ArrayList源码
ArrayList:
- 基于数组实现可自动扩容的集合列表
- 允许插入NULL元素。
- 非线程安全
- 基于位置查询速度快, O(1)
- 指定位置新增和删除慢,涉及元素拷贝移动
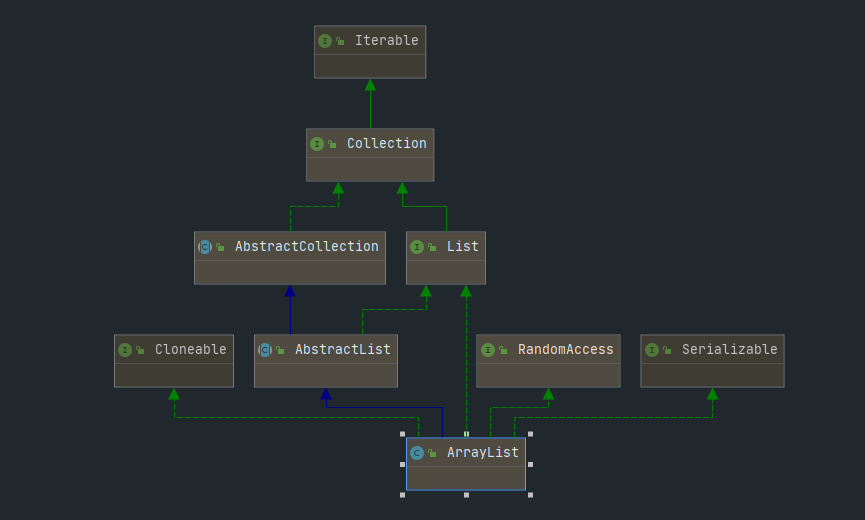
1、接口
1.1、Iterable
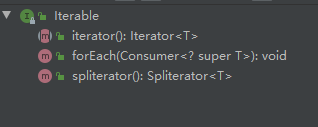
提供foreach循环支持,通过iterator方法可以得到集合的迭代器对象Iterator。
1.2、Collection
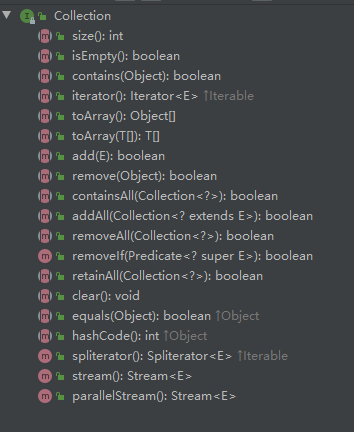
集合的顶层接口,抽象了集合的一些通用操作方法,实现此接口的类都是抽象类或其他接口
1.3、AbstractCollection
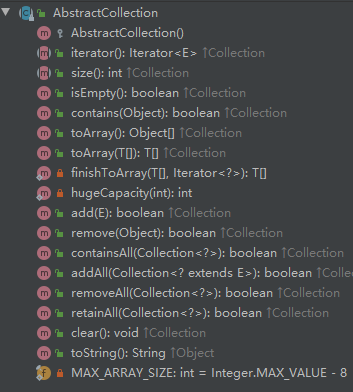
给出了Collection接口的骨架实现,Collection抽象了集合的通用操作,AbstractCollection则封装了操作的通用逻辑。
这里要注意三个方法
public boolean add(E e) {
// 直接抛异常,意味着需要子类去实现add方法,延迟到子类实现
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// 抽象方法,延迟到子类实现
public abstract Iterator<E> iterator();
// 抽象方法,延迟到子类实现
public abstract int size();
AbstractCollection的大部分逻辑都是依赖iterator完成的
1.4、List
定义了有序集合(插入顺序)的通用方法,允许插入null,在Collection的基础上又抽象了get(int)、add(int,E)等方法。进一步完善了集合的操作功能。
Collection提供了集合的最小化操作,List在Collection的基础上进行了扩展,对功能进行了增强。
1.5、AbstractList
给出了List接口的骨架实现,并继承了AbstractCollection的功能。
这个类主要服务于已数组为底层的支持RandomAccess访问的集合。
2、方法
2.1、add(E e)
向集合中添加元素,需要注意的是,由于列表无参构造器初始化默认返回空数组,在进行扩容计算时加了特殊判断
// 数组允许的最大长度,文档给的解释是有些虚拟机会在数组中保留一些头信息,即数组前几位可能存储的不是真正的数据
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 在数组元素末尾新增元素
public boolean add(E e) {
// 计算添加元素数组所需最小值,如果数组长度小于最小值则以1.5倍容量扩容,如果这里size=Integer.MAX_VALUE,则size + 1会溢出成为一个小于0的数
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 扩容处理
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
// 获取新增元素所需的最小数组长度值
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
// 这里做了初始化后的特殊判断,如果数组为空,则取默认长度与最小长度两者的最大值
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
// 扩容处理
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// 扩容,并做了溢出处理
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
// 扩容代码
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 以1.5倍扩容得到扩容长度,这个扩容长度值是存在溢出风险的,因为int的最大值是2147483647
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 这里主要是针对使用默认构造器初始化时,延迟初始化数组,直到第一个元素写入时创建数组。
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 溢出判断
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// 扩容溢出处理
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 溢出处理,当前数组长度已经是Integer.MAX_VALUE了,无法继续添加元素,抛出异常
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 虽然有数组最大值的兼容处理,但是还是可以继续扩容至Integer.MAX_VALUE
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}

2.1.1、逻辑
扩容逻辑是添加元素的难点和重点,因为这里做了溢出的逻辑处理,贴个图好理解一些,1431655765是一个临界值,扩容后会得到Integer.MAX_VALUE
假设当前数组 length = size = 1431655765,继续添加元素
- 取得新增元素数组下标,minCapacity = size + 1 = 1431655766
- 进入ensureExplicitCapacity方法 --> minCapacity - elementData.length = 1 > 0 --> 进入grow(minCapacity)方法
- oldCapacity = 1431655765,newCapacity = 2147483647 = Integer.MAX_VALUE,第一个if不满足[if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)],newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = 8,满足第二个if,进入hugeCapacity(minCapacity)方法
- minCapacity > 0,minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 为 true, 返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
