java中的线程池
知识点: 线程池的作用
线程池处理流程
通过Executors创建的四种线程池
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9beab78a3afe
一:线程池的作用
线程池的优点:
(1)降低资源消耗 :通过重复利用已经创建的线程,来降低线程的创建和销毁造成的资源消耗
(2)提高响应速度:当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程的创建就可以立即执行
(3)挺高线程的可管理性:线程时稀缺资源,如果不管理的话,无限地创建,不仅消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一分配调优,和监控线程
线程池的原理和作用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a166944f1e73
二:线程池处理任务的流程
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/519803f392dc
三:ThreadPoolExecutor
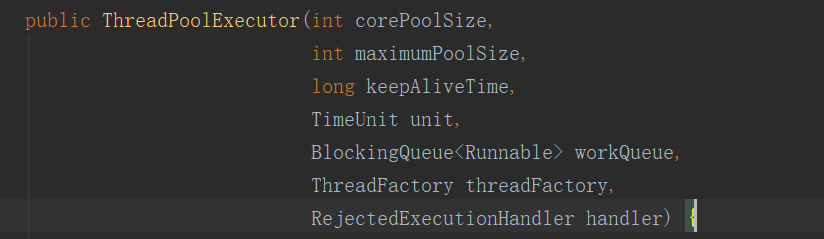
threadPoolExecutor构造函数参数含义:
corePoolSize:核心线程数量
maxmumPoolSize:最大线程数量
keepAliveTime:线程池维护线程允许的时间,当线程池中的线程数据大于核心线程的数量时,这时候如果没有新任务提交,非核心线程不会立即销毁,而是等待,直到等待时间超过keepAliveTime
TimeUnit:时间级别
workQueue:等待队列,当提交任务时,线程池中线程的数量大于等于corePoolSize数量时,把改任务封装成一个work对象放到等待队列中
threadFactory:是 ThreadFactory类,用于创建新线程
handler:是RejectedExecutionHandler类的一个变量,表示线程池的饱和策略,当阻塞队列满,并且没有空闲线程时,继续有新任务提交时,采取一种策略处理该任务。
三:通过Executors创建的四种线程池
Executors创建线程因为Interger.MAX_VALUE最大值,造成资源耗尽的情况参考: https://www.jianshu.com/p/4e34320bbfb1
(1) 缓存线程池: newCachedThreadPool
线程数量不定,线程最大数据Integer.MAX_VALUE,线程池中空闲线程有超时限制,超过60秒,闲置线程会被回收,适合执行大量耗时较少的任务。
Executors构造newCachedThreadPool
源代码:
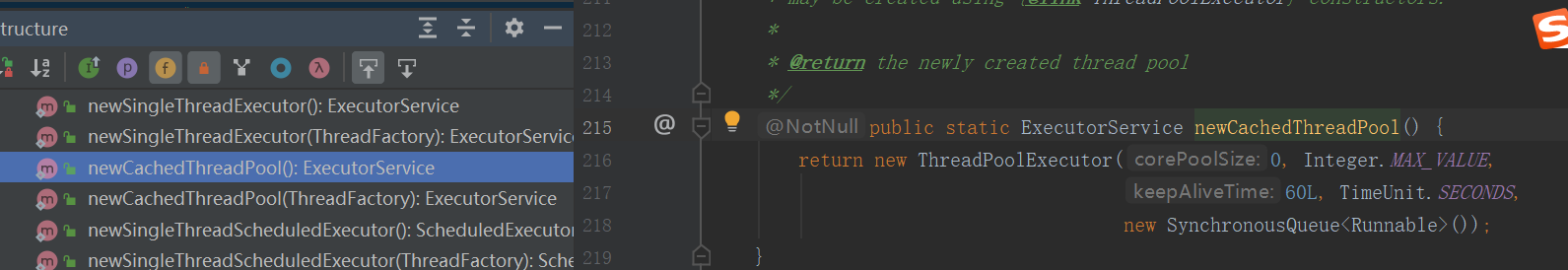
corePoolSize:0 : 线程池中没有核心线程,都是非核心线程
maxmumPoolSize:线程池容量Integer最大值
keeAliveTime:60秒:没有核心线程,设置空闲时间60秒,当非核心线程60秒没有被重用,将会被销毁,节约资源
workQueue:SynchronousQueue:一个不存储元素的阻塞队列
代码实例:
//可缓存线程池
public class NewCachedThreadPoolTest {
@Test
public void testNewCachedThreadPoolTest(){
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
final int index=i;
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("第"+index+"个线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
结果:

当一个任务完成以后,执行第二个任务时,不会创建新的线程,直接复用执行第一个任务的线程
(2) 固定数量线程池:newFixedThreadPool
Executors构造newFixedThreadPool
源代码:
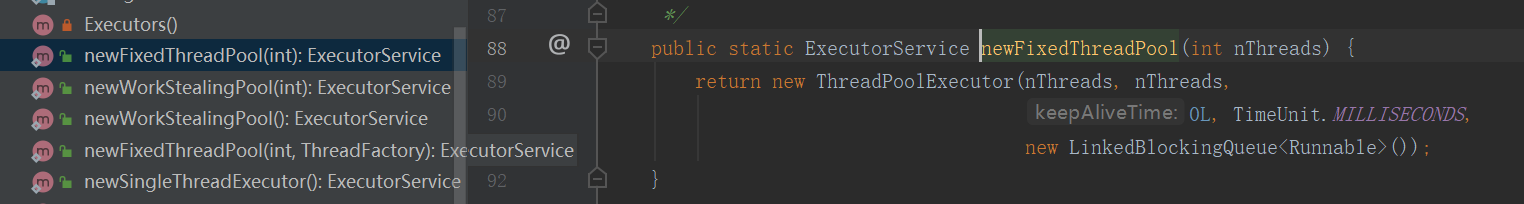
corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=初始化参数
workQueue:使用无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue链表阻塞队列
keepAliveTime=0:当corePoolSize满后,新的线程任务都会添加到LinkedBlockingQueue中,maximunPoolSize数,失去了意义,就没有必要设置空闲时间
代码实例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
