Python的reshape的用法:reshape(1,-1)
目录
numpy中reshape函数的三种常见相关用法
- numpy.arange(n).reshape(a, b) 依次生成n个自然数,并且以a行b列的数组形式显示
-
np.arange(16).reshape(2,8) #生成16个自然数,以2行8列的形式显示
-
# Out:
-
# array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
-
# [ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]])
- mat (or array).reshape(c, -1) 必须是矩阵格式或者数组格式,才能使用 .reshape(c, -1) 函数, 表示将此矩阵或者数组重组,以 c行d列的形式表示
-
reshape(m,-1) #改变维度为m行、1列
-
reshape(-1,m) #改变维度为1行、m列
-1的作用就在此: 自动计算d:d=数组或者矩阵里面所有的元素个数/c, d必须是整数,不然报错)
(reshape(-1, m)即列数固定,行数需要计算)
-
arr=np.arange(16).reshape(2,8)
-
arr
-
'''
-
out:
-
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
-
[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]])
-
'''
-
-
arr.reshape(4,-1) #将arr变成4行的格式,列数自动计算的(c=4, d=16/4=4)
-
'''
-
out:
-
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
-
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
-
[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
-
[12, 13, 14, 15]])
-
'''
-
arr.reshape(8,-1) #将arr变成8行的格式,列数自动计算的(c=8, d=16/8=2)
-
'''
-
out:
-
array([[ 0, 1],
-
[ 2, 3],
-
[ 4, 5],
-
[ 6, 7],
-
[ 8, 9],
-
[10, 11],
-
[12, 13],
-
[14, 15]])
-
'''
-
arr.reshape(10,-1) #将arr变成10行的格式,列数自动计算的(c=10, d=16/10=1.6 != Int)
-
'''
-
out:
-
ValueError: cannot reshape array of size 16 into shape (10,newaxis)
-
'''
- numpy.arange(a,b,c) 从 数字a起, 步长为c, 到b结束,生成array
- numpy.arange(a,b,c).reshape(m,n) :将array的维度变为m 行 n列。
-
np.arange(1,12,2)#间隔2生成数组,范围在1到12之间
-
# Out: array([ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11])
-
-
np.arange(1,12,2).reshape(3,2)
-
'''
-
Out:
-
array([[ 1, 3],
-
[ 5, 7],
-
[ 9, 11]])
-
'''
reshape(1,-1)转化成1行:

reshape(2,-1)转换成两行:
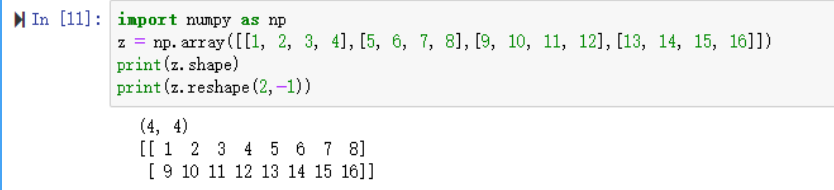
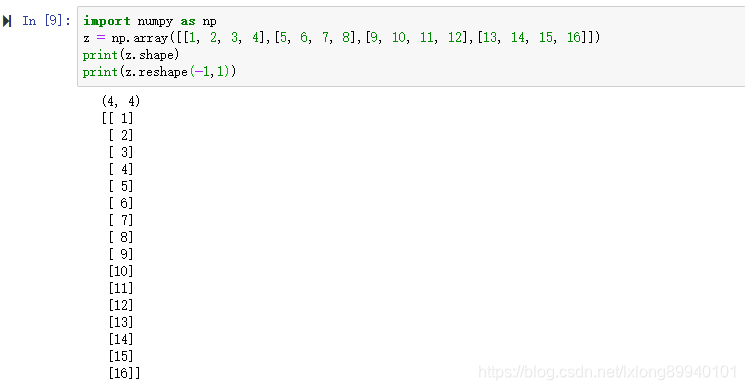
reshape(-1,1)转换成1列:
reshape(-1,2)转化成两列

本文参考了 Python的reshape(-1,1) 、Numpy中reshape函数、reshape(1,-1)的含义(浅显易懂,源码实例)
详内容可以参看reshape的官方文档:
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29831163/article/details/90112000


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号