Java-字节流读写文件
字节流通常以stream结尾,例如InputStream和OutputStream。记几个语法。
1.误区
以前总是以为Input就是输入,写入文件; Output就是输出,读出文件。这是错误的理解,以至于看不懂很多例子。
这里的入和出是以内存为角度的,程序运行在内存中,创建的数组就可以看作内存。
把文件里的东西弄入数组里就是Input;把数组里的东西弄出来,进文件就是Output。
所以Input是写入内存,而不是写入文件;Output是读出内存,而不是读出文件。
2.读取文件
把文件内容 写入 内存数组里,用的是Input。
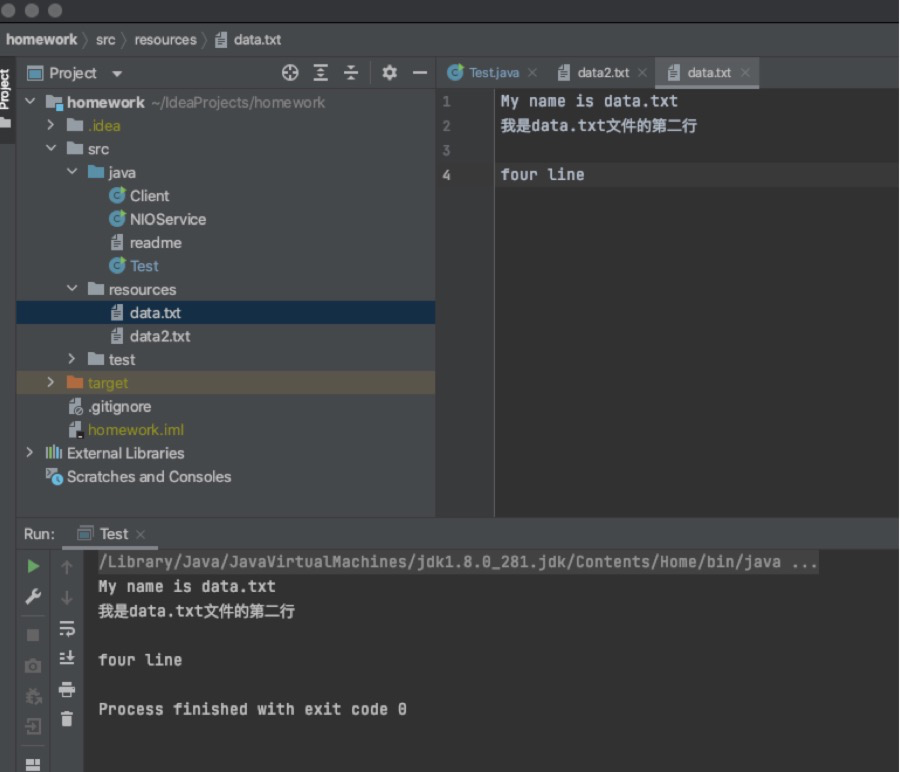
//读取文件 public static void test1() throws IOException{ //指定文件路径 File file = new File("src/resources/data.txt"); //为读取文件提供流通道 InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //创建字节数组存储数据 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; //读取指定文件中的内容要bytes数组 inputStream.read(bytes);//把文件里的数据 读入 内存数组bytes //关闭输出流 inputStream.close(); //输出bytes数组内容 System.out.println(new String(bytes)); }
效果是最后一行输出data.txt中的数据。
3.写入文件
把内存数组里的内容 读出内存,放入文件。
//写入文件 public static void test2() throws IOException { //指定文件路径 File file = new File("src/resources/data2.txt"); //为写入文件提供流通道 FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); //创建字节数组 byte[] bytes = "hello world".getBytes(); //将内存的字节数组内容 弄进 文件中 outputStream.write(bytes,0,bytes.length-1);//末尾长度-1后文件只获取了"hello word" //关闭流 outputStream.close(); }
4.Channel管道
流只能单向传输,要么输入要么输出。
管道可以双向,但必须经过缓冲区buffer。
这个多用于socket编程,现在记录一下读出文件,写入内存的用法。
//Channel一个用法 public static void test3() throws IOException{ //指定文件路径 File file2 = new File("src/resources/data2.txt"); FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file2); //管道 连着 流 FileChannel channel2 = outputStream.getChannel(); //通过Channel的读写必须经过Buffer缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //把string的内容写入data2文件 String string = "守林鸟 博客园"; buffer2.put(string.getBytes()); buffer2.flip();//此处必须要调用buffer的flip方法,具体原因自行百度 //再将内容放进管道,写入文件 channel2.write(buffer2); //关闭 管道和流 channel2.close(); outputStream.close(); /** 文件 --- 流 --- 缓冲区 --- 管道 --- 文件 */ }
5.BufferedReader用法
BufferedReader用法,键盘输入,效果和Scanner一样
//BufferedReader用法,键盘输入,效果和Scanner一样 public static void test4() throws IOException { String string; BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); string = buf.readLine(); System.out.println(string); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); string = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println(string); }