BBS第一天
一.BBS建表
其中包含七张真表,一张虚拟中间表
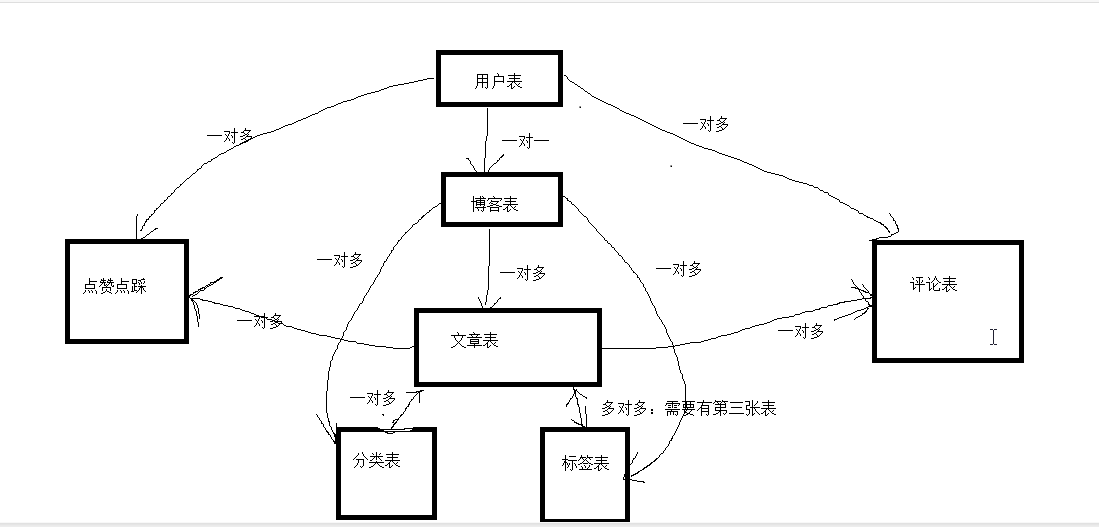
models.py文件:
from django.db import models # Create your models here. from django.db import models from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser class UserInfo(AbstractUser): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) # 头像:FileField文件(varchar类型),default:默认值,upload_to上传的路径 avatar = models.FileField(upload_to='avatar/', default='avatar/default.png') #跟blog表一对一 #OneToOneField本质就是ForeignKey,只不过有个唯一性约束 blog = models.OneToOneField(to='Blog', to_field='nid',null=True) # blog = models.ForeignKey(to='Blog', to_field='nid',null=True,unique=True) class Meta: # db_table='xxxx' # 在admin中显示的表名 verbose_name='用户表' #去掉 用户表 后的s verbose_name_plural = verbose_name class Blog(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) #站点名称 title = models.CharField(max_length=64) #站点副标题 site_name = models.CharField(max_length=32) #不同人不同主题 theme = models.CharField(max_length=64) def __str__(self): return self.site_name #分类表 class Category(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) #分类名称 title = models.CharField(max_length=64) #跟博客是一对多的关系,关联字段写在多的一方 #to 是跟哪个表关联 to_field跟表中的哪个字段做关联, null=True 表示可以为空 blog = models.ForeignKey(to='Blog', to_field='nid', null=True) def __str__(self): return self.title class Tag(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) #标签名字 title = models.CharField(max_length=64) # 跟博客是一对多的关系,关联字段写在多的一方 blog = models.ForeignKey(to='Blog', to_field='nid', null=True) def __str__(self): return self.title class Article(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) #verbose_name在admin中显示该字段的中文 title = models.CharField(max_length=64,verbose_name='文章标题') #文章摘要 desc = models.CharField(max_length=255) #文章内容 大文本 content = models.TextField() #DateTimeField 年月日时分秒(注意跟datafield的区别) #auto_now_add=True:插入数据会存入当前时间 #auto_now=True 修改数据会存入当前时间 create_time = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) # commit_num=models.IntegerField(default=0) # up_num=models.IntegerField(default=0) # down_num=models.IntegerField(default=0) #一对多的关系 blog = models.ForeignKey(to='Blog', to_field='nid', null=True) # 一对多的关系 category = models.ForeignKey(to='Category', to_field='nid', null=True) #多对多关系 through_fields 不能写反了: tag = models.ManyToManyField(to='Tag', through='ArticleTOTag', through_fields=('article', 'tag')) def __str__(self): return self.title+'----'+self.blog.userinfo.username class ArticleTOTag(models.Model): nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) article = models.ForeignKey(to='Article', to_field='nid') tag = models.ForeignKey(to='Tag', to_field='nid') class Commit(models.Model): #谁对那篇文章评论了什么内容 nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) user = models.ForeignKey(to='UserInfo', to_field='nid') article = models.ForeignKey(to='Article', to_field='nid') content = models.CharField(max_length=255) #评论时间 create_time = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) #自关联() parent = models.ForeignKey(to='self', to_field='nid',null=True,blank=True) class UpAndDown(models.Model): #谁对那篇文章点赞或点踩 nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) user = models.ForeignKey(to='UserInfo', to_field='nid') article = models.ForeignKey(to='Article', to_field='nid') #布尔类型,本质也还是0和1 is_up = models.BooleanField() class Meta: #联合唯一,一个用户只能给一片文章点赞或点踩 unique_together = (('user', 'article'),)
