SpringBoot自动装配源码解析
序:众所周知spring-boot入门容易精通难,说到底spring-boot是对spring已有的各种技术的整合封装,因为封装了所以使用简单,也因为封装了所以越来越多的"拿来主义"者们不愿意去关注其具体实现!为了更好的使用spring-boot所以必要的源码探索是非常有必要的!今天开始探索的第一步:自动装配原理-----------------(此处默认各位看官熟悉spring的各种基础注解)
1.要谈自动装配我们需要从项目的初始注解入手:@SpringBootApplication
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @SpringBootConfiguration 6 @EnableAutoConfiguration 7 @ComponentScan( 8 excludeFilters = {@Filter( 9 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, 10 classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} 11 ), @Filter( 12 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, 13 classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} 14 )} 15 ) 16 public @interface SpringBootApplication { 17 ...38 }
2.这个下面实现自动装配的注解为:@EnableAutoConfiguration
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @AutoConfigurationPackage 6 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) 7 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { 8 String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; 9 10 Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; 11 12 String[] excludeName() default {}; 13 }
3.在这个注解下我们需要关注两个注解:@AutoConfigurationPackage、@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
a.我们先来看看@AutoConfigurationPackage
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @Import({Registrar.class}) 6 public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { 7 }
这个下面引入了:Registrar
1 static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports { 2 Registrar() { 3 } 4 5 public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { 6 AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)).getPackageName()); 7 } 8 9 public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { 10 return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)); 11 } 12 }
这是AutoConfigurationPackage的一个静态类,标蓝处的动作为为指定@ComponentScan的扫描路径,此处打断点启动项目我们可以发现这个为项目的顶级包名。(这个下面不做深入介绍,此内容不属于本文重点,有兴趣自行深入了解)如图:
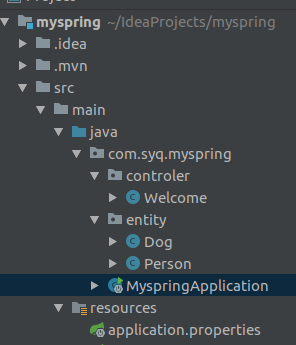
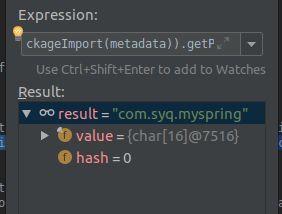
这儿确保了将项目目录下所有的bean注入到容器
b.接下来我们看看引入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector(个人觉得这个是自动配置的灵魂)
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { private static final AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry EMPTY_ENTRY = new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(); private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = new String[0]; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class); private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE = "spring.autoconfigure.exclude"; private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory; private Environment environment; private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
.... protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } else { AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata); List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); } } .... }
此处是去获取真正自动配置类的集合,我们需要关注标蓝的方法:
1 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { 2 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); 3 Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); 4 return configurations; 5 }
还看不出来什么,还需要往下走一层:
1 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { 2 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); 3 return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); 4 } 5 6 private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { 7 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); 8 if (result != null) { 9 return result; 10 } else { 11 try { 12 Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); 13 LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); 14 15 while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { 16 URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); 17 UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); 18 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); 19 Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); 20 21 while(var6.hasNext()) { 22 Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); 23 String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); 24 String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); 25 int var10 = var9.length; 26 27 for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) { 28 String factoryName = var9[var11]; 29 result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 cache.put(classLoader, result); 35 return result; 36 } catch (IOException var13) { 37 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13); 38 } 39 } 40 }
我们可以发现spring-boot会去META-INF/spring.factories找org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的value.这个的具体位置如图:
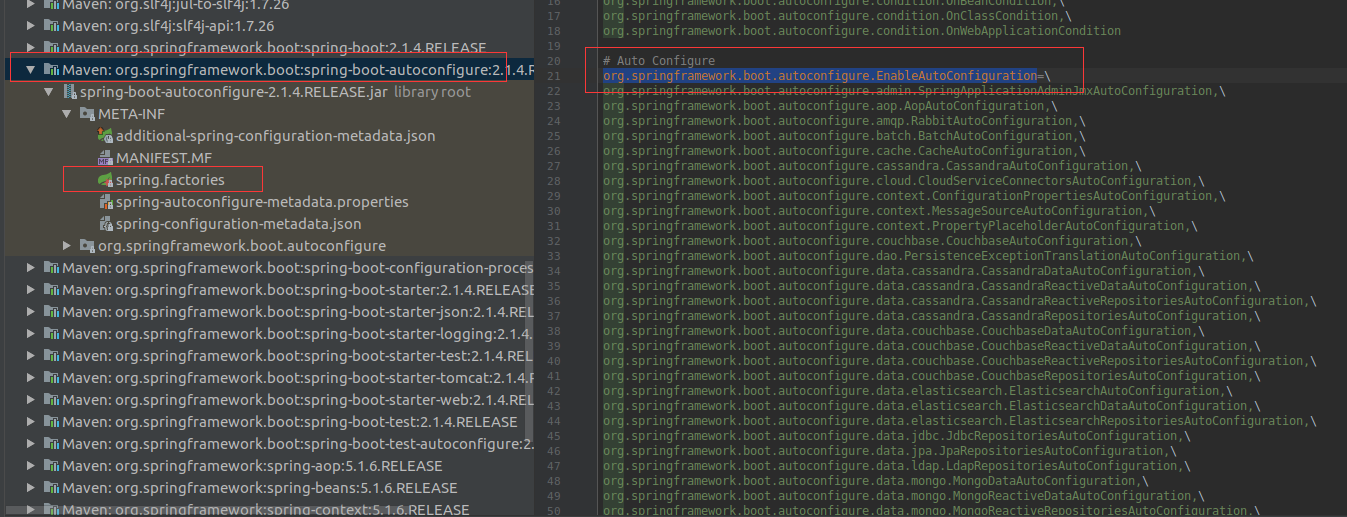
这个下面配置了所有自动配置,以其中一个为例(其余类似),分析其可配参数。(AopAutoConfiguration)
1 @Configuration 2 @ConditionalOnClass({EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class, Aspect.class, Advice.class, AnnotatedElement.class}) 3 @ConditionalOnProperty( 4 prefix = "spring.aop", 5 name = {"auto"}, 6 havingValue = "true", 7 matchIfMissing = true 8 ) 9 public class AopAutoConfiguration { 10 public AopAutoConfiguration() { 11 } 12 13 @Configuration 14 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy( 15 proxyTargetClass = true 16 ) 17 @ConditionalOnProperty( 18 prefix = "spring.aop", 19 name = {"proxy-target-class"}, 20 havingValue = "true", 21 matchIfMissing = true 22 ) 23 public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration { 24 public CglibAutoProxyConfiguration() { 25 } 26 } 27 28 @Configuration 29 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy( 30 proxyTargetClass = false 31 ) 32 @ConditionalOnProperty( 33 prefix = "spring.aop", 34 name = {"proxy-target-class"}, 35 havingValue = "false", 36 matchIfMissing = false 37 ) 38 public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration { 39 public JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration() { 40 } 41 } 42 }
我们可以在spring-configuration-metadata.json中找到其对应的配置如下:
{ "name": "spring.aop.proxy-target-class", "type": "java.lang.Boolean", "description": "Whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created (true), as opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies (false).", "defaultValue": true },
介绍到这里spring-boot的自动装配过程我们就基本看完了~