- 执行elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity),将原数组扩容复制到新数组。新数组容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 在1431655766设置元素值
- 返回true,新增结束
接着继续新增一个元素 - 取得新增元素数组下标,minCapacity = size + 1 = -2147483648,
- 进入ensureExplicitCapacity方法 --> minCapacity - elementData.length = 1 > 0 --> 进入grow(minCapacity)方法
- oldCapacity = 2147483647,newCapacity = -1073741826,newCapacity - minCapacity = 1073741822 > 0, 第一个if不满足,newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = 1073741831 > 0,满足第二个if,进入hugeCapacity(minCapacity)方法
- minCapacity = -2147483648 < 0,抛出异常
2.2、E remove(int index)
删除集合中指定位置的元素, 位置右边的元素会左移一位, 并置空末位元素
public E remove(int index) {
// 边界校验
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
// 获取指定位置元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
// 移动元素, elementData中index+1位置开始往后numMoved个元素复制到elementData中index开始往后numMoved个位置的元素, 即删除元素位置后边的元素左移一位
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
2.3、E set(int index, E element)
修改指定位置元素
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
2.4、boolean contains(Object o)
查询元素信息
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
循环数组,比较查询值,返回下标
3、迭代器
3.1、Itr
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
// 即将返回的元素下标,next返回的下标数据
int cursor; // index of next element to return
// 上一个元素下标,remove删除此下标数据, 虽然是上一个元素的下标,但是如果调用remove,lastRet会被重置,所以并不可靠
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 右移即将返回的元素下标
cursor = i + 1;
// 右移上一个元素下标,并返回移动后的下标元素
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
// 清空上一个元素的下标数据,并将后边的数据左移一位
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
// 将上一个元素的下标赋值为将要返回的下标,例如,删除下标为2的元素,2后边的元素会左移一位,下次next将要返回的下标元素还是2
cursor = lastRet;
// 重置上一个元素的下标,防止连续调用remove
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
从源码看出,iterator仅支持顺序迭代集合元素,支持迭代过程中删除元素,不支持新增和修改。
3.2、ListIterator
ListIterator接口是一个集合列表迭代器,允许前序和后序遍历集合,迭代期间修改列表,并获得迭代器在列表中的当前位置。
3.3、ListItr
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 左移即将返回的下标值
cursor = i;
// 即将返回的下标赋值给上一个元素下标,即两个下标指向同一位置,并返回元素
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
// 修改上一个元素下标对应的数据
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
// 右移下标后的所有元素,并在即将返回的元素之前插入一个元素信息
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
// 右移即将返回的元素下标
cursor = i + 1;
// 重置上一个元素下标
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
/** 从指定位置开始获取迭代器 */
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
// 从头开始获取迭代器
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
ListItr继承了Itr类并实现了ListIterator,意味着ListItr可以对集合进行前序和后序遍历,并且在Itr的基础上可以在迭代过程中对集合进行修改操作。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| next() | Ltr实现,lastRet表示当前返回数据的下标,cursor为即将返回数据的下标。 |
| previous() | 用临时变量记录cursor-1,然后lastRet和cursor指向了同一个下标值,返回临时变量的下标元素。 |
| set(E) | 修改lastRet位置的元素信息 |
| add(E) | cursor后面所有的元素右移一位,然后在cursor位置插入元素,然后重置lastRet为-1,由于cursor右移,所以插入的数据在调用next方法会跳过插入值 |
| remove(),set(E),add(E)方法由于会重置lastRet,所以三个是互斥的,不能连续出现。 |




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号