muduo网络库源码学习————线程本地单例类封装
muduo库中线程本地单例类封装代码是ThreadLocalSingleton.h
如下所示:
//线程本地单例类封装
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_THREADLOCALSINGLETON_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_THREADLOCALSINGLETON_H
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
namespace muduo
{
template<typename T>
class ThreadLocalSingleton : boost::noncopyable//不可被拷贝
{
public:
//返回单例对象的引用
static T& instance()
{
if (!t_value_)//如果指针为空
{
t_value_ = new T();//创建对象
deleter_.set(t_value_);//将t_value_传入deleter_,以便deleter_可以调用destructor销毁
}
return *t_value_;//返回
}
//返回单例对象的指针
static T* pointer()
{
return t_value_;
}
private:
//销毁对象
static void destructor(void* obj)
{
assert(obj == t_value_);
typedef char T_must_be_complete_type[sizeof(T) == 0 ? -1 : 1];
delete t_value_;
t_value_ = 0;
}
//一个嵌套类只是为了能够调用destructor自动销毁t_value_
class Deleter
{//借助线程特定数据来实现
public:
Deleter()//构造函数的回调函数为ThreadLocalSingleton::destructor
{
pthread_key_create(&pkey_, &ThreadLocalSingleton::destructor);
}
~Deleter()
{
pthread_key_delete(pkey_);
}
void set(T* newObj)
{
assert(pthread_getspecific(pkey_) == NULL);
pthread_setspecific(pkey_, newObj);
}
pthread_key_t pkey_;
};
static __thread T* t_value_;//T类型的指针,__thread关键字表示每个线程都有一份
static Deleter deleter_;//主要用于销毁上面那个指针所指向的对象
};
template<typename T>
__thread T* ThreadLocalSingleton<T>::t_value_ = 0;
template<typename T>
typename ThreadLocalSingleton<T>::Deleter ThreadLocalSingleton<T>::deleter_;
}
#endif
测试程序如下:
//线程本地单例类封装测试程序
#include <muduo/base/ThreadLocalSingleton.h>
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <muduo/base/Thread.h>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
class Test : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, constructing %p\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this);
}
~Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, destructing %p %s\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this, name_.c_str());
}
const std::string& name() const { return name_; }
void setName(const std::string& n) { name_ = n; }
private:
std::string name_;
};
void threadFunc(const char* changeTo)
{//打印线程tid,线程单例对象地址,线程单例对象名称
printf("tid=%d, %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance(),
muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance().name().c_str());
//重新设置一下名称
muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance().setName(changeTo);
//再次打印
printf("tid=%d, %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance(),
muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance().name().c_str());
//线程退出时会自动销毁,对象周期结束
// no need to manually delete it
// muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::destroy();
}
int main()
{//muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance()返回一个线程单例对象,每个线程都有一个Test对象
muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance().setName("main one");
//创建两个线程,threadFunc为回调函数
muduo::Thread t1(boost::bind(threadFunc, "thread1"));
muduo::Thread t2(boost::bind(threadFunc, "thread2"));
//启动两个线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
//打印主线程的
printf("tid=%d, %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance(),
muduo::ThreadLocalSingleton<Test>::instance().name().c_str());
t2.join();
//退出主线程
pthread_exit(0);
}
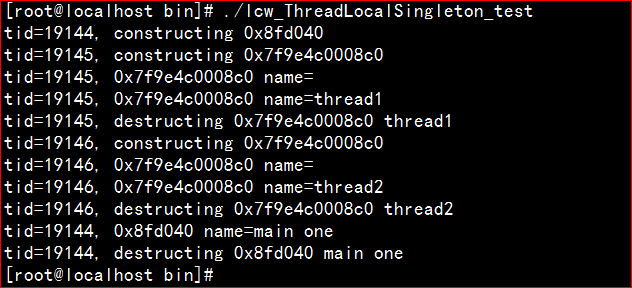
运行结果如下: