springMvc 支持hibernate validator
5月23日 西安 OSC 源创会开始报名啦,存储、虚拟机、Docker 等干货分享
一、基础框架 SpringMVC-4.0.3.RELEASE,使用的maven来管理jar依赖
二、依赖的jar,
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.Final</version> </dependency> |
上面是对Hibernate Validator 支持所需要的包,spring的jar省略。
三、spring配置文件 applicationContext.xml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator" /> <!-- 以下 validator ConversionService 在使用 mvc:annotation-driven 会 自动注册--> <bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean"> <property name="providerClass" value="org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator"/> <!-- 如果不加默认到 使用classpath下的 ValidationMessages.properties --> <property name="validationMessageSource" ref="messageSource"/> </bean> <!-- 国际化的消息资源文件(本系统中主要用于显示/错误消息定制) --> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basenames"> <list> <!-- 在web环境中一定要定位到classpath 否则默认到当前web应用下找 --> <value>classpath:messages</value> <value>classpath:org/hibernate/validator/ValidationMessages</value> </list> </property> <property name="useCodeAsDefaultMessage" value="false"/> <property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="cacheSeconds" value="60"/> </bean> |
经过上面三步,就可以让SpringMVC支持hibernate Validator,可以说整合已大功告成。现在看看具体使用
四、需要验证的实体类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class IssueMessageBO { @NotNull(message="{message.content.empty}") // 将验证消息写在classpath下message.properties @Size(min = 2, max = 140,message="{message.content.length}") private String content;//发布内容 private String qiniuImgInfo;//七牛图片信息 @NotNull(message="{message.schoolIds.empty}") private String schoolIds;//学校 private int publisherType;//发布者类型 private boolean hasTop;//是否置顶 private int topDay; //置顶的天数 ....} |
JSR-303只是一个规范,而Spring也没有对这一规范进行实现,那么当我们在SpringMVC中需要使用到JSR-303的时候就需要我们提供一个对JSR-303规范的实现,Hibernate Validator是实现了这一规范的,这里我将以它作为JSR-303的实现来讲解SpringMVC对JSR-303的支持。
JSR-303的校验是基于注解的,它内部已经定义好了一系列的限制注解,我们只需要把这些注解标记在需要验证的实体类的属性上或是其对应的get方法上.
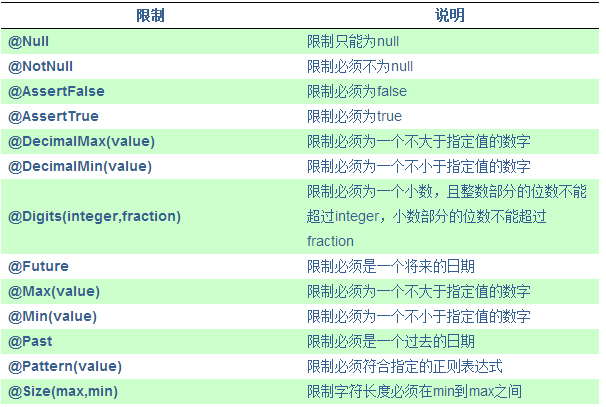
JSR-303原生支持的限制有如下几种:
除了JSR-303原生支持的限制类型之外我们还可以定义自己的限制类型。定义自己的限制类型首先我们得定义一个该种限制类型的注解,而且该注解需要使用@Constraint标注。
五、controller中的数据验证
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@RequestMapping(value = "/addMessage.action", method = RequestMethod.POST) public @ResponseBody String addMessage(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Valid IssueMessageBO issueMessageBO,BindingResult result)throws IOException{ Result retVal = ValidatorResultHandler.handle(result); if(retVal.getStatus() == Const.FAILURE){ response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(retVal)); }else{ response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(treeholeMessageService.issueMessage(issueMessageBO))); } return null; } |
在 applicationContext.xml 加入了
|
1
|
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator" /> |
Spring会自动检测classpath下的JSR-303提供者并自动启用对JSR-303的支持,把对应的校验错误信息放到Spring的Errors对象中
然后我使用了 validatorResultHandler 类来处理验证结果
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class ValidatorResultHandler { public static Result handle(BindingResult result){ Result retVal = new Result(); if(result.hasErrors()){ List<ObjectError> list = result.getAllErrors(); ObjectError oe = list.get(0); retVal.setMessage(oe.getDefaultMessage()); }else{ retVal.setStatus(Const.SUCCESS); } return retVal; }} |
这样处理就完成了。
六、有的时候,我们对一个实体类需要有多中验证方式,在不同的情况下使用不同验证方式,比如说对于一个实体类来的id来说,保存的时候是不需要的,对于更新时是必须的,可以如下配置:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
public class UserModel { private int id; private String username; private String content; @NotNull(message="{id.empty}",groups={First.class}) public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } @NotNull(message="{username.empty}",groups = {First.class, Second.class}) public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } @NotNull(message="{content.empty}",groups = {First.class, Second.class}) public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; }} |
通过 groups 对验证进行分组
在controler中的代码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
@RequestMapping(value = "/save.action", method = RequestMethod.POST)public @ResponseBody String save(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Validated({ Second.class}) UserModel userModel,BindingResult result) throws IOException{ response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); System.out.println("----"+userModel.getUsername()); if(result.hasErrors()){ List<ObjectError> list = result.getAllErrors(); for(ObjectError objectError:list){ System.out.println(objectError.getDefaultMessage()); } response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(list)); return null; } response.getWriter().write("rrrrrr"); return null;}@RequestMapping(value = "/update.action", method = RequestMethod.POST)public @ResponseBody String update(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Validated({First.class, Second.class}) UserModel user,BindingResult result) throws IOException{ response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); if(result.hasErrors()){ List<ObjectError> list = result.getAllErrors(); for(ObjectError objectError:list){ System.out.println(objectError); } response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(list)); return null; } response.getWriter().write("rrrrrr"); return null;} |