注:
在settings.py文件中需要配置:
# 引用Django自带的User表,继承使用时需要设置 AUTH_USER_MODEL = "app01.UserInfo"
利用admin超级用户登录查看创建的表及字段:
在run manage.py task 工具中createsuperuser即可登录
from django.contrib import admin from app01 import models # Register your models here. admin.site.register(models.UserInfo) admin.site.register(models.Tag) admin.site.register(models.Category) admin.site.register(models.Commit) admin.site.register(models.Article) admin.site.register(models.Blog) admin.site.register(models.UpAndDown) admin.site.register(models.ArticleTOTag)
二.登录form表单及验证码的形成方式
引入静态文件
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">
<h1>登录</h1>
<form action="">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_name">用户名</label>
<input type="text" name="name" id="id_name" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_pwd">密码</label>
<input type="password" name="pwd" id="id_pwd" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_code">验证码</label>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<input type="text" name="code" id="id_code" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<a href="/login/"> <img src="/get_code/" height="40" width="350"></a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="提交" class="btn-success">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect from django.http import JsonResponse #Image导入 #ImageDraw在图片上写字 #ImageFont 写字的格式 from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont import random # 相当于把文件以byte格式存到内存中 from io import BytesIO # Create your views here. def login(request): if request.method=='GET': return render(request,'login.html') def get_random_color(): return (random.randint(0,255),random.randint(0,255),random.randint(0,255)) def get_code(request): #方式一,返回固定图片 # with open('static/img/code.png','rb') as f: # data=f.read() # return HttpResponse(data)
#方式二,自动生成图片(需要借助第三方模块pillow)图像处理的模块 #新生成一张图片 # img=Image.new('RGB',(350,40),get_random_color()) # #把图片保存起来 # with open('static/img/code.png','wb') as f: # #把图片保存起来(注意,用img对象的save方法,把f传入) # img.save(f) # #打开返回 # with open('static/img/code.png','rb') as f: # data=f.read() # return HttpResponse(data)
#方式三(不把文件保存在硬盘上,保存在内存中) #新生成一张图片 # img=Image.new('RGB',(350,40),get_random_color()) # #生成一个Byteio对象 # f=BytesIO() # #把文件保存到对象中 # img.save(f,'png') # #f.getvalue() 把文件从对象中取出来 # return HttpResponse(f.getvalue())
#方式四:在图片上写文件,并且保存到内存中 # img = Image.new('RGB', (350, 40), get_random_color()) # #写文字 # #生成一个字体对象 # font=ImageFont.truetype('static/font/kumo.ttf',34) # #调用方法,返回一个画板对象 # draw=ImageDraw.Draw(img) # draw.text((0,10),'python',font=font) # # f=BytesIO() # img.save(f,'png') # return HttpResponse(f.getvalue()) #最终版本 img = Image.new('RGB', (350, 40), get_random_color()) font=ImageFont.truetype('static/font/kumo.ttf',34) draw=ImageDraw.Draw(img) #动态生成大写,小写,数字 5个 # draw.text((0,10),'python',font=font) for i in range(5): num=str(random.randint(0,9)) up_chr=str(chr(random.randint(65,90))) lower_chr=str(chr(random.randint(97,122))) #从三个字符中选一个字符 