OpenSees开发(二)源码分析——平面桁架静力有限元分析实例
这是一个平面桁架静力分析算例,代码位于 OpenSees2.3.0\EXAMPLES\Example1\main.cpp
这里先给出原始源代码:
// standard C++ includes
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <OPS_Globals.h>
#include <StandardStream.h>
#include <ArrayOfTaggedObjects.h>
// includes for the domain classes
#include <Domain.h>
#include <Node.h>
#include <Truss.h>
#include <ElasticMaterial.h>
#include <SP_Constraint.h>
#include <LoadPattern.h>
#include <LinearSeries.h>
#include <NodalLoad.h>
// includes for the analysis classes
#include <StaticAnalysis.h>
#include <AnalysisModel.h>
#include <Linear.h>
#include <PenaltyConstraintHandler.h>
#include <DOF_Numberer.h>
#include <RCM.h>
#include <LoadControl.h>
#include <BandSPDLinSOE.h>
#include <BandSPDLinLapackSolver.h>
// init the global variabled defined in OPS_Globals.h
StandardStream sserr;
OPS_Stream *opserrPtr = &sserr;
double ops_Dt = 0;
// Domain *ops_TheActiveDomain = 0;
Element *ops_TheActiveElement = 0;
// main routine
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//
// now create a domain and a modelbuilder
// and build the model
//
Domain *theDomain = new Domain();
// create the nodes using constructor:
// Node(tag, ndof, crd1, crd2)
// and then add them to the domain
Node *node1 = new Node(1, 2, 0.0, 0.0);
Node *node2 = new Node(2, 2, 144.0, 0.0);
Node *node3 = new Node(3, 2, 168.0, 0.0);
Node *node4 = new Node(4, 2, 72.0, 96.0);
theDomain->addNode(node1);
theDomain->addNode(node2);
theDomain->addNode(node3);
theDomain->addNode(node4);
// create an elastic material using constriuctor:
// ElasticMaterialModel(tag, E)
UniaxialMaterial *theMaterial = new ElasticMaterial(1, 3000);
// create the truss elements using constructor:
// Truss(tag, dim, nd1, nd2, Material &,A)
// and then add them to the domain
Truss *truss1 = new Truss(1, 2, 1, 4, *theMaterial, 10.0);
Truss *truss2 = new Truss(2, 2, 2, 4, *theMaterial, 5.0);
Truss *truss3 = new Truss(3, 2, 3, 4, *theMaterial, 5.0);
theDomain->addElement(truss1);
theDomain->addElement(truss2);
theDomain->addElement(truss3);
// create the single-point constraint objects using constructor:
// SP_Constraint(tag, nodeTag, dofID, value)
// and then add them to the domain
SP_Constraint *sp1 = new SP_Constraint(1, 1, 0, 0.0);
SP_Constraint *sp2 = new SP_Constraint(2, 1, 1, 0.0);
SP_Constraint *sp3 = new SP_Constraint(3, 2, 0, 0.0);
SP_Constraint *sp4 = new SP_Constraint(4, 2, 1, 0.0);
SP_Constraint *sp5 = new SP_Constraint(5, 3, 0, 0.0);
SP_Constraint *sp6 = new SP_Constraint(6, 3, 1, 0.0);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp1);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp2);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp3);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp4);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp5);
theDomain->addSP_Constraint(sp6);
// construct a linear time series object using constructor:
// LinearSeries()
TimeSeries *theSeries = new LinearSeries();
// construct a load pattren using constructor:
// LoadPattern(tag)
// and then set it's TimeSeries and add it to the domain
LoadPattern *theLoadPattern = new LoadPattern(1);
theLoadPattern->setTimeSeries(theSeries);
theDomain->addLoadPattern(theLoadPattern);
// construct a nodal load using constructor:
// NodalLoad(tag, nodeID, Vector &)
