驱动学习2:简单驱动创建
本文使用三种方法创建设备驱动,同时使用应用程序测试驱动是否安装成功。
其中,前两种方法都是手工创建设备节点,最后一种方法使用混杂设备的方法不需手工创建设备节点
在/dev/目录下创建设备文件hello,应用程序helltest.c为:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd; printf("enter driver test %s %s \r\n", argv[1], argv[2]); char *hello = "/dev/hello"; if((fd = open(hello, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY)) < 0) { printf("open %s failed\n", hello); } else { printf("%s fd is %d \r\n", hello, fd); ioctl(fd, atoi(argv[1]), atoi(argv[2])); } close(fd); return 1; }
第一种:手动创建驱动
加载之前首先通过 cat /proc/devices来查看字符主设备号230是否被占用
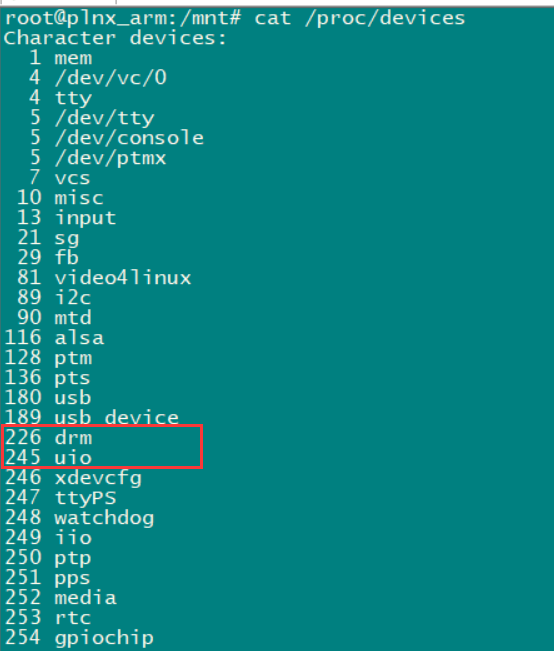
然后通过 insmod first_drv.ko来挂载, 通过 cat /proc/devices就能看到hello驱动模块是否已挂载好
root@plnx_arm:/mnt# cat /proc/devices | grep hello 230 hello
通过应用程序测试:
使用./hellotest来运行,发现如果open()打不开,会返回-1

是因为我们没有创建dev/xxx这个设备节点,然后我们来创建,使它等于刚刚挂载好的hello模块
//模块的主设备号为230
mknod -m 660 /dev/hello c 230 0
ls /dev/hello -l
crw-rw---- 1 root root 230, 0 Jun 4 11:05 /dev/hello
再次测试:
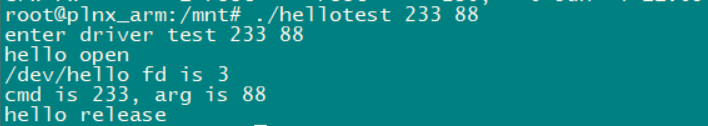
其中open()函数返回值为3,是因为描述符0,1,2都已经被控制台占用了,所以从3开始
第二种:自动分配设备号
除了使用第一种方法手工创建设备号外,也可以让系统自动为我们驱动设备自动分配设备号
仅仅修改代码如下:
int major; //定义一个全局变量,用来保存主设备号 //register_chrdev作用:在VFS虚拟文件系统中找到字符设备,然后通过主设备号找到内核数组里对应位置,最后将设备名字和fops结构体填进去 static int hello_init(void) { /*如果设置major为0,表示由内核动态分配主设备号,函数的返回值是主设备号*/ major =register_chrdev (0, DEVICE_NAME, &hello_fops); //230:主设备号,”hello”:设备名 printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been init!\n"); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { //释放设备号、注销设备 unregister_chrdev(major,DEVICE_NAME); printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been exit!\n"); //卸载驱动, 将major填入即可 }
如下图,通过动态分配得出它的主设备号是244,然后重新创建设备文件(主设备号为244),运行测试程序
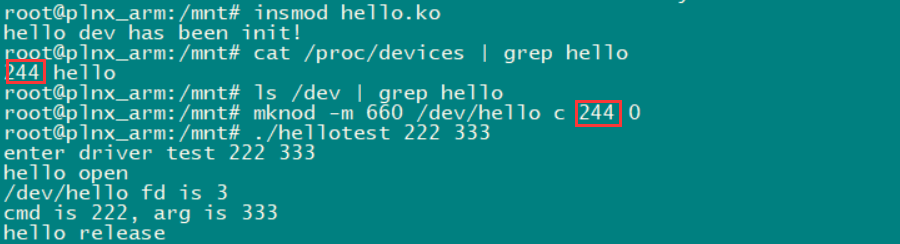
附完整代码:

//参考内核源码:gpio.c #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/miscdevice.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define DEVICE_NAME "hello" MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("pp"); /////////////////////////dev////////////////////////////////////// static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){ printk(KERN_EMERG "hello open\n"); return 0; } static int hello_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){ printk(KERN_EMERG "hello release\n"); return 0; } /*设备文件的读函数中,参数filp为文件结构体指针,buf为用户空间内存地址,count为要读取的字节数,ppos为写的位置相对于文件开头的偏移*/ //copy_to_user 完成用户空间缓冲区到内核空间的复制 static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t len,loff_t *ppos) { printk("hello_read\n"); return 0; } /*设备文件的写函数中,参数filp为文件结构体指针,buf为用户空间内存地址,count为要写入的字节数,ppos为写的位置相对于文件开头的偏移*/ //copy_from_user 完成内核空间到用户空间缓冲区的复制 static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos) { printk("hello_write\n"); return 0; } //ioctl函数 static long hello_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){ printk("cmd is %d, arg is %d\n", cmd, arg); return 0; } static struct file_operations hello_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = hello_open, .read = hello_read, .write = hello_write, .release = hello_release, .unlocked_ioctl = hello_ioctl, }; int major; //定义一个全局变量,用来保存主设备号 //register_chrdev作用:在VFS虚拟文件系统中找到字符设备,然后通过主设备号找到内核数组里对应位置,最后将设备名字和fops结构体填进去 static int hello_init(void) { /*如果设置major为0,表示由内核动态分配主设备号,函数的返回值是主设备号*/ major =register_chrdev (0, DEVICE_NAME, &hello_fops); //230:主设备号,”hello”:设备名 printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been init!\n"); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { //释放设备号、注销设备 unregister_chrdev(major,DEVICE_NAME); printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been exit!\n"); //卸载驱动, 将major填入即可 } module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
第三种:自动创建驱动(混杂设备)
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/miscdevice.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define DEVICE_NAME "hello" MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("pp"); /////////////////////////dev////////////////////////////////////// static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){ printk(KERN_EMERG "hello open\n"); return 0; } static int hello_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){ printk(KERN_EMERG "hello release\n"); return 0; } static long hello_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){ printk("cmd is %d, arg is %d\n", cmd, arg); return 0; } static struct file_operations hello_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = hello_open, .release = hello_release, .unlocked_ioctl = hello_ioctl, }; static struct miscdevice hello_dev = { .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, .name = DEVICE_NAME, .fops = &hello_fops, }; static int hello_init(void) { misc_register(&hello_dev); printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been init!\n"); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { misc_deregister(&hello_dev); printk(KERN_EMERG "hello dev has been exit!\n"); } module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
我们通过 ls /dev -l 可以看到混杂设备的主设备号为10,验证了书上所讲:
root@plnx_arm:/mnt# ls -l /dev | grep hello crw-rw---- 1 root root 10, 58 Jun 4 10:28 hello
通过应用程序测试:
root@plnx_arm:/mnt# ./hellotest 2 3 enter driver test 2 3 hello open /dev/hello fd is 3 hello release




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号