数据结构--稀疏数组
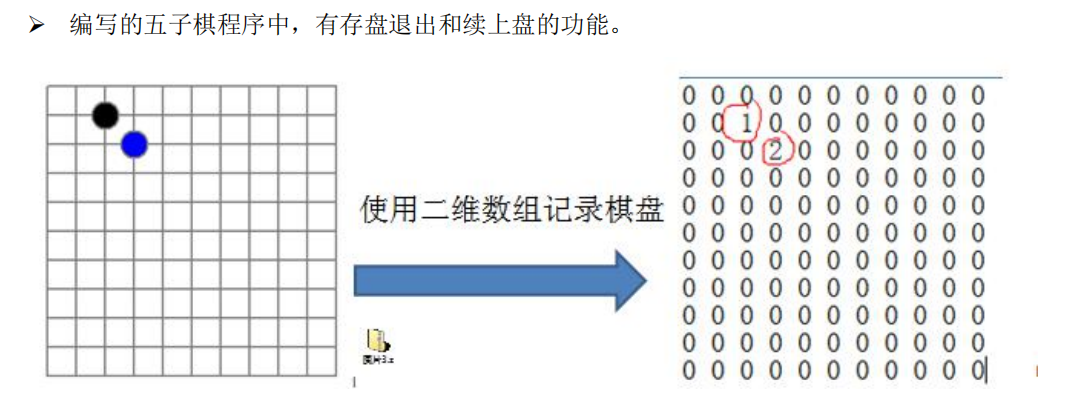
实际场景
如下图:棋盘可以看做是一个二维数组,如果将黑子用1表示,蓝子用2表示,空白的地方用0表示,如果我们直接将棋盘数据存入二维数组,则数组中会存在大量的0,因此记录了很多没有意义的数据,于是,我们便想到将数据进行压缩,用稀疏数组来存放数据更佳。
代码实现
数据不存入文件
package edu.cqupt._01链表;
/**
* @description: 稀疏数组存放五子棋棋盘数据
* @author: lin.z
* @Date: 2020/08/27
*/
public class SparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] chessArr = new int[11][11]; // 默认0 没有棋子
chessArr[1][2] = 1; // 1表示黑子
chessArr[2][3] = 2; // 0表示白子
int count=0;
int index = 0;
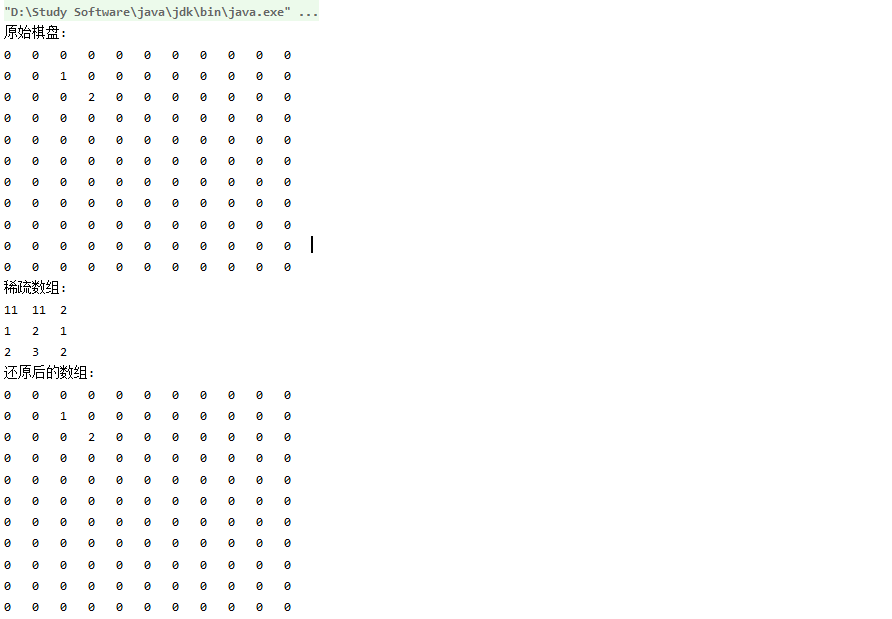
System.out.println("原始棋盘:");
showArray(chessArr);
// 统计非棋子数
for (int[]chessrow:chessArr) {
for(int chess: chessrow){
if(chess !=0){
count++;
}
}
}
// 存盘
int[][] sparseArr = new int[count+1][3];
sparseArr[index][0] = chessArr.length;
sparseArr[index][1] = chessArr.length;
sparseArr[index][2] = count;
for (int row = 0; row <chessArr.length ; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col <chessArr[row].length ; col++) {
if(chessArr[row][col]!=0){
index++;
sparseArr[index][0] = row;
sparseArr[index][1] = col;
sparseArr[index][2] = chessArr[row][col];
}
}
}
System.out.println("稀疏数组:");
showArray(sparseArr);
// 稀疏数组 -----还原到棋盘
int row = sparseArr[0][0];
int col = sparseArr[0][1];
int num = sparseArr[0][2];
int[][] chessArrBack = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 1; i <= num ; i++) {
chessArrBack[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]] = sparseArr[i][2];
}
System.out.println("还原后的数组:");
showArray(chessArrBack);
}
public static void showArray(int[][] arr){
for (int row = 0; row < arr.length; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col <arr[row].length ; col++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][col] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
数据存入文件
package edu.cqupt._01链表;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @description: 稀疏数组存放五子棋棋盘数据,将稀疏数组存入文件,然后从文件读出稀疏数组数据进行还原
* @author: lin.z
* @Date: 2020/08/27
*/
public class SparseArrayToFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int[][] chessArr = new int[11][11]; // 默认0 没有棋子
chessArr[1][2] = 1; // 1表示黑子
chessArr[2][3] = 2; // 0表示蓝子
int count=0;
int index = 0;
System.out.println("原始棋盘:");
showArray(chessArr);
// 统计非棋子数
for (int[]chessrow:chessArr) {
for(int chess: chessrow){
if(chess !=0){
count++;
}
}
}
// 存盘
int[][] sparseArr = new int[count+1][3];
sparseArr[index][0] = chessArr.length;
sparseArr[index][1] = chessArr.length;
sparseArr[index][2] = count;
for (int row = 0; row <chessArr.length ; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col <chessArr[row].length ; col++) {
if(chessArr[row][col]!=0){
index++;
sparseArr[index][0] = row;
sparseArr[index][1] = col;
sparseArr[index][2] = chessArr[row][col];
}
}
}
System.out.println("稀疏数组:");
showArray(sparseArr);
arrayWritetoFile(sparseArr); //将稀疏数组保存到文件
sparseArr = fileReadtoArray(); //从文件读出稀疏数组
System.out.println("文件读出的数组为:");
showArray(sparseArr);
// 稀疏数组 -----还原到棋盘
int row = sparseArr[0][0];
int col = sparseArr[0][1];
int num = sparseArr[0][2];
int[][] chessArrBack = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 1; i <= num ; i++) {
chessArrBack[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]] = sparseArr[i][2];
}
System.out.println("还原后的数组:");
showArray(chessArrBack);
}
public static void showArray(int[][] arr){
for (int row = 0; row < arr.length; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col <arr[row].length ; col++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][col] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void arrayWritetoFile(int[][]arr) throws IOException {
File file = new File("map.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <arr[i].length ; j++) {
fw.write(arr[i][j]);
}
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
public static int[][] fileReadtoArray() throws IOException {
File file = new File("map.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
int data;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((data = fr.read()) != -1) {
list .add(data);
}
int[][] arr = new int[list.size()/3][3];
for (int i = 0; i <list .size()/3 ; i++) {
arr[i][0] = list.get(3*i);
arr[i][1] = list.get(3*i+1);
arr[i][2] = list.get(3*i+2);
}
fr.close();
return arr;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号