std::copy的使用
看到有人在用std::copy这个东西,很简洁和爽啊,,所以找些帖子学习学习
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8655aeca0100t6qe.html
https://www.so.com/s?q=std%3A%3Acopy%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0&ie=utf-8&src=se7_newtab_new
copy函数的函数原型:
1 //fist [IN]: 要拷贝元素的首地址 2 //last [IN]:要拷贝元素的最后一个元素的下一个地址 3 //x [OUT] : 拷贝的目的地的首地址 4 5 template<class InIt, class OutIt> 6 OutIt copy(InIt first, InIt last, OutIt x);
如果要把一个序列(sequence)拷贝到一个容器(container)中去,通常用std::copy算法,代码如下:std::copy(start, end, std::back_inserter(container));
这里,start和end是输入序列(假设有N各元素)的迭代器(iterator)[例如start = iterator.begin(); end = iterator.end()],container是一个容器[例如vector],该容器的接口包含函数push_back。
假设container开始是空的,那么copy完毕后它就包含N个元素,并且顺序与原来队列中的元素顺序一样。标准库提供的back_inserter模板函数很方便,因为它为container返回一个back_insert_iterator迭代器,这样,复制的元素都被追加到container的末尾了。
现在假设container开始非空(例如:container必须在循环中反复被使用好几次)。那么,要达到原来的目标,必须先调用clear函数然后才能插入新序列。这会导致旧的元素对象被析构,新添加进来的被构造。不仅如此,container自身使用的动态内存也会被释放然后又创建,就像list,map,set的节点。某些vector的实现在调用clear的时候甚至会释放所有内存。
通常,考虑到在一个已有的元素上直接copy覆盖更高效。keyi这样做:
std::copy(start, end, container.begin());
在这里你在container的头部执行了copy-over(覆盖赋值)操作,但是,如果container的大小小于输入序列的长度N的话,这段代码会导致崩溃(crash)。
eg1: //可以使用copy给数组赋值啊!!! 但是要注意 sizeof(b) 必须大于 [(a+3) - (a)] 的长度
int a[3]={1,2,3};
int b[3];
std::copy(a,(a+3),b); ------>[a, a+3)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cout<<b[j]
eg2:
vector<int> temp(3); //初始化一个有3个元素的vector
int a[3]={1,2,3};
std::copy(a,a+3,&temp.front()); // 或者是 std::copy(a, a+3, temp.begin())也可以
cout<<<endl;
for(int j=0;j < temp.size(); j++)
cout<<temp[j];
copy只负责复制,不负责申请空间,所以复制前必须有足够的空间
copy只负责复制,不负责申请空间,所以复制前必须有足够的空间
copy只负责复制,不负责申请空间,所以复制前必须有足够的空间
copy只负责复制,不负责申请空间,所以复制前必须有足够的空间
接下来,让我们来看看数组之间直接用for拷贝和用copy拷贝的效率比较 http://blog.csdn.net/zhouxuguang236/article/details/10834567
在C++编程中,经常会配到数据的拷贝,如数组之间元素的拷贝,一般的人可能都会用for循环逐个元素进行拷贝,在数据量不大的情况下还可以,如果数据量比较大,那么效率会比较地下。而STL中就提供了一个专门用来进行容器元素拷贝的函数copy
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 #include<sys/time.h> 4 #include<time.h> 5 #include<iosfwd> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 #include<stdio.h> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const long SECOND_IN_NS = 10000000001; //1second in nanoseconds 12 13 class Timer //计算时间差的类 14 { 15 private: 16 struct timespec m_start; 17 struct timespec m_end; 18 clockid_t m_clockId; 19 public: 20 Timer(){ 21 init(true, true); 22 } 23 24 Timer(bool realTime){ 25 init(realTime, true); 26 } 27 28 Timer(bool realTime, bool startImmediately){ 29 init(realTime, startImmediately); 30 } 31 32 void init(bool realTime, bool startImmediately){ 33 if (realTime){ 34 //Real time 35 m_clockId = CLOCK_REALTIME; // is not a system call 36 //m_clockId = CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW; //is a system call 37 } 38 else{ 39 //Process CPU time across all CPU core (threads) 40 m_clockId = CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID; 41 } 42 if (startImmediately){ 43 start(); 44 } 45 } 46 47 void start(){ 48 clock_gettime(m_clockId, &m_start); 49 m_end = m_start; 50 } 51 52 void stop(){ 53 clock_gettime(m_clockId, &m_end); 54 } 55 56 //return - the passed time between start and last stop in