final int index=i;
newFixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"第"+index+"个线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
结果:
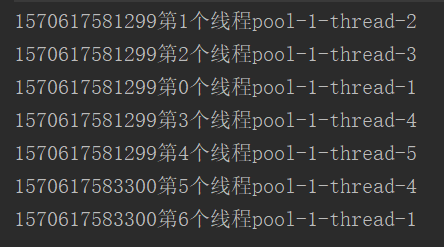
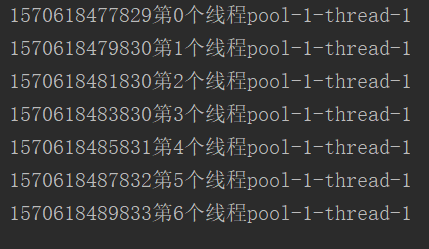
最大线程数为5,执行完5个线程后,等待两秒后,执行后面的两个线程
(3) 定时线程池: newScheduledThreadPool
Executors构造newScheduledExecutor
源代码:

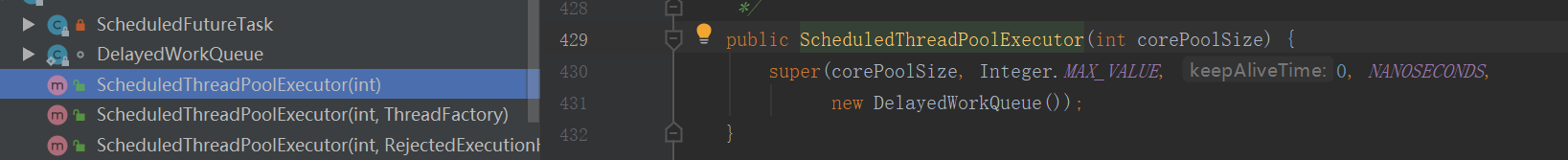
workQeueu:DelayedWorkQueue 延迟队列作为缓存队列
四种提交方式:
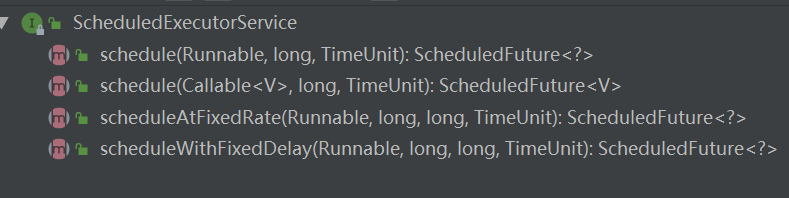
Schedule(Callable<V> callable,long delay,TimeUnit unit);
callable:提交Callable或者Runnable任务
delay:延迟时间
unit:时间级别
该方法表示:在给定的延时时间后执行一次,有返回结果
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long period,TimeTUnit unit)
command:提交Runnable任务
initialDelay:初始延迟时间
period:表示第一个任务开始到第二个任务开始,包含了任务的执行时间
unit:时间级别
该方法表示:在initialDelay时间后,开始周期的按period时间间隔执行任务
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long delay,TimeUnit unit);
command:提交Runnable任务
initialDelay:初始延迟时间
delay:表示延迟时间,第一个任务结束到第二个任务开始的时间间隔
unit:时间级别
代码实例:
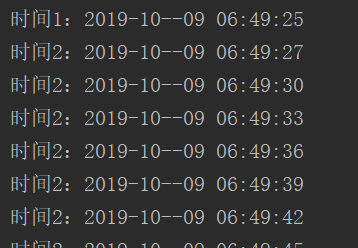
public static void main(String[] args) {
//核心线程2个
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService= Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
String pattern;
SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM--dd hh:mm:ss");
System.out.println("时间1:"+format.format(new Date()));
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("时间2:"+format.format(new Date()));
}
},2,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//开始延时2秒执行,之后每隔3秒执行一次任务
}
结果:
![]()
(4) 单例线程池 :newSingleThreadExecutor
适用于按顺序执行各个任务,不会出现多线程的场景
Executors构造newSingleThreadExecutor
源代码:
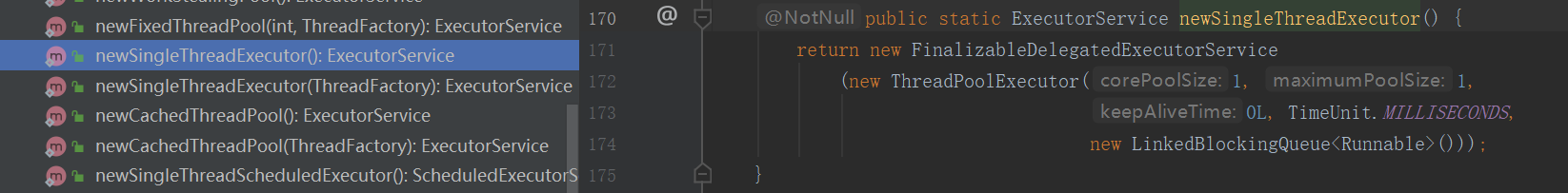
corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=1 单例线程池,线程池中重用一个线程
workQueue:使用无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue链表阻塞队列
keepAliveTime:0
代码实例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService newSingleThreadExcutor= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
final int n=i;
newSingleThreadExcutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+"第"+n+"个线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
结果:
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号