ss=random.choice([num,up_chr,lower_chr]) draw.text((20+i*50, 5), ss, font=font,fill=get_random_color()) #画点和线 # width = 320 # height = 35 # for i in range(10): # x1 = random.randint(0, width) # x2 = random.randint(0, width) # y1 = random.randint(0, height) # y2 = random.randint(0, height) # # 在图片上画线 # draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y2), fill=get_random_color()) # # for i in range(100): # # 画点 # draw.point([random.randint(0, width), random.randint(0, height)], fill=get_random_color()) # x = random.randint(0, width) # y = random.randint(0, height) # # 画弧形 # draw.arc((x, y, x + 4, y + 4), 0, 90, fill=get_random_color()) f=BytesIO() img.save(f,'png') return HttpResponse(f.getvalue())
登录html的完善(ajax请求):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.css">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">
<h1>登录</h1>
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_name">用户名</label>
<input type="text" name="name" id="id_name" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_pwd">密码</label>
<input type="password" name="pwd" id="id_pwd" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_code">验证码</label>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<input type="text" name="code" id="id_code" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="col-md-6" >
<img src="/get_code/" height="40" width="350" id="id_imgcode">
</div>
</div>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-danger" id="id_login">登录</button><span class="error" style="color: red; margin-left: 10px"></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
$("#id_imgcode").click(function () {
//改变图片路径,重新请求,加载图片
//$("#id_imgcode")[0].src += '?'
//var aa='/getcode/?random='+Math.random()
//console.log(aa)
//$("#id_imgcode")[0].src=aa
// $("#id_imgcode").attr('src',aa)
var aa=$("#id_imgcode").attr('src')+'?'
console.log(aa)
$("#id_imgcode").attr('src',aa)
})
$("#id_login").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/login/',
type: 'post',
data: {
'name': $("#id_name").val(),
'pwd': $("#id_pwd").val(),
'auth_code': $("#id_code").val(),
// 'csrfmiddlewaretoken':'{{ csrf_token }}',
'csrfmiddlewaretoken': $("[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val(),
},
success:function (data) {
if(data.status==100){
location.href='/index/'
}else{
$(".error").text(data.msg)
setTimeout(function () {
$(".error").text("")
},3000)
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
登录视图函数的完善:
from django.contrib import auth def login(request): if request.method == 'GET': return render(request, 'login.html') else: response_dic={'status':100,'msg':None} name=request.POST.get('name') pwd=request.POST.get('pwd') auth_code=request.POST.get('auth_code') # 不区分大小写 # request.session.get('auth_code') 把存在session中的验证码取出来,跟前台传入的验证码做对比 if request.session.get('auth_code').upper()==auth_code.upper(): # 校验用户 user=auth.authenticate(username=name,password=pwd) if user: # 如果有值,登陆成功,要login一下 auth.login(request,user) response_dic['msg']='登陆成功' else: response_dic['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误' response_dic['status'] = 101 else: response_dic['msg'] = '验证码错误' response_dic['status'] = 102 return JsonResponse(response_dic)
效果图:



