哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树是所有树之中最优秀的品种之一,是带权路径长度最短的最小二叉树,比之前的数据结构要多考验逻辑一点。该程序可以实现哈夫曼树的编码还有解码,代码如下所示:
lcwHuffmantree.c主要是哈夫曼树的基本操作函数
//start from the very beginning,and to create greatness
//@author: Chuangwei Lin
//@E-mail:979951191@qq.com
//@brief: 哈夫曼树的基本操作函数
#include "lcwHuffmantree.h"
/******************************************************
函数名:SelectNode(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *bt1,int *bt2)
参数:哈夫曼树,查找范围,返回的两个节点指针
功能:从1~i-1个结点选择parent结点为0,权重最小的两个结点
*******************************************************/
void SelectNode(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *bt1,int *bt2)
{
int i;
HuffmanTree *ht1,*ht2,*t;
ht1=ht2=NULL; //初始化两个结点为空
for(i=1;i<=n;++i) //循环处理1~n个结点(包括叶结点和非叶结点)
{
if(!ht[i].parent) //父结点为空(结点的parent=0),父节点非空则说明已经组成子树
{
if(ht1==NULL) //结点指针1为空
{
ht1=ht+i; //指向第i个结点
continue; //继续循环
}
if(ht2==NULL) //结点指针2为空
{
ht2=ht+i; //指向第i个结点
if(ht1->weight > ht2->weight) //比较两个结点的权重,使ht1指向的结点权重小
{
t=ht2;
ht2=ht1;
ht1=t;
}
continue; //继续循环
}
if(ht1 && ht2) //若ht1、ht2两个指针都有效
{
if(ht[i].weight <= ht1->weight)
{//第i个结点权重小于ht1指向的结点,说明此时第i个节点的值为最小的,应该赋给ht1
ht2=ht1; //ht2保存ht1,因为这时ht1指向的结点成为第2小的
ht1=ht+i; //ht1指向第i个结点,ht1一直指向最小权值的节点
}
else if(ht[i].weight < ht2->weight)
{ //若第i个结点权重小于ht2指向的结点,说明此时第i个节点的值为次小的,应该赋给ht2
ht2=ht+i; //ht2指向第i个结点
}
}
}
}
if(ht1 > ht2)
{ //增加比较,使二叉树左侧为叶结点
*bt2=ht1-ht;
*bt1=ht2-ht;
}
else
{//bt1是最小的
*bt1=ht1-ht;
*bt2=ht2-ht;
}
}
/******************************************************
函数名:CreateTree(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *w)
参数:哈夫曼树数组,权重数组
功能:创建哈夫曼树
*******************************************************/
void CreateTree(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *w)
{
int i,m=2*n-1;//总的节点数
int bt1,bt2; //二叉树结点序与
if(n<=1) return ; //只有一个结点,无法创建
for(i=1;i<=n;++i) //初始化叶结点,就是先存放权重
{
ht[i].weight=w[i-1];
ht[i].parent=0;
ht[i].left=0;
ht[i].right=0;
}
//此时i是等于n的
for(;i<=m;++i)//初始化后续结点
{
ht[i].weight=0;
ht[i].parent=0;
ht[i].left=0;
ht[i].right=0;
}
//哈夫曼树是不断从子树(最初的子树其实就是所有的权重节点)中选出权重最小的来构成树,
//其根的权重为原来两个子节点的和,直到剩下最后一棵树就是哈夫曼树
for(i=n+1;i<=m;++i) //逐个计算非叶结点,创建Huffman树
{//m为总的节点数
SelectNode(ht,i-1,&bt1,&bt2); //从1~i-1个结点选择parent结点为0,权重最小的两个结点
ht[bt1].parent=i;//从最初的权值后面开始存放新的权值节点
ht[bt2].parent=i;
ht[i].left=bt1;//存放左子树
ht[i].right=bt2;//存放右子树
ht[i].weight=ht[bt1].weight+ht[bt2].weight;//更新新的权重
}
}
/******************************************************
函数名:HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,HuffmanCode *hc)
参数:哈夫曼树指针,需要生成哈夫曼编码的字符数量,返回编码的字符串首地址
功能:根据哈夫曼树生成哈夫曼编码
*******************************************************/
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,HuffmanCode *hc)
{
char *cd;
int start,i;
int current,parent;
cd=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*n);//用来临时存放一个字符的编码结果
cd[n-1]='\0'; //设置字符串结束标志
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
start=n-1;//从后往前存,因为我们是从叶子节点开始往根走
current=i;
parent=ht[current].parent;//获取当前结点的父结点
//从第一个节点开始,寻找其父节点,若此节点为父节点的左子树,则编码0,右子树则编码1
while(parent) //父结点不为空
{
if(current==ht[parent].left)//若该结点是父结点的左子树
cd[--start]='0'; //编码为0
else //若结点是父结点的右子树
cd[--start]='1'; //编码为1
current=parent; //设置当前结点指向父结点
parent=ht[parent].parent; //获取当前结点的父结点序号
