多路复用epoll
epoll基本原理
- epoll 相对于 select 与 poll 有较大的不同,主要是针对前面两种多路复用 IO 接口的不足
- 与 select/poll 方案对比
- select 方案使用数组存储文件描述符,最大支持 1024
- select 每次调用都需要将描述符集合拷贝到内核中,非常消耗资源
- poll 方案解决文件描述符存储数量限制问题,但其他问题没有得到解决
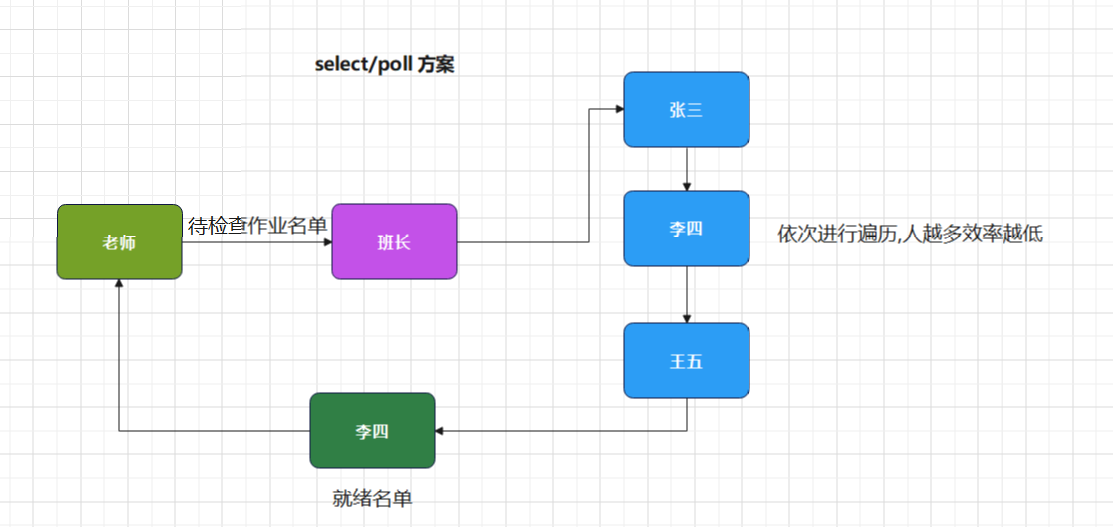
- select / poll 底层使用轮询的方式检测文件描述符是否就绪,文件描述符越多,则效率越低
- epoll 底层使用红黑树,没有文件描述符数量的限制,并且可以动态增加与删除节点,不用重复拷贝
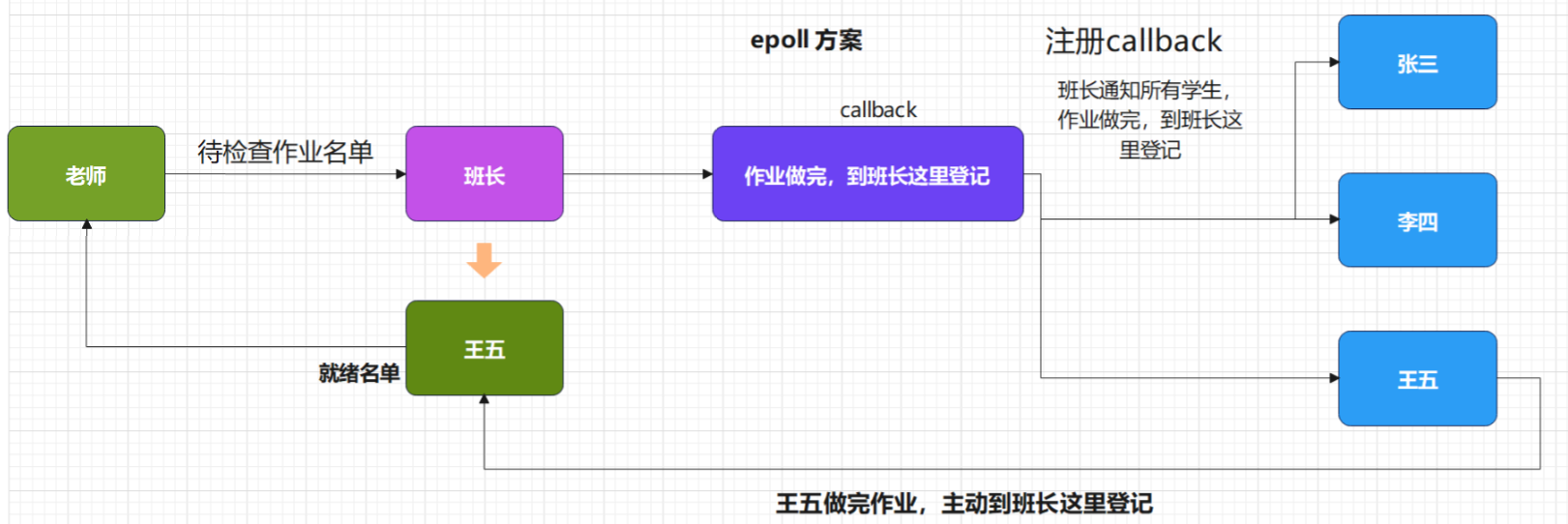
- epoll 底层使用callback 机制,没有采用遍历所有描述符的方式,效率较高
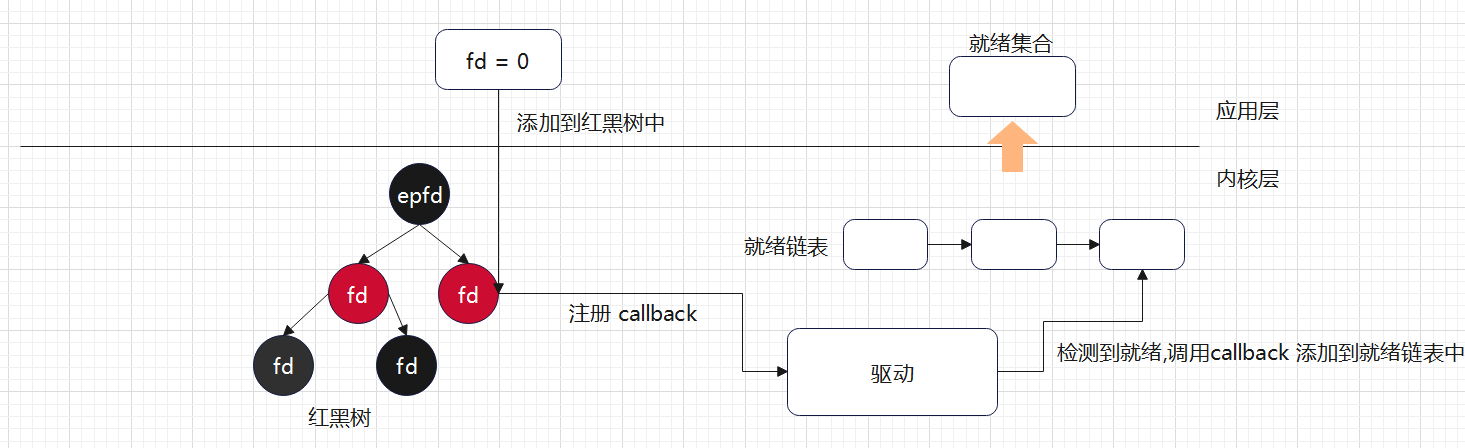
- 与 select/poll 方案对比
- 下面以老师检查学生作业为例,来看两种方案
- select/poll方案
- epoll方案
- select/poll方案
epoll创建
- epoll 创建需要调用 epoll_create 函数,用于创建 epoll 实例
- 函数头文件
- #include <sys/epoll.h>
- 函数原型
- int epoll_create(int size);
- 函数功能
- 创建一个 epoll 实例,分配相关的数据结构空间
- 函数参数
- size: 需要填一个大于0的数,从 Linux 2.6.8 开始,size 参数被忽略
- 函数返回值
- 成功 : 返回 epoll 文件描述符
- 失败: 返回-1,并设置 errno
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int main(void){
int fid = epoll_create(1);
if(fid == -1){
perror("[ERROR] epoll_create();");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("%d\n",fid);
return 0;
}
epoll控制函数
- epoll 控制函数主要用于文件描述符集合的管理,包括增加、修改、删除等操作,具体需要调用 epoll_ctl 函数
- 函数详细信息如下:
- 函数头文件
- #include <sys/epoll.h>
- 函数原型
- int epoll _ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll event *event);
- 函数参数
- epfd : epoll 实例
- op : epoll 操作命令字
- fd: 操作的文件描述符
- event : struct_epoll_event 结构体对象指针
- 函数头文件
- 相关参数具体说明
- op 为 epoll 操作命令字,具体定义如下
- EPOLL_CTL_ADD:在 epoll 实例中添加新的文件描述符(相当于添加到红黑树),并将事件链接到 fd
- EPOLL CTL MOD: 更改与目标文件描述符fd相关联的事件
- EPOLL_CTL_DEL : 从 epoll 实例中删除目标文件描述符 fd,事件参数被忽略
- 在系统中定义如下:
- op 为 epoll 操作命令字,具体定义如下
#define EPOLL CTL ADD 1 /* Add a file descriptor to the interface.*/
#define EPOLL CTL DEL 2 /* Remove a file descriptor from the interface.*/
#define EPOLL CTL MOD 3 /* Change file descriptor epoll event structure. */
- struct_epoll_event 结构体定义如下
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
}
- events : epoll 事件,事件具体定义如下:
- EPOLLIN : 读事件有效
- EPOLLOUT: 写事件有效
- EPOLLET: 将EPOLL设为边缘触发(Edge Triggered)模式
- epoll_data 是一个共用体,主要使用 fd 成员用于存储文件描述符
epoll等待函数
-
epoll 等待事件发生(关联的文件描述符就绪)这里调用 epoll_wait 函数
-
epoll wait 函数具体信息如下:
- 函数头文件
- #include <sys/epoll.h>
- 函数原型
- int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout );
- 函数功能
- 等待文件描述符关联的事件发生
- 函数参数
- epfd: epoll 实例对象
- events : 存储就绪集合的数组的地址
- maxevents: 就绪集合的最大值
- timeout: 超时时间
- 函数返回值
- 成功:返回就绪的文件描述符数量
- 超时返回,0
- 失败返回-1,并设置errno
- 成功:返回就绪的文件描述符数量
- 函数头文件
-
等待用户输入数据,如果没有则打印 timeout,否则获取用户输入,并输出
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#define MAXEVENTS 10
int main(void){
int fid = epoll_create(1);
if(fid == -1){
perror("[ERROR] epoll_create();");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("%d\n",fid);
int ret;
char buffer[64];
struct epoll_event ev;
struct epoll_event ret_ev[MAXEVENTS];
ev.data.fd = 0;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ret = epoll_ctl(fid,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,0,&ev);
if(ret == -1){
perror("[ERROR] epoll_ctl():");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for(;;){
ret = epoll_wait(fid,ret_ev,MAXEVENTS,1000);
if(ret == -1){
perror("[ERROR] epoll_wait():");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}else if(ret == 0){
printf("Timeout\n");
}else if(ret > 0){
fgets(buffer,sizeof(buffer),stdin);
printf("buffer : %s\n",buffer);
}
}
return 0;
}



