解题笔记-CodeForces-908B New Year and Buggy Bot
0 题面
B. New Year and Buggy Bot
Bob programmed a robot to navigate through a 2d maze.
The maze has some obstacles. Empty cells are denoted by the character '.', where obstacles are denoted by '#'.
There is a single robot in the maze. It's start position is denoted with the character 'S'. This position has no obstacle in it. There is also a single exit in the maze. It's position is denoted with the character 'E'. This position has no obstacle in it.
The robot can only move up, left, right, or down.
When Bob programmed the robot, he wrote down a string of digits consisting of the digits 0 to 3, inclusive. He intended for each digit to correspond to a distinct direction, and the robot would follow the directions in order to reach the exit. Unfortunately, he forgot to actually assign the directions to digits.
The robot will choose some random mapping of digits to distinct directions. The robot will map distinct digits to distinct directions. The robot will then follow the instructions according to the given string in order and chosen mapping. If an instruction would lead the robot to go off the edge of the maze or hit an obstacle, the robot will crash and break down. If the robot reaches the exit at any point, then the robot will stop following any further instructions.
Bob is having trouble debugging his robot, so he would like to determine the number of mappings of digits to directions that would lead the robot to the exit.
Input
The first line of input will contain two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50), denoting the dimensions of the maze.
The next n lines will contain exactly m characters each, denoting the maze.
Each character of the maze will be '.', '#', 'S', or 'E'.
There will be exactly one 'S' and exactly one 'E' in the maze.
The last line will contain a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100) — the instructions given to the robot. Each character of s is a digit from 0 to 3.
Output
Print a single integer, the number of mappings of digits to directions that will lead the robot to the exit.
Examples
input
5 6
.....#
S....#
.#....
.#....
...E..
333300012
output
1
input
6 6
......
......
..SE..
......
......
......
01232123212302123021
output
14
input
5 3
...
.S.
###
.E.
...
3
output
0
Note
For the first sample, the only valid mapping is 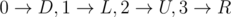 , where D is down, L is left, U is up, R is right.
, where D is down, L is left, U is up, R is right.
中文大意:
给予一张字符表示的迷宫地图,其中空格子用 '.' 表示,障碍物用 '#' 表示,起点用 'S' 表示,终点用 'E' 表示。
机器人一旦碰到障碍物就会宕机,不再进行其它操作;一旦碰到终点,也不再进行其它操作。
一个机器人从起点出发,给予一串指令字符,由 '0', '1', '2', '3' 组成,每个数字代表不同的方向,根据对应指令机器人进行行动。
'0', '1', '2', '3' 代表的方向未知,问 '0', '1', '2', '3' 代表的方向有多少种组合,能够使机器人成功到达终点。
1 代码
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; char mat[51][51]; char command[101]; int r = 0; int s_i, s_j; char real[4]; void dir(char a, char b, char c, char d) { real[0] = a; real[1] = b; real[2] = c; real[3] = d; } void go() { int x = s_i, y = s_j; for(int i = 0; i < strlen(command); i++) { int t = command[i] - '0'; switch(real[t]) { case 'U': x--; break; case 'D': x++; break; case 'L': y--; break; case 'R': y++; break; } if(mat[x][y] == '#') break; if(mat[x][y] == '!' || (x < 0) || (y < 0)) break; if(mat[x][y] == 'E') { r++; break; } } } int main() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < 50; j++) { mat[i][j] = '!'; } } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) { cin >> mat[i][j]; if(mat[i][j] == 'S') { s_i = i; s_j = j; } } } cin >> command; // U dir('U', 'D', 'L', 'R'); go(); dir('U', 'D', 'R', 'L'); go(); dir('U', 'L', 'R', 'D'); go(); dir('U', 'L', 'D', 'R'); go(); dir('U', 'R', 'D', 'L'); go(); dir('U', 'R', 'L', 'D'); go(); // D dir('D', 'L', 'R', 'U'); go(); dir('D', 'L', 'U', 'R'); go(); dir('D', 'R', 'U', 'L'); go(); dir('D', 'R', 'L', 'U'); go(); dir('D', 'U', 'L', 'R'); go(); dir('D', 'U', 'R', 'L'); go(); // L dir('L', 'R', 'U', 'D'); go(); dir('L', 'R', 'D', 'U'); go(); dir('L', 'U', 'D', 'R'); go(); dir('L', 'U', 'R', 'D'); go(); dir('L', 'D', 'R', 'U'); go(); dir('L', 'D', 'U', 'R'); go(); // R dir('R', 'U', 'D', 'L'); go(); dir('R', 'U', 'L', 'D'); go(); dir('R', 'D', 'L', 'U'); go(); dir('R', 'D', 'U', 'L'); go(); dir('R', 'L', 'U', 'D'); go(); dir('R', 'L', 'D', 'U'); go(); cout << r; }
理论上是要全排列的,不过图时间快我就强行手动排列了。



