Linux程序设计:进程通信
日期:忘了。
关键词:Linux程序设计;System-V;进程通信;共享内存;消息队列。
一、共享内存
1.1 基本知识
(待补充)
1.2 代码
一个基于share memory实现的客户-服务模型。
- shm_comm.h
#define TEXT_SZ 2048 struct shared_use_st { int written_by_you; char some_text[TEXT_SZ]; }; typedef struct shared_use_st shared_use_st; |
- shm1.c
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include "shm_com.h"
int main() { int running = 1; void *shm_ptr = NULL; struct shared_use_st *shared_stuff; int shmid;
srand((unsigned int)getpid());
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(shared_use_st), 0666 | IPC_CREAT); printf("shmid = %x\n", shmid); if (shmid == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmget fail\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } shm_ptr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); //该值应该是shm在当前进程空间中的虚拟地址,而不是shm真实的物理地址 //所以shm1和shm2的返回值不一样
if (shm_ptr == (void *)-1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
printf("Memory attached at %p\n", shm_ptr);
shared_stuff = (struct shared_use_st *)shm_ptr; shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0; while (running) { if (shared_stuff->written_by_you) { printf("You wrote %s\n", shared_stuff->some_text); sleep(5); shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0; if (strncmp(shared_stuff->some_text, "end", 3) == 0) { running = 0; } } }
if(shmdt(shm_ptr) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
if(shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmctl(IPC_RMID) failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } |
- shm2.c
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include "shm_com.h"
int main() { int running = 1; void *shm_ptr = NULL; struct shared_use_st *share_stuff; char buff[TEXT_SZ]; int shmid;
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(struct shared_use_st), 0666|IPC_CREAT); printf("shmid = %x\n", shmid); if(shmid == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmget failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
shm_ptr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); if(shm_ptr == (void *)-1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("Memory attached at %p\n", shm_ptr);
share_stuff = (struct shared_use_st*)shm_ptr;
while(running) { if(share_stuff->written_by_you == 1) { sleep(1); printf("waiting for client\n"); } printf("Enter texts:"); fgets(buff, TEXT_SZ, stdin); strncpy(share_stuff->some_text, buff, TEXT_SZ); share_stuff->written_by_you = 1;
if(strncmp(share_stuff->some_text, "end", 3) == 0) { running = 0; } }
if(shmdt(shm_ptr) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} |
- 运行结果

二、消息队列
2.1 基本知识
待补充。
2.2 代码
- msg1.c
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/msg.h> struct msg_t { long int msg_type; char content[BUFSIZ]; };
int main() { int running = 1; int msgid; long int msg_to_receive = 0; //决定队列消息优先级,0表示获取队列第一个可用消息 struct msg_t msg;
msgid = msgget((key_t)1234, 0666 | IPC_CREAT); printf("msgid = %d\n", msgid); if (msgid == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "msgget failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
while (running) { if (msgrcv(msgid, (void *)&msg, BUFSIZ, msg_to_receive, 0) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "msgrcv failde\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("You wrote %s", msg.content); if(strncmp(msg.content, "end", 3) == 0) running = 0; } if (msgctl(msgid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "msgcntl failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} |
- msg2.c
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/msg.h> #define MAX_TEXT 512 struct msg_t { long int msg_type; char content[BUFSIZ]; };
int main() { int running = 1; struct msg_t msg; int msgid; char buffer[BUFSIZ];
msgid = msgget((key_t)1234, 0666 | IPC_CREAT); printf("msgid = %d\n", msgid);
if (msgid == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "msgget failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
while (running) { printf("Enter texts:"); fgets(buffer, BUFSIZ, stdin); msg.msg_type = 1; strcpy(msg.content, buffer);
if(msgsnd(msgid, (void *)&msg, BUFSIZ, 0) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "msgsnd failed\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if(strncmp(msg.content, "end", 3) == 0) { running = 0; } }
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } |
- 运行结果
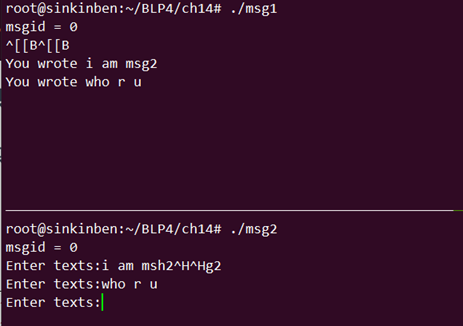
三、信号量
3.1 基本知识
待补充。
3.2 代码
- semun.h
#if defined(__GNU_LIBRARY__) && !defined(_SEM_SEMUN_UNDEFINED) /* union semun is defined by including <sys/sem.h> */ #else /* according to X/OPEN we have to define it ourselves */ union semun { int val; /* value for SETVAL */ struct semid_ds *buf; /* buffer for IPC_STAT, IPC_SET */ unsigned short int *array; /* array for GETALL, SETALL */ struct seminfo *__buf; /* buffer for IPC_INFO */ }; #endif
|
- sema.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/sem.h> #include "semun.h"
static int sem_id; static int set_semvalue() { union semun sem_union; sem_union.val = 1; if (semctl(sem_id, 0, SETVAL, sem_union) == -1) return 0; return 1; } static void del_semvalue() { union semun sem_union; if (semctl(sem_id, 0, IPC_RMID, sem_union) == -1) fprintf(stderr, "Fail to delete semaphore\n"); } static int sema_p() { struct sembuf sem_b; sem_b.sem_num = 0;//信号量编号,除非是一组信号量,否则0 sem_b.sem_op = -1;//-1操作 sem_b.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;//与操作系统对信号量的操作相关,一般是UNDO if (semop(sem_id, &sem_b, 1) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "sema_p failed\n"); return 0; } return 1; } static int sema_v() { struct sembuf sem_b; sem_b.sem_num = 0; sem_b.sem_op = 1; sem_b.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO; if (semop(sem_id, &sem_b, 1) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "sema_v failed\n"); return 0; } return 1; }
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; int pause_time; char op_char = 'O'; srand((unsigned int)getpid()); sem_id = semget((key_t)1234, 1, 0666 | IPC_CREAT); if (argc > 1) { if(set_semvalue() == 0) { fprintf(stderr, "init fail\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } op_char = 'X'; sleep(2); }
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if (sema_p() == 0) exit(EXIT_FAILURE); printf("%c", op_char); fflush(stdout);
pause_time = rand() % 3; sleep(pause_time); printf("%c", op_char); fflush(stdout);
if (!sema_v()) exit(EXIT_FAILURE); pause_time = rand() % 2; sleep(pause_time); } printf("\n%d - finished\n", getpid()); if (argc > 1) { sleep(10); del_semvalue(); } exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } |


