工厂模式
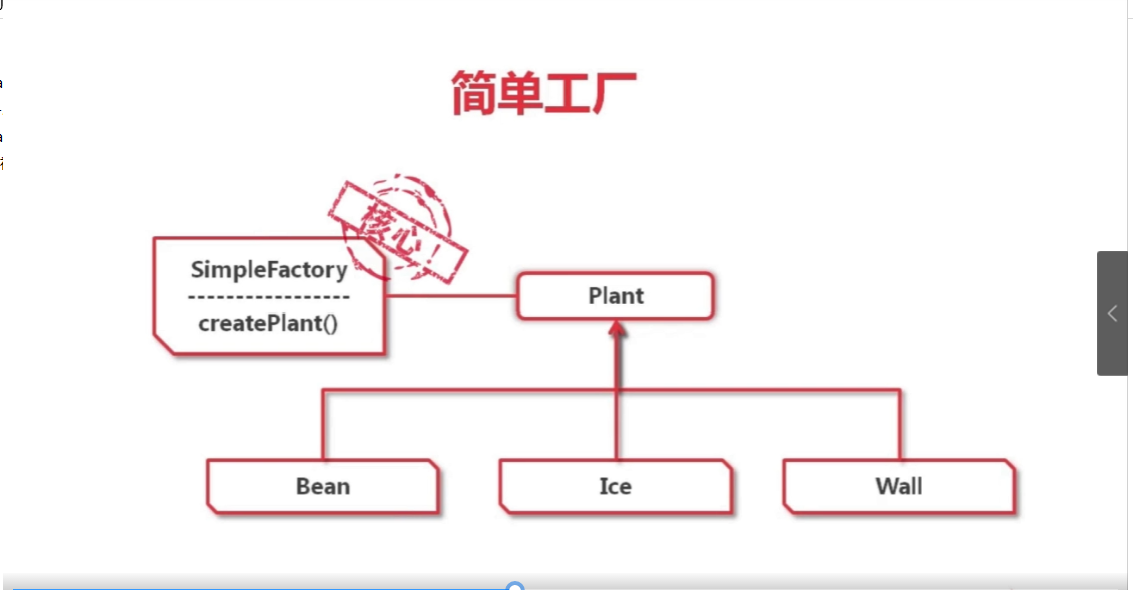
例子1:开发一个类似植物大战僵尸的游戏,有三种不同的植物:绿豆,蓝冰,坚果
分析:可以使用简单工厂模式:因为每个植物都需使用new()方法创建实例,所以我们将所以不同的植物实现一个名叫植物的接口,然后在在工厂类中判断所需创建的植物,若要创建指定的植物只需调用工厂类中的createPlant方法即可
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.component.Arms; import org.imooc.component.Hair; import org.imooc.component.Shell; import org.imooc.plant.*; public class SimpleFactory { /** * 创建植物对象的静态方法 */ public static Plant createPlant(String name) { Plant plant = null; if(PlantNameConstant.BEAN_NAME.equals(name)) { plant = new Bean(); } else if (PlantNameConstant.ICE_NAME.equals(name)) { plant = new Ice(); } else if (PlantNameConstant.WALL_NAME.equals(name)) { plant = new Wall(); } return plant; } public static Plant createPlantByClassName(String name) throws Exception { //使用反射可使代码更加简洁 return (Plant)Class.forName(name).newInstance(); } }
例子2:开发一个类似植物大战僵尸的游戏,有三种不同的植物:绿豆,蓝冰,坚果 ;每个植物有不同的装备和武器
分析:此时再使用上述的简单工厂模式会使原来代码变为以下样子:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.component.Arms; import org.imooc.component.Hair; import org.imooc.component.Shell; import org.imooc.plant.*; public class SimpleFactory { /** * 创建植物对象的静态方法 */ public static Plant createPlant(String name) { Plant plant = null; if(PlantNameConstant.BEAN_NAME.equals(name)) { Bean bean = new Bean(); Hair hair = new Hair(); hair.setColor("绿色"); bean.setHair(hair); Arms arms = new Arms(); arms.setBulletType("普通的豆子"); bean.setArms(arms); plant = bean; } else if (PlantNameConstant.ICE_NAME.equals(name)) { Ice ice = new Ice(); Hair hair = new Hair(); hair.setColor("蓝色"); ice.setHair(hair); Arms arms = new Arms(); arms.setBulletType("冰冻的豆子"); ice.setArms(arms); plant = ice; } else if (PlantNameConstant.WALL_NAME.equals(name)) { Wall wall = new Wall(); Shell shell = new Shell(); shell.setHardness(5); wall.setShell(shell); plant = wall; } else if ("new_Wall".equals(name)) { Wall wall = new Wall(); Shell shell = new Shell(); shell.setHardness(10); wall.setShell(shell); plant = wall; } return plant; } }
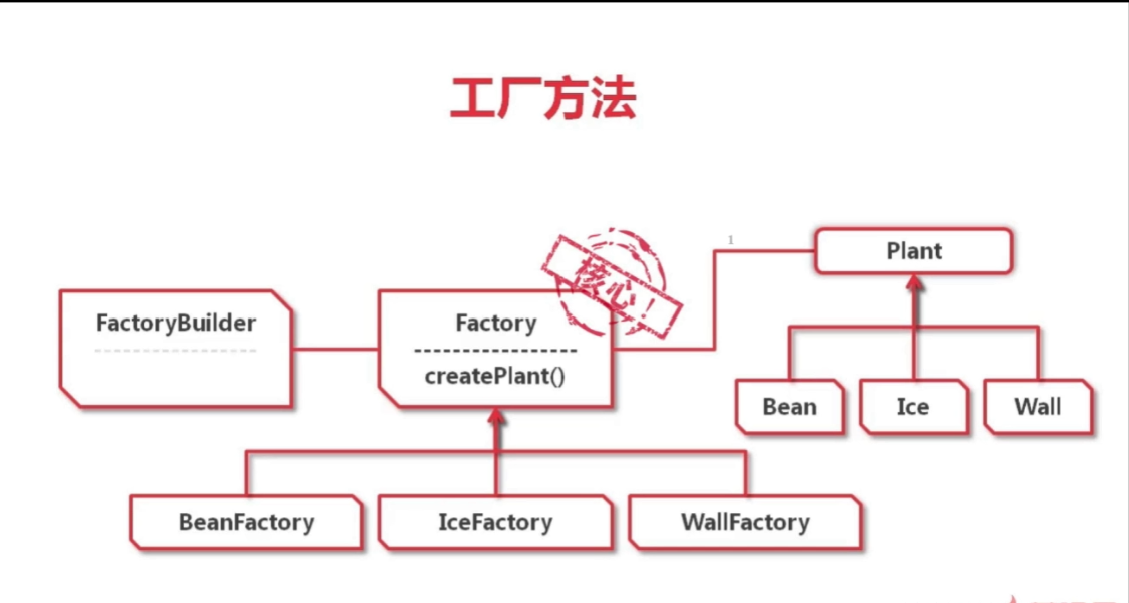
分析:此时代码变得过于复杂且复用性会变差,所以便可以把每个植物设为工厂类并且实现一个公共的工厂接口(都需要有create()方法),然后再由一个总工厂来创建这些植物工厂:
绿豆植物的工厂类:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.component.Arms; import org.imooc.component.Hair; import org.imooc.plant.Bean; import org.imooc.plant.Plant; public class BeanFactory implements Factory { public Plant createPlant() { Bean bean = new Bean(); Hair hair = new Hair(); hair.setColor("绿色"); bean.setHair(hair); Arms arms = new Arms(); arms.setBulletType("普通的豆子"); bean.setArms(arms); return bean; } }
蓝冰植物的工厂类:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.component.Arms; import org.imooc.component.Hair; import org.imooc.plant.Ice; import org.imooc.plant.Plant; public class IceFactory implements Factory { public Plant createPlant() { Ice ice = new Ice(); Hair hair = new Hair(); hair.setColor("蓝色"); ice.setHair(hair); Arms arms = new Arms(); arms.setBulletType("冰冻的豆子"); ice.setArms(arms); return ice; } }
坚果植物的工厂类:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.component.Shell; import org.imooc.plant.Plant; import org.imooc.plant.Wall; public class WallFactory implements Factory { public Plant createPlant() { Wall wall = new Wall(); Shell shell = new Shell(); shell.setHardness(5); wall.setShell(shell); return wall; } }
所以植物类需实现的接口:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.plant.Plant; public interface Factory { public Plant createPlant(); }
创建植物工厂的总工厂类:
package org.imooc.factory; import org.imooc.plant.PlantNameConstant; public class FactoryBuilder { public static Factory build(String name) { Factory factory = null; if(PlantNameConstant.BEAN_NAME.equals(name)) { factory = new BeanFactory(); } else if (PlantNameConstant.ICE_NAME.equals(name)) { factory = new IceFactory(); } else if (PlantNameConstant.WALL_NAME.equals(name)) { factory = new WallFactory(); } return factory; } public static Factory buildByClassName(String name) throws Exception { return (Factory)Class.forName(name).newInstance(); } }
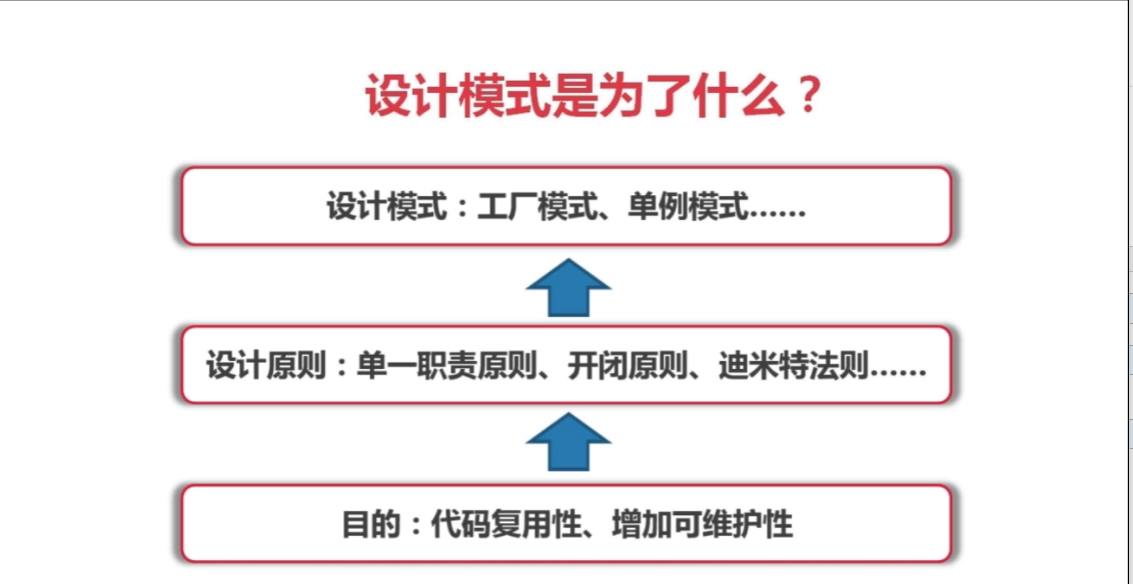
总结:
例子1:开发一个类似植物大战僵尸的游戏,有三种不同的植物:绿豆,蓝冰,坚果