}
hc[i-1]=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(n-start));//分配保存编码的内存
strcpy(hc[i-1],&cd[start]); //复制生成的编码
}
free(cd); //释放编码占用的内存
}
/******************************************************
函数名:Encode(HuffmanCode *hc,char *alphabet,char *str,char *code)
参数:hc为Huffman编码表 ,alphabet为对应的字母表,str为需要转换的字符串,code返回转换的结果
功能:将一个字符串转换为Huffman编码
*******************************************************/
void Encode(HuffmanCode *hc,char *alphabet,char *str,char *code)
{
int len=0,i=0,j;
code[0]='\0';
while(str[i])//字符串未结束
{
j=0;
while(alphabet[j]!=str[i])//找到欲转换的字符
j++;
strcpy(code+len,hc[j]); //将对应字母的Huffman编码复制到code指定位置
len=len+strlen(hc[j]); //累加字符串长度
i++;//转换下一个字符
}
code[len]='\0';//来个结尾
}
/******************************************************
函数名:Decode(HuffmanTree *ht,int m,char *code,char *alphabet,char *decode)
参数:ht为Huffman二叉树,m为字符数量,alphabet为对应的字母表,str为需要转换的字符串,decode返回转换的结果:
功能:将一个Huffman编码组成的字符串转换为明文字符串
*******************************************************/
void Decode(HuffmanTree *ht,int m,char *code,char *alphabet,char *decode)
{
int position=0,i,j=0;
m=2*m-1;//原来的m是字符的个数,编码后的节点为2*m-1
while(code[position]) //字符串未结束
{//这里得到哈夫曼树的根节点,从根节点开始往下匹配,最快匹配到的就是所解码的值
for(i=m;ht[i].left && ht[i].right; position++) //在Huffman树中查找左右子树为空 ,以构造一个Huffman编码
{
if(code[position]=='0') //编码位为0
i=ht[i].left; //处理左子树
else //编译位为 1
i=ht[i].right; //处理右子树
}
decode[j]=alphabet[i-1]; //得到一个字母
j++;//处理下一字符
}
decode[j]='\0'; //字符串结尾
}
lcwHuffmantree.h是基本数据结构的头文件
//start from the very beginning,and to create greatness
//@author: Chuangwei Lin
//@E-mail:979951191@qq.com
//@brief: 哈夫曼树基本操作的头文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义哈夫曼树的树节点
typedef struct
{
int weight; //权值
int parent; //父结点序号
int left; //左子树序号
int right; //右子树序号
}HuffmanTree;
typedef char *HuffmanCode; //Huffman编码
void SelectNode(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *bt1,int *bt2);
void CreateTree(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,int *w);
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree *ht,int n,HuffmanCode *hc);
void Encode(HuffmanCode *hc,char *alphabet,char *str,char *code);
void Decode(HuffmanTree *ht,int m,char *code,char *alphabet,char *decode);
主函数实现了哈夫曼树的验证
//start from the very beginning,and to create greatness
//@author: Chuangwei Lin
//@E-mail:979951191@qq.com
//@brief: 哈夫曼树基本操作的验证
#include "lcwHuffmantree.h"
int main()
{
int i,n=4,m;
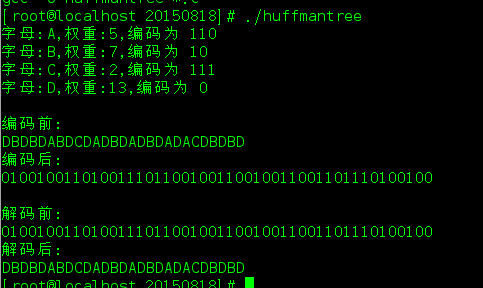
char test[]="DBDBDABDCDADBDADBDADACDBDBD";
char code[100],code1[100];
char alphabet[]={'A','B','C','D'}; //4个字符
int w[]={5,7,2,13} ;//4个字符对应的权重
HuffmanTree *ht;
HuffmanCode *hc;
m=2*n-1; //根据字符个数求出所需的节点总数
ht=(HuffmanTree *)malloc((m+1)*sizeof(HuffmanTree));//申请内存,保存哈夫曼树
if(!ht)
{
printf("内存申请失败\n");
exit(0);//退出
}
hc=(HuffmanCode *)malloc(n*sizeof(char*));
if(!hc)
{
printf("内存申请失败\n");
exit(0);//退出
}
CreateTree(ht,n,w); //创建哈夫曼树
HuffmanCoding(ht,n,hc); //根据哈夫曼树生成哈夫曼编码
for(i=1;i<=n;i++) //循环输出哈夫曼编码
printf("字母:%c,权重:%d,编码为 %s\n",alphabet[i-1],ht[i].weight,hc[i-1]);
Encode(hc,alphabet,test,code); //由哈夫曼编码将字母编码
printf("\n编码前:\n%s\n编码后:\n%s\n",test,code);
Decode(ht,n,code,alphabet,code1);//解码之前生成的码值
printf("\n解码前:\n%s\n解码后:\n%s\n",code,code1);
return 0;
}
运行结果: