机器学习算法之异常点检测
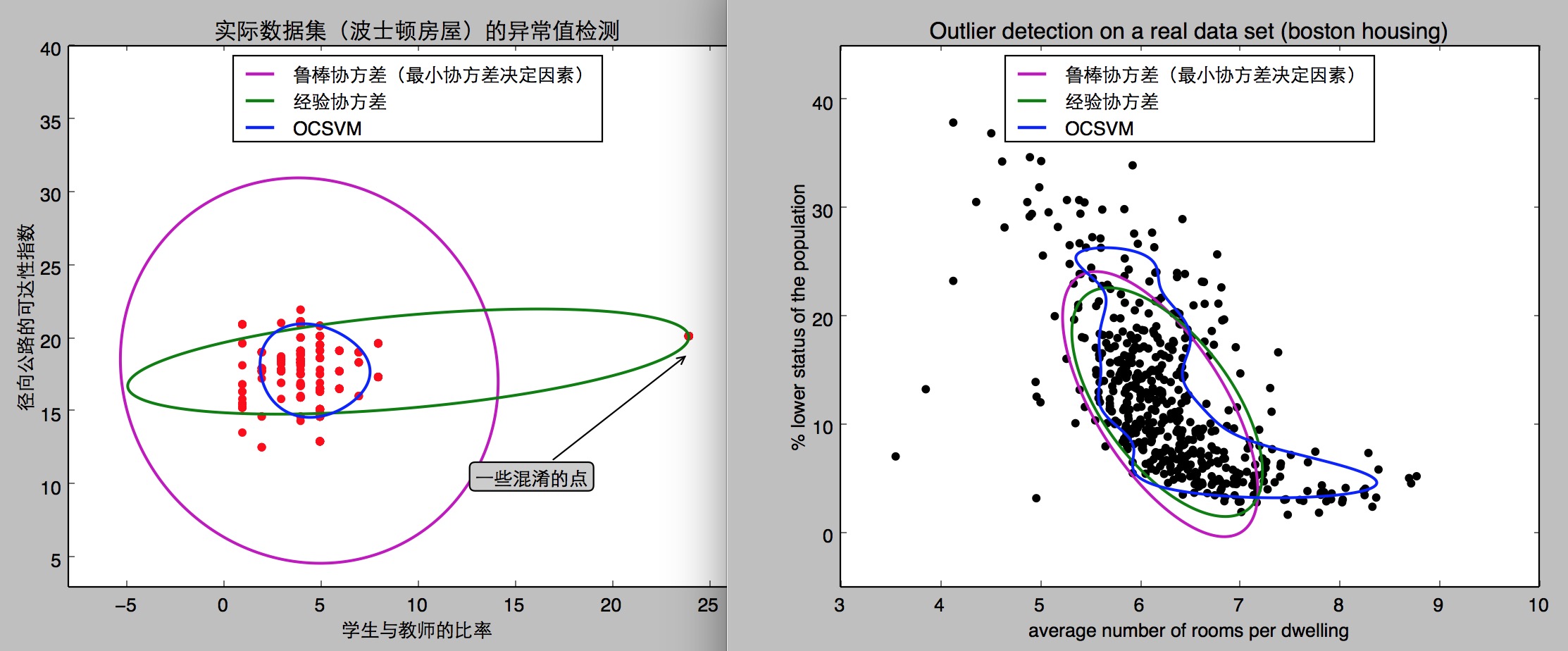
#coding:utf-8 import numpy as np from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager from sklearn.datasets import load_boston ''' 机器学习 鲁棒的基于高斯概率密度的异常点检测(novelty detection) ellipticalenvelope算法 算法理解: 这个算法的思想很好理解, 就是求出训练集在空间中的重心, 和方差, 然后根据高斯概率密度估算每个点被分配到重心的概率. 数据说明: [ 0CRIM,城镇人均犯罪率, 1ZN,占地面积超过25,000平方呎的住宅用地比例, 2INDUS,每个城镇非零售商业地的比例, 3,查尔斯河虚拟变量(= 1有河;否则为0), 4,一氧化氮浓度(百万分之一), 5,每间住宅的平均客房数, 6,1940年之前建成的自用单位比例, 7,加权距离到五个波士顿就业中心, 8,径向公路的可达性指数, 9,每10,000美元的税赋全值财产税率, 10,学生与教师的比率, 11,1000*(Bk-0.63)^2 其中Bk是城镇中黑人的比例, 12,%降低人口状态, 13,自住房价值在1000美元的中位数,[数据不包含该项] ] ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD','TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT'] [0.00632, 18.0, 2.31, 0.0, 0.538, 6.575, 65.2, 4.09, 1.0, 296.0, 15.3, 396.9, 4.98] ''' # Get data #X1[径向公路的可达性指数,学生与教师的比率,] X1 = load_boston()['data'][:, [8, 10]] # two clusters #X2[每间住宅的平均客房数,降低人口状态,] X2 = load_boston()['data'][:, [5, 12]] # "banana"-shaped # Define "classifiers" to be used classifiers = { #EllipticEnvelope:一种用于在高斯分布式数据集中检测异常值的对象。contamination:数据集的污染量,即数据集中异常值的比例。 u"经验协方差": EllipticEnvelope(support_fraction=1,contamination=0.261), #基于协方差的稳健估计,假设数据是高斯分布的,那么在这样的案例中执行效果将优于One-Class SVM; u"鲁棒协方差(最小协方差决定因素)":EllipticEnvelope(contamination=0.261), #SVM 利用One-Class SVM,它有能力捕获数据集的形状,因此对于强非高斯数据有更加优秀的效果,例如两个截然分开的数据集; "OCSVM": OneClassSVM(nu=0.261, gamma=0.05)} colors = ['m', 'g', 'b'] legend1 = {} legend2 = {} # Learn a frontier for outlier detection with several classifiers xx1, yy1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-8, 28, 500), np.linspace(3, 40, 500)) xx2, yy2 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(3, 10, 500), np.linspace(-5, 45, 500)) for i, (clf_name, clf) in enumerate(classifiers.items()): plt.figure(1) clf.fit(X1) #decision_function 计算给定观察的决策函数 #我们知道数据集中一部分的异常值。由此我们通过对decision_function设置阈值来分离出相应的部分,而不是使用'预测'方法。 Z1 = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx1.ravel(), yy1.ravel()]) #reshape 将Z1矩阵转换成 xx1的行列形式 Z1 = Z1.reshape(xx1.shape) #画函数图像的 contour:表示绘制轮廓 使数组的等值线图。水平值自动选择。 legend1[clf_name] = plt.contour(xx1, yy1, Z1, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors=colors[i]) plt.figure(2) clf.fit(X2) Z2 = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx2.ravel(), yy2.ravel()]) Z2 = Z2.reshape(xx2.shape) legend2[clf_name] = plt.contour(xx2, yy2, Z2, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors=colors[i]) legend1_values_list = list(legend1.values()) legend1_keys_list = list(legend1.keys()) # Plot the results (= shape of the data points cloud) plt.figure(1) # two clusters plt.title(u"实际数据集(波士顿房屋)的异常值检测") #画点图 plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], color='red') #设置注释文本框 fc设置透明度 bbox_args = dict(boxstyle="round", fc="0.8") #arrow_args 表示使用箭头线 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="->") #控制注解 xy=(24,19)表示箭头的终点位置 xytext=(13, 10)注解文本框的位置 plt.annotate(u"一些混淆的点", xy=(24, 19),xycoords="data", textcoords="data",xytext=(13, 10), bbox=bbox_args, arrowprops=arrow_args) plt.xlim((xx1.min(), xx1.max())) plt.ylim((yy1.min(), yy1.max())) #loc 控制说明的摆放位置 plt.legend((legend1_values_list[0].collections[0], legend1_values_list[1].collections[0], legend1_values_list[2].collections[0]), (legend1_keys_list[0], legend1_keys_list[1], legend1_keys_list[2]), loc="upper center", prop=matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=12)) plt.ylabel(u"径向公路的可达性指数") plt.xlabel(u"学生与教师的比率") legend2_values_list = list(legend2.values()) legend2_keys_list = list(legend2.keys()) plt.figure(2) # "banana" shape plt.title("Outlier detection on a real data set (boston housing)") plt.scatter(X2[:, 0], X2[:, 1], color='black') plt.xlim((xx2.min(), xx2.max())) plt.ylim((yy2.min(), yy2.max())) plt.legend((legend2_values_list[0].collections[0], legend2_values_list[1].collections[0], legend2_values_list[2].collections[0]), (legend2_keys_list[0], legend2_keys_list[1], legend2_keys_list[2]), loc="upper center", prop=matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=12)) plt.ylabel("% lower status of the population") plt.xlabel("average number of rooms per dwelling") plt.show()