线性回归算法-4.多元线性回归算法
多元线性回归算法
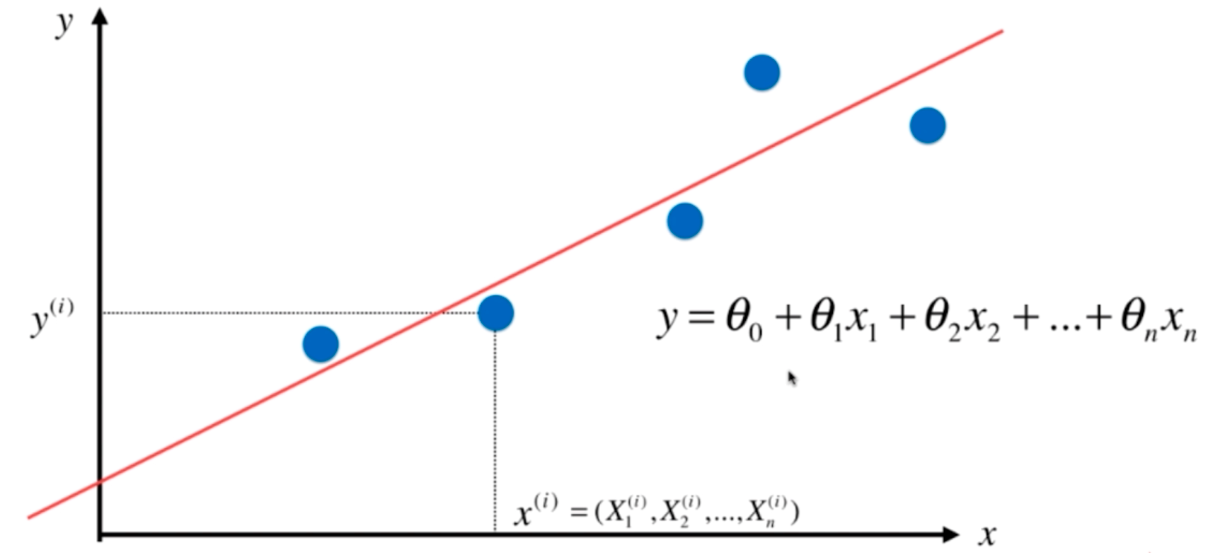
\(x^{(i)}\)由一个特征变为多个特征,此时拟合函数不是简单的\(y^{(i)} = ax^{(i)}+b\), 而是:
**$$\hat y^{(i)} = \theta _0x^{(i)}_0 + \theta _1x^{(i)}_1+ \theta _2x^{(i)}_2+...+\theta _{n}x{(i)}_n,x_0\equiv 1 $$ **
注:上标i为第i个样本,下标1-n为样本i的多个特征值
由上式可得:
\[\theta = (\theta_0,\theta_1,\theta_2,\theta _0,...,\theta _n)^T
\]
\[X^{(i)} = (X^{(i)}_0,X^{(i)}_1,X^{(i)}_2,...,X^{(i)}_n)
\]
\[\hat y^{(i)} = X^{(i)}\cdot \theta
\]
把上式推广到所有样本中:
\[ X_b = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & x^{(1)}_1 & x^{(1)}_2 & ... & x^{(1)}_n\\
1 & x^{(2)}_1 & x^{(2)}_2 & ... & x^{(2)}_n\\
... & & & & ...\\
1 & x^{(m)}_1 & x^{(m)}_2 & ... & x^{(m)}_n
\end{bmatrix}. \theta = \begin{bmatrix}
\theta_0\\
\theta_1\\
\theta_2\\
...\\
\theta_n\\
\end{bmatrix}\]
\[\hat y = X_b\cdot \theta
\]
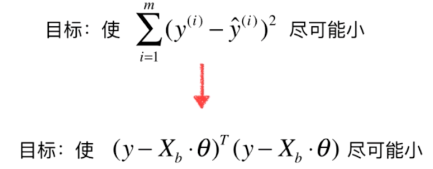
得到\(\theta\)的表达式(此推导过程较为复杂,感兴趣的话在网上找):
\[\theta = (X^{T}_bX_b)^{-1}X^{T}_by
\]
上式为多元线性回归的正规方程解(Normal Equation)
问题:时间复杂度较高,\(O(n^3)\)
多元线性回归的实现
封装LineRegression算法库
import numpy
from .metrics import r2_score
class LineRegression(object):
"""docstring fos LineRegression"""
def __init__(self):
self.coef_ = None
self.interception_ = None
self._theta = None
def fit_normal(self,X_train,y_train):
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0],\
"size of x_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
X_b = numpy.hstack([numpy.ones((len(X_train),1)),X_train])
self._theta = numpy.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:] #系数
self.interception_ = self._theta[0] #截距
return self
def predict(self,X_predict):
assert self.coef_ is not None and self.interception_ is not None,\
"must be fit before predict"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_),\
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal X_train"
X_b = numpy.hstack([numpy.ones((len(X_predict),1)),X_predict])
y_predict = X_b.dot(self._theta)
return y_predict
def score(self,x_test,y_test):
y_predict = self.predict(x_test)
return r2_score(y_test,y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LineRegression"
算法调用
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
# 加载波士顿房产数据集
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[y<50]
y = y[y<50]

from mylib.model_selection import train_test_split
from mylib.LineRegression import LineRegression
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,seed=666)
reg = LineRegression()
reg.fit_normal(X_train,y_train)
# reg.predict(X_test)
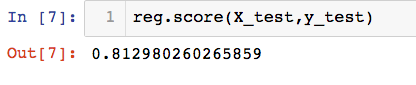
reg.score(X_test,y_test)
scikit-learn 中的LinearRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
line_reg = LinearRegression()
line_reg.fit(X,y)


