C++多线程编程二
1. 死锁与解锁:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> using namespace std; //thread引用类型函数,模板,避免类型转换,尽量指针,引用 //锁住一个变量之后,尽快操作完解锁,不要再锁,否则互锁 #define COUNT 100000 mutex g_mutex1, g_mutex2;//互斥量 void add1(int *p1, int *p2) { for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++) { /*g_mutex1.lock(); p1++; g_mutex2.lock(); p2++; g_mutex1.unlock(); g_mutex2.unlock();*/ g_mutex1.lock(); (*p1)++; g_mutex1.unlock(); g_mutex2.lock(); (*p2)++; g_mutex2.unlock(); } } void add2(int *p1, int *p2) { for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++) { /*g_mutex2.lock(); g_mutex1.lock(); p1++; g_mutex1.unlock(); p2++; g_mutex2.unlock();*/ g_mutex2.lock(); (*p2)++; g_mutex2.unlock(); g_mutex1.lock(); (*p1)++; g_mutex1.unlock(); } } void main() { int a = 0; int b = 0; thread th1(add1, &a, &b); thread th2(add2, &a, &b); th1.join(); th2.join(); while (1) { cout << a << endl; cout << b << endl; this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1)); } cin.get(); }
2. 迅雷面试题:
编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,
要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。
【参考答案】
//编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍, //要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。 #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> using namespace std; int LOOP = 10; //循环次数 int flag = 0; //标识符 012012012012 mutex m; condition_variable cv; void fun(int id) { for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) { unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m); //设定锁定 while ((id-65) != flag) { cv.wait(ulk); //不是该出现的场合,就等待 } cout << (char)id; //转换id flag = (flag + 1) % 3; //012,012,012,... cv.notify_all(); //通知全部 } } void main() { thread t1(fun, 65); thread t2(fun, 66); thread t3(fun, 67); t1.join(); t2.join(); t3.join(); cin.get(); }
运行结果:
【分析】若题目变为:4个线程,输出结果要求为: ABCDABCDABCD...又该如何做呢?
//编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍, //要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。 #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> using namespace std; int LOOP = 10; //循环次数 int flag = 0; //标识符 012012012012 mutex m; condition_variable cv; void fun(int id) { for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) { unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m); //设定锁定 while ((id-65) != flag) { cv.wait(ulk); //不是该出现的场合,就等待 } cout << (char)id; //转换id flag = (flag + 1) % 4; //012,012,012,... cv.notify_all(); //通知全部 } } void main() { thread t1(fun, 65); thread t2(fun, 66); thread t3(fun, 67); thread t4(fun, 68); t1.join(); t2.join(); t3.join(); t4.join(); cin.get(); }
运行结果:
3. 思考:上题中若变为开启5个线程,ID分别为1,2,3,4,5,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,要求输出结果为:12345,54321,12345,54321,...依此类推。
4. 线程交换 swap:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> using namespace std; void main() { thread t1([]() {cout << "ZhangShan"<<endl; }); thread t2([]() {cout << "LiSi"<<endl; }); cout << "t1.get_id():" << t1.get_id() << " t2.get_id():" << t2.get_id() << endl; swap(t1, t2); //交换句柄 cout << "t1.get_id():" << t1.get_id() << " t2.get_id():" << t2.get_id() << endl; t1.join(); t2.join(); cin.get(); }
5. 线程移动 move:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; void main() { thread t1([]() { int i = 0; while (1) { i++; if (i > 1000000000) { break; } } cout << i << endl; system("pause"); }); cout << "t1:" << t1.get_id() << endl; //6872 //t1.join(); thread t2 = move(t1);//线程移动,t2具备了t1的属性,t1挂了 cout << "t1:" << t1.get_id() << endl; //0 cout << "t2:" << t2.get_id() << endl; //6872 t2.join(); cin.get(); }
运行结果: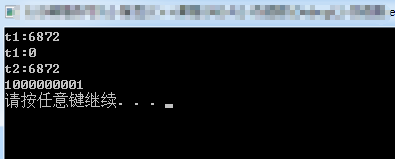
6. 线程自动加解锁:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> using namespace std; #define N 10000000 mutex g_mutex;//全局互斥量 void add(int *p) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { unique_lock<mutex> ulk(g_mutex); //没有mutex所有权,自动加锁自动解锁,根据块语句锁定 //根据mutex属性来决定,是否可以加锁 //lock_guard<mutex> lgd(g_mutex); //拥有mutex所有权,自动加锁自动解锁 //读取mutex失败的情况下就会一直等待 (*p)++; } } void main() { int a = 0; thread t1(add, &a); thread t2(add, &a); t1.join(); t2.join(); cout << a << endl; cin.get(); }
7. 线程等待固定时间:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; condition_variable cv; mutex m; bool done=false; void run() { auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间 auto end = start + chrono::seconds(3); unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m); while (!done) { if (cv.wait_until(ulk, end) == cv_status::timeout)//超时 { done = true; break; } } //this_thread::sleep_until(end); system("pause"); } void main1601() { thread th(run); cin.get(); } void main() { time_t t1, t2; auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间 t1 = time(&t1); double db = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { db += i; } auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间 t2 = time(&t2); cout << (end - start).count() << endl; //10^-9秒(ns) cout << difftime(t2, t1) << endl; cin.get(); }
8. 多线程实现生产者、消费者:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> #include <array> #include <vector> using namespace std; mutex m; condition_variable isfull, isempty;//处理两种情况 bool flag = true;//标志,消费完了就退出 vector<int> myint(10);//开辟10个元素 void produce(int num) //生产 { for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { unique_lock<mutex> lk(m); //锁定 while (myint.size()>=10) { isempty.wait(lk); //满了一直等待 } myint.push_back(i);//插入 cout << "生产" << i << endl; isfull.notify_all();//通知消费者 } this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(5));//休眠5秒 flag = false; } void consume() //消费 { while (flag) { unique_lock<mutex> lk(m); //锁定 while (myint.size()==0) { isfull.wait(lk);//等待 } if (flag) { cout << "消费" << myint[myint.size() - 1] << " " << this_thread::get_id() << endl; myint.pop_back();//剔除最后一个 isempty.notify_all();//通知生产者继续生产 } } } void main() { thread t1(consume); //消费者 thread t2(consume); thread t3(consume); //produce(100); thread s1(produce,15);//消费者 thread s2(produce,15); t1.join(); t2.join(); t3.join(); cin.get(); }
文章写来不易,转载请标注。。。欢迎关注!