// first construct a Vector of size 2 and set the values NOTE C INDEXING
// then construct the load and add it to the domain
Vector theLoadValues(2);
theLoadValues(0) = 100.0;
theLoadValues(1) = -50.0;
NodalLoad *theLoad = new NodalLoad(1, 4, theLoadValues);
theDomain->addNodalLoad(theLoad, 1);
// create an Analysis object to perform a static analysis of the model
// - constructs:
// AnalysisModel of type AnalysisModel,
// EquiSolnAlgo of type Linear
// StaticIntegrator of type LoadControl
// ConstraintHandler of type Penalty
// DOF_Numberer which uses RCM
// LinearSOE of type Band SPD
// and then the StaticAnalysis object
AnalysisModel *theModel = new AnalysisModel();
EquiSolnAlgo *theSolnAlgo = new Linear();
StaticIntegrator *theIntegrator = new LoadControl(1.0, 1, 1.0, 1.0);
ConstraintHandler *theHandler = new PenaltyConstraintHandler(1.0e8,1.0e8);
RCM *theRCM = new RCM();
DOF_Numberer *theNumberer = new DOF_Numberer(*theRCM);
BandSPDLinSolver *theSolver = new BandSPDLinLapackSolver();
LinearSOE *theSOE = new BandSPDLinSOE(*theSolver);
StaticAnalysis theAnalysis(*theDomain,
*theHandler,
*theNumberer,
*theModel,
*theSolnAlgo,
*theSOE,
*theIntegrator);
// perform the analysis & print out the results for the domain
int numSteps = 1;
theAnalysis.analyze(numSteps);
opserr << *theDomain;
exit(0);
} 接下去一步一步解释代码:
// 创建一个有限元模型 Domain *theDomain = new Domain();
// 创建4个节点,详细见说明1 Node *node1 = new Node(1, 2, 0.0, 0.0); Node *node2 = new Node(2, 2, 144.0, 0.0); Node *node3 = new Node(3, 2, 168.0, 0.0); Node *node4 = new Node(4, 2, 72.0, 96.0);
说明1:Node构造函数
位于OpenSees2.3.0\SRC\domain\node\Node.cpp
源码定义如下:
*****************************************************
Node::Node(int tag, int ndof, double Crd1, double Crd2)
:DomainComponent(tag,NOD_TAG_Node),
numberDOF(ndof), theDOF_GroupPtr(0),
Crd(0), 。。。。。。。
{
Crd = new Vector(2);
(*Crd)(0) = Crd1;
(*Crd)(1) = Crd2;
。。。。。。
*****************************************************
参数tag为该节点的标签,指定给基类
:DomainComponent(tag,NOD_TAG_Node), NOD_TAG_Node是一个枚举值,表明该DomainComponent对象是一个节点类型;
ndof该节点的自由度,本例中,节点都为两个自由度;
Crd1, Crd2为该2维节点的坐标,赋于成员变量Crd,这是一个类数组的数据类型,创建了一个含该点坐标信息的数组。
// 将4个节点对象加入有限元模型中 // 如果两个node对象tag相同,则会返回失败 theDomain->addNode(node1); theDomain->addNode(node2); theDomain->addNode(node3); theDomain->addNode(node4);
// 创建一个弹性材料,见说明2 UniaxialMaterial *theMaterial = new ElasticMaterial(1, 3000);
说明2:创建材料对象
*****************************************************
UniaxialMaterial *theMaterial = new ElasticMaterial(1,3000);
*****************************************************
UniaxialMaterial类官方说明:
http://opensees.berkeley.edu/OpenSees/api/doxygen2/html/classElasticMaterial.html
其中,ElasticMaterial为UniaxialMaterial派生类
意为理想弹性材料
http://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Elastic_Uniaxial_Material
构造函数
申明:
*****************************************************
ElasticMaterial(int tag, double E, double eta =0.0);
*****************************************************
实现:
*****************************************************
ElasticMaterial::ElasticMaterial(int tag, double e, doubleet)
:UniaxialMaterial(tag,MAT_TAG_ElasticMaterial),
trialStrain(0.0), trialStrainRate(0.0),
E(e), eta(et), parameterID(0)
{
}
*****************************************************
其中,第一个参数tag为标签,传递给基类构造函数,e为弹性模型,et为材料阻尼比,默认为0.
