(一)爬虫之网页下载
1,相关知识
robots.txt: 一些网站会定义robots.txt文件(https://www.example.com/robots.txt),规定了网页爬取的相关限制,查看其内容,遵守规则可以避免过早IP被封。
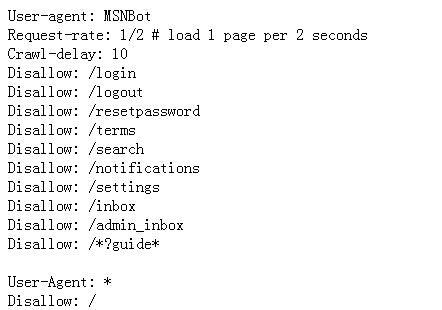
下面为知乎robots.txt部分内容(https://www.zhihu.com/robots.txt)。(disallow 表示不允许爬取的url;Crawl-delay:10,表示两次抓取之间需要10秒延迟)
sitemap:有的robots.txt的html源码中会给出网站的sitemap,获得网站的sitemap,可以了解网站整体架构和各url路径格式。
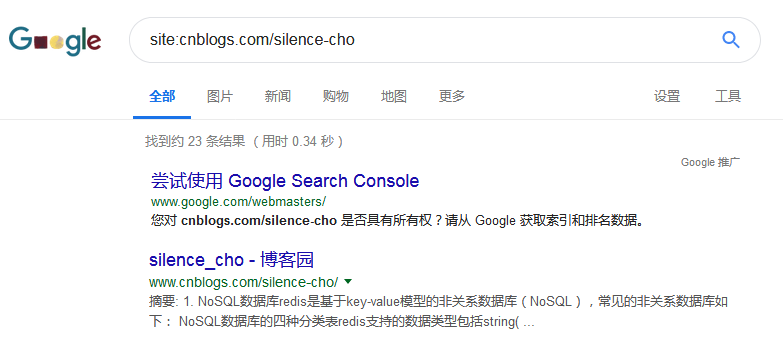
网站大小估计: 利用谷歌搜索 site:example.com,根据显示结果估计。如下图23条结果,说明该域名下大概有23个子网页。
识别网站所用技术:利用python第三方模块builtwith能够返回网站使用相关技术。(安装:pip install builtwith)
下图查看知乎使用的技术:builtwith.parse('https://www.zhihu.com')

查看网站所有者:利用python第三方模块python-whois, 返回服务器,邮箱等相关信息。(pip install python-whois)
使用:whois.whois('https://www.zhihu.com')
2.网页下载器和url队列
网页下载器:应该支持重试下载,用户代理(user-agent),proxy代理等。代码如下:
def download(url,user_agent=None,proxies=None,num_retries=3): #支持user-agent和proxy #proxies = {"http": "http://10.10.1.10:3128", "https": "http://10.10.1.10:1080",} response=requests.get(url,headers={'User-Agent':user_agent},proxies=proxies) if response.status_code and 500<=response.status_code<600: # 出现服务器端错误时重试三次 if num_retries > 0: response = download(url,user_agent,proxies,num_retries-1) return response
url队列:管理需要下载的url。即从下载的网页中提取出有用的url加入队列,从队列中取出下一个url进行爬取。需要实现url去重,下载延迟等。代码如下:
#coding:utf-8 import requests import re import urlparse from datetime import datetime import time def link_carwl(start_url,link_regex,max_depth): #link_regex 正则表达式,提取感兴趣的url url_queue = [start_url] seen = set(url_queue) while url_queue: url = url_queue.pop() throttle =Throttle(3) #相同域名延迟3秒访问 throttle.wait(url) response = download(url) for link in get_links(response.text): if re.match(link_regex,link): #urlparse.urljoin(url,link) #link可能为相对路径 if link not in seen: #不访问重复的url seen.add(url) url_queue.append(link) #url提取 def get_links(html): webpage_regex = re.compile('<a[^>]+href=["\'](.*?)["\']',re.IGNORECASE) #["\']匹配单引号或双引号 return webpage_regex.findall(html) #同一个域名的下载延迟 class Throttle(object): def __init__(self,delay): self.delay = delay self.domains={} def wait(self,url): domain = urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc #提取网址的域名 last_accessed = self.domains.get(domain) if self.delay>0 and last_accessed!=None: sleep_secs = self.delay-(datetime.now()-last_accessed).seconds if sleep_secs>0: time.sleep(sleep_secs) self.domains[domain]=datetime.now()
如果需要设置网页爬取深度,对于上面的link_carwl()方法可以改进如下:
#深度设置,防止爬虫陷阱(同一个域名下的网页链接,一直向下访问下去) def link_carwl(start_url,link_regex,max_depth=5): #设置最大深度为5 url_queue = [start_url] seen = {start_url:0} while url_queue: url = url_queue.pop() throttle =Throttle(3) #相同域名延迟3秒访问 throttle.wait(url) response = download(url) depth = seen[url] if depth<max_depth: for link in get_links(response.text): if re.match(link_regex,link): #urlparse.urljoin(url,link) #link可能为相对路径 if link not in seen: #不访问重复的url seen[link] =depth+1 #在url的深度基础上加一 url_queue.append(link)
如果需要设置网页内容提取函数,可以在link_carwl()方法添加回调函数。代码如下:
#添加回调函数处理提取的内容 def link_carwl(start_url,link_regex,max_depth=5,callback=None): url_queue = [start_url] seen = {start_url:0} while url_queue: url = url_queue.pop() throttle =Throttle(3) #相同域名延迟3秒访问 throttle.wait(url) response = download(url) if callback!=None: callback(url,response.text) depth = seen[url] if depth<max_depth: for link in get_links(response.text): if re.match(link_regex,link): #urlparse.urljoin(url,link) #link可能为相对路径 if link not in seen: #不访问重复的url seen[link] =depth+1 #在url的深度基础上加一 url_queue.append(link)



