4------自动装配
自动装配
- 自动装配是使用spring满足bean依赖的一种方法
- spring会在应用上下文为某个bean寻找其依赖的bean。
方式种类
- 在xml中显示配置;前面的博客讲过了!
- 在java中显示配置;通过注解实现的
- 隐式的bean发现机制和自动装配
重点讲第三种:隐式的bean发现机制和自动装配
component scanning(组件扫描):spring会自动发现应用上下文所创建的bean
自动装配(autowiring):spring自动满足bean之间的依赖,也就是我们说的IOC/DI
正常的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="dog" class="com.kuang.pojo.Dog"/> <bean id="cat" class="com.kuang.pojo.Cat"/> <bean id="user" class="com.kuang.pojo.User"> <property name="cat" ref="cat"/> <property name="dog" ref="dog"/> <property name="str" value="qinjiang"/> </bean> </beans>
使用第三种方法:
通过名字:
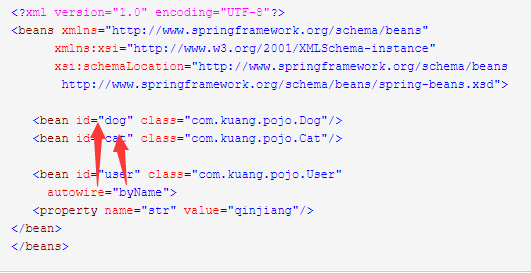
通过类型:
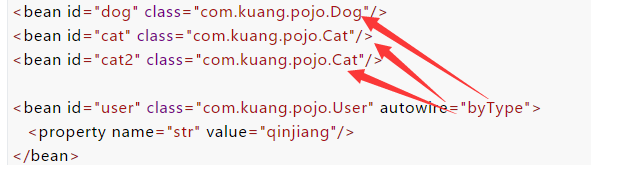
来吧 ,小小的使用注解,任性一次吧
添加头文件
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
实体类
package demo1.com.sicheng.entity; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import java.util.List; public class Hello { private String name; @Autowired private List<Person> person; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public List<Person> getPerson() { return person; } public void setPerson(List<Person> person) { this.person = person; } public Hello(String name, List<Person> person) { this.name = name; this.person = person; } public Hello() { } @Override public String toString() { return "Hello{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", person=" + person + '}'; } }
package demo1.com.sicheng.entity; public class Person { private int age; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Person(int age) { this.age = age; } public Person() { } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "age=" + age + '}'; } }
xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <bean id="person" class="demo1.com.sicheng.entity.Person"> <property name="age" value="10"/> </bean> <bean id="hello" class="demo1.com.sicheng.entity.Hello"/> </beans>
测试文件
import demo1.com.sicheng.entity.Hello; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTest { @Test public void HelloTest(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Hello hello = (Hello)context.getBean("hello"); System.out.println(hello.toString()); } }

