialog dialog; private JColorChooser chooser; public ModelessListener() { chooser = new JColorChooser(); dialog = JColorChooser.createDialog(ColorChooserPanel.this, "Background Color", false /* not modal */, chooser, event -> setBackground(chooser.getColor()), null /* no Cancel button listener */); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { chooser.setColor(getBackground()); dialog.setVisible(true); } } /** * This listener pops up a modeless color chooser. The panel color is changed * immediately when the user picks a new color. */ private class ImmediateListener implements ActionListener { private JDialog dialog; private JColorChooser chooser; public ImmediateListener() { chooser = new JColorChooser(); chooser.getSelectionModel().addChangeListener(event -> setBackground(chooser.getColor())); dialog = new JDialog((Frame) null, false /* not modal */); dialog.add(chooser); dialog.pack(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { chooser.setColor(getBackground()); dialog.setVisible(true); } } }
实验2:组内讨论反思本组负责程序,理解程序总体结构,梳理程序GUI设计中应用的相关组件,整理相关组件的API,对程序中组件应用的相关代码添加注释。
实验3:组间协同学习:在本班课程QQ群内,各位同学对实验1中存在的问题进行提问,提问时注明实验1中的测试程序编号,负责对应程序的小组需及时对群内提问进行回答。
三:实验总结:
这次实验量比较多,知识点较多,学起来比较费劲,通过小组讨论,更好的解读代码,分工合作自主学习,小组讨论分享自己所了解的知识,对学习有很大的帮助,但对有些知识理解还不够透彻。







