AC自动机入门和几道例题
一直被AC自动机这个名字唬住,以为很难,自动AC?其实不是。
AC自动机=字典树+KMP。字典树是必须要懂的;KMP主要了解一下回溯思想,问题不大。
- KMP解决的是一个母串和一个模式串的匹配问题。
- 字典树解决的是许多字符串的前缀和问题。
- AC自动机解决的是一个母串和许多模式串的匹配问题,把所有的模式串搞成一棵字典树,再用母串去字典树上跑。
引入失配指针的概念,对于当前遍历到的母串某个字符,在字典树中找不下去了,不从根开始,像KMP一样回溯到某个位置,而失配指针 指向的就是应该回溯的位置。
1.失配指针如何构造?BFS
根root当作第0层,root的fail指针指向null;往下数,特殊的第1层的fail指针都指向root层;对于第2层往下 的节点,假设当前遍历到的节点为now,now的儿子的失配指针 指向 now的失配指针指向的上层节点(假设为p)的儿子。例如下图
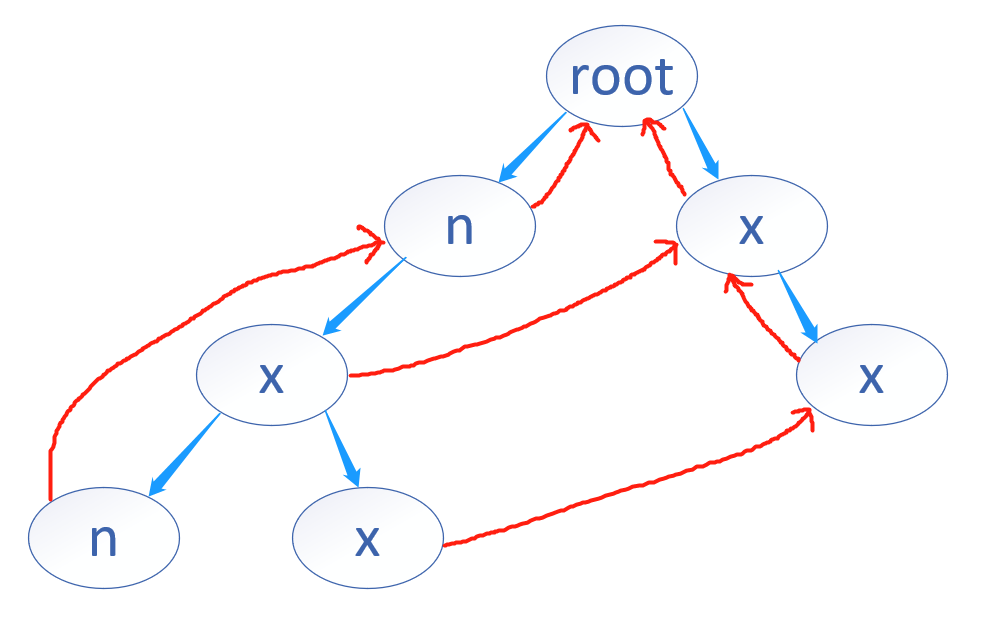
root是第0层
例1,当前遍历到的now为第1层的'n',now有个儿子为'x',now的失配指针指向root,root还有个右儿子叫'x',则now的儿子'x'(第2层左边的x)的失配指针 指向 root的右儿子'x'。
例2,当前遍历到的now为第2层左边的'x',now的右儿子为'x'(第3层右边的'x'),now的失配指针指向的上层节点(第1层右边的'x')假设为p,p刚好有一个儿子'x'(第2层右边的'x')与now的儿子'x'相同,则now的右儿子'x'的失配指针 指向p的儿子'x'。
例3,当前遍历到的now为第2层左边的'x',now的左儿子为'n'(第3层左边的'n'),now的失配指针指向的上层节点(第1层右边的'x')假设为p,p没有儿子与now的儿子'n'相同,就再找p失配指针指向的root,root的左儿子'n',则now左儿子'n'的失配指针指向root的左儿子'n'。
如果没有符合条件的节点,则指向root,表示失配的时候重新开始。
这是一种公共前缀的思想,确定回溯到的位置,敲一两次就能够理解了。
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3796
在字典树上标记模式串,用母串跑字典树遇到终止节点就计数,找出最大,再用num判断最大值输出结果。

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<math.h> #include<string> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<ctime> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f const double pi=3.1415926; using namespace std; struct node { int id; int flag;///判断是否单词在这里就完了,作为前缀 node *next[27]; node *fail;///失配指针 node() ///构造函数,创建的时候执行清0。不写也没关系,全局变量定义都是默认0 { id=0; flag=0; fail=NULL; for(int i=0;i<26;i++) next[i]=NULL; } }; int n; char a[155][77]; int num[155]; char s[1000005]; node* root; int maxx=-inf; void insert(char * s,int id) { node* p=root; int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=s[i]-'a'; if((p->next[x])==NULL)///当前遍历到的字母还没有开创节点 p->next[x]=new node();///新开一个节点 p=p->next[x]; } p->flag++;///标记有单词在这里结束 p->id=id; } void get_fail() { queue<node*>que; que.push(root); while(!que.empty()) { node* now=que.front();///now是当前处理的节点,对now的儿子的fail进行处理 que.pop(); for(int i=0;i<26;i++) { if(now->next[i]!=NULL)///寻找非空子节点 { que.push(now->next[i]); if(now==root)///特判根节点 now->next[i]->fail=root;///根节点的儿子即第一层的节点 的失配指针 指向根节点 else { node* p=now->fail;///p此时是now的失配指针,往上 指向 上层节点 while(p!=NULL) { if(p->next[i]!=NULL)///如果 上层节点p 有一个 和now的i儿子相同 的儿子 { now->next[i]->fail=p->next[i];///就把(now的儿子的 失配指针) 指向 (now的失配指针指向的上层节点p的儿子) break; } p=p->fail;///没有就不断回溯,最后会回溯到根节点root,再回溯到root的失配指针NULL } if(p==NULL)///此时已经回溯到NULL,走投无路了 now->next[i]->fail=root; } } } } } void query(char *s) { node* p=root;///p为模式串指针 int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=s[i]-'a'; while(p->next[x]==NULL && p!=root)///匹配不到就找失配指针,如果是根节点就不允许找失配指针 p=p->fail; p=p->next[x]; if(p==NULL)///p如果是空的,即匹配不到,直接重新来过,也不满足接下来的while p=root; node* temp=p; while(temp!=root) { if( temp->flag >0 ) { num[ temp->id ]++;///计数 maxx=max(maxx,num[temp->id]); } temp=temp->fail; } } } int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n) && n) { root=new node(); maxx=-inf; memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); memset(num,0,sizeof(num)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { getchar(); scanf("%s",a[i]); insert(a[i],i); } get_fail(); getchar(); scanf("%s",s); query(s); printf("%d\n",maxx); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(num[i]==maxx) printf("%s\n",a[i]); } } return 0; }
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2222
找出母串包含多少种子串,因为是找种类,所以找到末尾节点标记,下一次不再累计。

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<math.h> #include<string> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<ctime> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f const double pi=3.1415926; using namespace std; struct node { int flag;///判断是否单词在这里就完了,作为前缀 node *next[27]; node *fail;///失配指针 node() ///构造函数,创建的时候执行清0。不写也没关系,全局变量定义都是默认0 { flag=0; fail=NULL; for(int i=0;i<26;i++) next[i]=NULL; } }; node* root;///根节点始终为空 int n; char s[1000005]; void insert(char* s) { node* p=root; int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=s[i]-'a'; if((p->next[x])==NULL)///当前遍历到的字母还没有开创节点 p->next[x]=new node();///新开一个节点 p=p->next[x]; } p->flag++;///标记有单词在这里结束 } void get_fail() { queue<node*>que; que.push(root); while(!que.empty()) { node* now=que.front();///now是当前处理的节点,对now的儿子的fail进行处理 que.pop(); for(int i=0;i<26;i++) { if(now->next[i]!=NULL)///寻找非空子节点 { que.push(now->next[i]); if(now==root)///特判根节点 now->next[i]->fail=root;///根节点的儿子即第一层的节点 的失配指针 指向根节点 else { node* p=now->fail;///p此时是now的失配指针,往上 指向 上层节点 while(p!=NULL) { if(p->next[i]!=NULL)///如果 上层节点p 有一个 和now的i儿子相同 的儿子 { now->next[i]->fail=p->next[i];///就把(now的儿子的 失配指针) 指向 (now的失配指针指向的上层节点p的儿子) break; } p=p->fail;///没有就不断回溯,最后会回溯到根节点root,再回溯到root的失配指针NULL } if(p==NULL)///此时已经回溯到NULL,走投无路了 now->next[i]->fail=root; } } } } } int query(char *s) { int res=0; node* p=root;///p为模式串指针 int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=s[i]-'a'; while(p->next[x]==NULL && p!=root)///匹配不到就找失配指针,如果是根节点就不允许找失配指针 p=p->fail; p=p->next[x]; if(p==NULL)///p如果是空的,即匹配不到,直接重新来过,也不满足接下来的while p=root; node* temp=p; while(temp!