Spring异常处理@ExceptionHandler
最近学习Spring时,认识到Spring异常处理的强大。之前处理工程异常,代码中最常见的就是try-catch-finally,有时一个try,多个catch,覆盖了核心业务逻辑:
1 try{ 2 .......... 3 }catch(Exception1 e){ 4 .......... 5 }catch(Exception2 e){ 6 ........... 7 }catch(Exception3 e){ 8 ........... 9 }
Spring能够较好的处理这种问题,核心如下,文章主要关注前两个:
- @ExceptionHandler:统一处理某一类异常,从而能够减少代码重复率和复杂度
- @ControllerAdvice:异常集中处理,更好的使业务逻辑与异常处理剥离开;其是对Controller层进行拦截
- @ResponseStatus:可以将某种异常映射为HTTP状态码
@ExceptionHandler
源码如下:
1 @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 public @interface ExceptionHandler { 5 Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {}; 6 }
该注解作用对象为方法,并且在运行时有效,value()可以指定异常类。由该注解注释的方法可以具有灵活的输入参数(详细参见Spring API):
- 异常参数:包括一般的异常或特定的异常(即自定义异常),如果注解没有指定异常类,会默认进行映射。
- 请求或响应对象 (Servlet API or Portlet API): 你可以选择不同的类型,如ServletRequest/HttpServletRequest或PortleRequest/ActionRequest/RenderRequest
。 - Session对象(Servlet API or Portlet API): HttpSession或PortletSession。
- WebRequest或NativeWebRequest
- Locale
- InputStream/Reader
- OutputStream/Writer
Model
方法返回值可以为:
- ModelAndView对象
- Model对象
- Map对象
- View对象
- String对象
- 还有@ResponseBody、HttpEntity<?>或ResponseEntity<?>,以及void
@ControllerAdvice
源码如下:
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Component 5 public @interface ControllerAdvice { 6 @AliasFor("basePackages") 7 String[] value() default {}; 8 9 @AliasFor("value") 10 String[] basePackages() default {}; 11 12 Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; 13 14 Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {}; 15 16 Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {}; 17 }
该注解作用对象为TYPE,包括类、接口和枚举等,在运行时有效,并且可以通过Spring扫描为bean组件。其可以包含由@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder 和@ModelAttribute标注的方法,可以处理多个Controller类,这样所有控制器的异常可以在一个地方进行处理。
实例
异常类:
1 public class CustomGenericException extends RuntimeException{ 2 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 3 4 private String errCode; 5 private String errMsg; 6 7 public String getErrCode() { 8 return errCode; 9 } 10 11 public void setErrCode(String errCode) { 12 this.errCode = errCode; 13 } 14 15 public String getErrMsg() { 16 return errMsg; 17 } 18 19 public void setErrMsg(String errMsg) { 20 this.errMsg = errMsg; 21 } 22 23 public CustomGenericException(String errCode, String errMsg) { 24 this.errCode = errCode; 25 this.errMsg = errMsg; 26 } 27 }
控制器:
1 @Controller 2 @RequestMapping("/exception") 3 public class ExceptionController { 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/{type}", method = RequestMethod.GET) 6 public ModelAndView getPages(@PathVariable(value = "type") String type) throws Exception{ 7 if ("error".equals(type)) { 8 // 由handleCustomException处理 9 throw new CustomGenericException("E888", "This is custom message"); 10 } else if ("io-error".equals(type)) { 11 // 由handleAllException处理 12 throw new IOException(); 13 } else { 14 return new ModelAndView("index").addObject("msg", type); 15 } 16 } 17 }
异常处理类:
1 @ControllerAdvice 2 public class ExceptionsHandler { 3 4 @ExceptionHandler(CustomGenericException.class)//可以直接写@ExceptionHandler,不指明异常类,会自动映射 5 public ModelAndView customGenericExceptionHnadler(CustomGenericException exception){ //还可以声明接收其他任意参数 6 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("generic_error"); 7 modelAndView.addObject("errCode",exception.getErrCode()); 8 modelAndView.addObject("errMsg",exception.getErrMsg()); 9 return modelAndView; 10 } 11 12 @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)//可以直接写@EceptionHandler,IOExeption继承于Exception 13 public ModelAndView allExceptionHandler(Exception exception){ 14 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("generic_error"); 15 modelAndView.addObject("errMsg", "this is Exception.class"); 16 return modelAndView; 17 } 18 }
JSP页面:
正常页面index.jsp:
1 <%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%> 2 <html> 3 <body> 4 <h2>Spring MVC @ExceptionHandler Example</h2> 5 6 <c:if test="${not empty msg}"> 7 <h2>${msg}</h2> 8 </c:if> 9 10 </body> 11 </html>
异常处理页面generic_error.jsp
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%> <html> <body> <c:if test="${not empty errCode}"> <h1>${errCode} : System Errors</h1> </c:if> <c:if test="${empty errCode}"> <h1>System Errors</h1> </c:if> <c:if test="${not empty errMsg}"> <h2>${errMsg}</h2> </c:if> </body> </html>
测试运行如下:
正常情况:
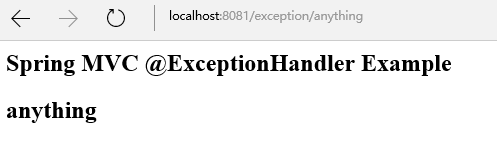
CustomGenericException异常情况:
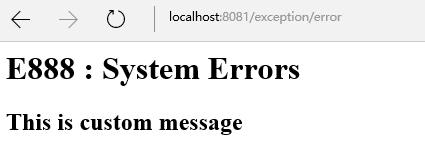
IOException异常情况:
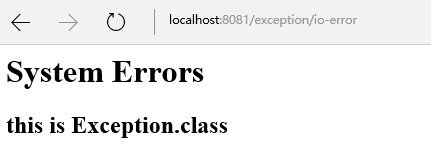
总结
- @ExceptionHandler和@ControllerAdvice能够集中异常,使异常处理与业务逻辑分离
- 本文重点理解两种注解方式的使用
参考:
- Spring API:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/javadoc-api/
- 《Spring in Action》
- Spring MVC @ExceptionHandler Example
这是水木竹水的博客