nanoseconds 57 double getNseconds() const{ 58 return (m_end.tv_sec - m_start.tv_sec) * SECOND_IN_NS + (m_end.tv_nsec - m_start.tv_nsec); 59 } 60 61 //return - the passed time between start and last stop in seconds 62 double getSeconds() const{ 63 return (m_end.tv_sec - m_start.tv_sec) + double(m_end.tv_nsec - m_start.tv_nsec) / SECOND_IN_NS; 64 } 65 66 //return - the passed seconds without need of stopping the execution 67 double getSecondsAndContinue() const{ 68 struct timespec tempEnd; 69 clock_gettime(m_clockId, &tempEnd); 70 return (tempEnd.tv_sec - m_start.tv_sec) + double(tempEnd.tv_nsec - m_start.tv_nsec) / SECOND_IN_NS; 71 } 72 73 time_t getS() const{ 74 time_t ret = m_end.tv_sec - m_start.tv_sec; 75 if (m_end.tv_nsec < m_start.tv_nsec){ 76 ret -= 1; 77 } 78 79 return ret; 80 } 81 82 time_t getNs() const{ 83 if (m_end.tv_nsec >= m_start.tv_nsec){ 84 return m_end.tv_nsec - m_start.tv_nsec; 85 } 86 return SECOND_IN_NS + m_end.tv_nsec - m_start.tv_nsec; 87 } 88 89 friend std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Timer& timer); 90 }; 91 92 std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Timer& timer){ 93 char nsBuf[10]; //999, 999, 999 94 if (timer.m_end.tv_nsec >= timer.m_start.tv_nsec){ 95 os << timer.m_end.tv_nsec - timer.m_start.tv_sec; 96 snprintf(nsBuf, sizeof(nsBuf), "%09li", timer.m_end.tv_nsec - timer.m_start.tv_nsec); 97 } 98 else{ 99 os << timer.m_end.tv_nsec - timer.m_start.tv_sec - 1; 100 snprintf(nsBuf, sizeof(nsBuf), "%09li", SECOND_IN_NS + timer.m_end.tv_nsec - timer.m_start.tv_nsec); 101 } 102 return os<<"."<<nsBuf; 103 } 104 105 void set(int& n){ //被for_each调用 106 static int value = 0; 107 n = value++; 108 } 109 110 void print(int n){ //被for_each调用 111 cout<<n<<endl; 112 } 113 114 int main(){ 115 /*test short copy*/ 116 vector<int> iVec(1000); 117 for_each(iVec.begin(), iVec.end(), set); 118 //for_each(iVec.begin(), iVec.end(), print); 119 120 int* pInt = new int[iVec.size()]; 121 122 Timer timer; 123 copy(iVec.begin(), iVec.end(), pInt); 124 timer.stop(); 125 cout<<"the short copy cost("<<timer.getSeconds()<<")'s"<<endl; 126 127 timer.start(); 128 int size = iVec.size(); 129 for (int i = 0; i < iVec.size(); i++) 130 { 131 pInt[i] = iVec[size - i - 1]; 132 } 133 timer.stop(); 134 cout<<"the short loop cost("<<timer.getSeconds()<<")'s"<<endl; 135 delete []pInt; 136 cout<<"---------------------------------------"<<endl; 137 138 /*test long copy*/ 139 vector<int> iVec2(1000000); 140 for_each(iVec2.begin(), iVec2.end(), set); 141 //for_each(iVec.begin(), iVec.end(), print); 142 143 int* pInt2 = new int[iVec2.size()]; 144 145 Timer timer2; 146 copy(iVec2.begin(), iVec2.end(), pInt2); 147 timer2.stop(); 148 cout<<"the long copy cost("<<timer2.getSeconds()<<")'s"<<endl; 149 150 timer2.start(); 151 int size2 = iVec2.size(); 152 for (int i = 0; i < iVec2.size(); i++) 153 { 154 pInt2[i] = iVec2[size2 - i - 1]; 155 } 156 timer2.stop(); 157 cout<<"the long loop cost("<<timer2.getSeconds()<<")'s"<<endl; 158 delete []pInt2; 159 return 0; 160 }
编译命令: g++ -o test main.cpp -lrt
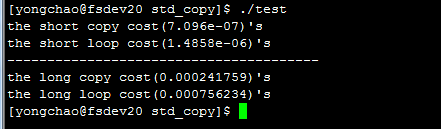
测试结果,跟作者的大相径庭,不知是和原因:

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号