// 创建一个工况,编号为1,暂时未知 LoadPattern *theLoadPattern = new LoadPattern(1); theDomain->addLoadPattern(theLoadPattern); // 暂时未知这句话什么意思 theLoadPattern->setTimeSeries(new LinearSeries()); // 创建一个节点荷载向量 Vector theLoadValues(2); theLoadValues(0) = 100.0; theLoadValues(1) = -50.0; // 第一个参数tag标签,第二个参数表明施加点荷载的节点tag,第三个参数是一个向量,表明在第一维度施加100个单位力,第二维度施加反方向50单位力 NodalLoad *theLoad = new NodalLoad(1, 4, theLoadValues); // 将NodalLoad对象加入模型,1表示加入的工况编号 theDomain->addNodalLoad(theLoad, 1); // 如果new NodalLoad后的节点编号未在模型中找到,返回失败 // 如果addNodalLoad第2个参数所表示的工况编号不存在,返回失败
这里为了避免内存泄漏,也为了使代码的封装性更强,我更改了一部分代码:
AnalysisModel *theModel = new AnalysisModel();
EquiSolnAlgo *theSolnAlgo = new Linear();
StaticIntegrator *theIntegrator = new LoadControl(1.0, 1, 1.0, 1.0);
ConstraintHandler *theHandler = new PenaltyConstraintHandler(1.0e8,1.0e8);
RCM *theRCM = new RCM();
DOF_Numberer *theNumberer = new DOF_Numberer(*theRCM);
BandSPDLinSolver *theSolver = new BandSPDLinLapackSolver();
LinearSOE *theSOE = new BandSPDLinSOE(*theSolver);
StaticAnalysis theAnalysis(*theDomain,
*theHandler,
*theNumberer,
*theModel,
*theSolnAlgo,
*theSOE,
*theIntegrator);改为: // 分析对象封装
struct MyStaticAnalysis : public StaticAnalysis
{
ConstraintHandler *pConstraintHandler;
DOF_Numberer *pDOF_Numberer;
AnalysisModel *pAnalysisModel;
EquiSolnAlgo *pEquiSolnAlgo;
LinearSOE *pLinearSOE;
StaticIntegrator *pStaticIntegrator;
MyStaticAnalysis(Domain *theDomain) : StaticAnalysis(*theDomain,
*(pConstraintHandler = new PenaltyConstraintHandler(1.0e8,1.0e8)),
*(pDOF_Numberer = new DOF_Numberer(*(new RCM()))),
*(pAnalysisModel = new AnalysisModel()),
*(pEquiSolnAlgo = new Linear()),
*(pLinearSOE = new BandSPDLinSOE(*(new BandSPDLinLapackSolver()))),
*(pStaticIntegrator = new LoadControl(1.0, 1, 1.0, 1.0))) {}
~MyStaticAnalysis(){
delete pConstraintHandler;
delete pDOF_Numberer;
delete pAnalysisModel;
delete pEquiSolnAlgo;
delete pLinearSOE;
delete pStaticIntegrator;
}
};// 实例化分析模型对象 MyStaticAnalysis &theAnalysis = *(new MyStaticAnalysis(theDomain)); // perform the analysis & print out the results for the domain int numSteps = 1; theAnalysis.analyze(numSteps); // 释放分析对象 delete &theAnalysis; // 模型信息打印 opserr << *theDomain;
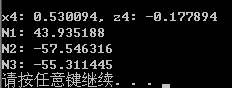
// 查看4节点两个自由度上的位移
Vector const &disp4node = theDomain->getNode(4)->getDisp();
printf("x4: %lf, z4: %lf\n", disp4node[0], disp4node[1]);
// 查看3个桁架单元的轴力
Information trussInfo;
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
Truss *pTruss = (Truss *)theDomain->getElement(i+1);
pTruss->getResponse(2, trussInfo);
printf("N%d: %lf\n", i+1, trussInfo.theDouble);
}
// Domain类的析构会释放加入domain的所有元素,所以node之类的对象不用单独析构
delete theDomain;编译——运行——屏幕输出:
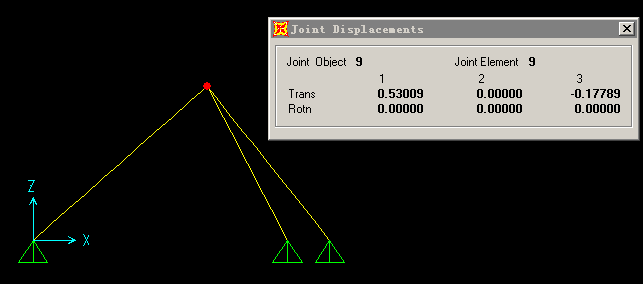
第一自由度位移 0.530094,第二自由度位移-0.177894
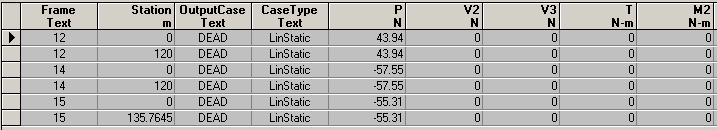
杆件1轴力:43.94
杆件2轴力:-57.55
杆件3轴力:-55.31
与sap2000计算结果一致:
sap2000模型文件*.SDB(v14)和*.s2k文件,及修改后的源文件 first.cpp下载:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dDDKnb7

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号