=root) { if(temp->flag >=0 ) { res=res+temp->flag;///本题是算种类,不是个数,某个模式串已经累计过了就不再匹配 temp->flag=-1; } else break;///哪怕break了,p依旧在字典树上走下去 temp=temp->fail; } } return res; } int main()///hdu2222 { int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { root=new node();///每个测试样例对root清空 scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { getchar(); scanf("%s",s); insert(s); } get_fail(); getchar(); scanf("%s",s); printf("%d\n",query(s)); } return 0; }
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2896
RE后发现此题字符不仅仅是大小写字母,next数组改用128大小,然后MTE,每次用new node()新开节点改成数组节点多次利用,再次MTE,把next数组改成95,仅用可见字符,再次MTE。简直吐血,原本用G++提交改成C++提交直接AC,wtm...!
可见字符:算上空格, 从32到126共95个可见字符;不算上空格则为94个。

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<math.h> #include<string> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<ctime> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f const double pi=3.1415926; using namespace std; struct node { int id; int flag;///判断是否单词在这里就完了,作为前缀 node *next[95];///95个可见字符 node *fail;///失配指针 }; node b[100005]; node* root; int n,m; int num; int cnt; char word[205]; char s[10005]; void init(int j)///清空节点 { b[j].id=b[j].flag=0; b[j].fail=NULL; for(int i=0;i<95;i++) b[j].next[i]=NULL; } void insert(char * s,int id) { node* p=root; int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=(int)s[i]-32; if((p->next[x])==NULL)///当前遍历到的字母还没有开创节点 { init(cnt);///清空原来的节点,多次利用,不然一次次new会爆内存 p->next[x]=b+cnt;///指针指向数组 cnt++; } p=p->next[x]; } p->flag++;///标记有单词在这里结束 p->id=id; } void get_fail() { queue<node*>que; que.push(root); while(!que.empty()) { node* now=que.front();///now是当前处理的节点,对now的儿子的fail进行处理 que.pop(); for(int i=0;i<95;i++) { if(now->next[i]!=NULL)///寻找非空子节点 { que.push(now->next[i]); if(now==root)///特判根节点 now->next[i]->fail=root;///根节点的儿子即第一层的节点 的失配指针 指向根节点 else { node* p=now->fail;///p此时是now的失配指针,往上 指向 上层节点 while(p!=NULL) { if(p->next[i]!=NULL)///如果 上层节点p 有一个 和now的i儿子相同 的儿子 { now->next[i]->fail=p->next[i];///就把(now的儿子的 失配指针) 指向 (now的失配指针指向的上层节点p的儿子) break; } p=p->fail;///没有就不断回溯,最后会回溯到根节点root,再回溯到root的失配指针NULL } if(p==NULL)///此时已经回溯到NULL,走投无路了 now->next[i]->fail=root; } } } } } void query(char *s,int cnt) { set<int>se; node* p=root;///p为模式串指针 int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int x=(int)s[i]-32; while(p->next[x]==NULL && p!=root)///匹配不到就找失配指针,如果是根节点就不允许找失配指针 p=p->fail; p=p->next[x]; if(p==NULL)///p如果是空的,即匹配不到,直接重新来过,也不满足接下来的while p=root; node* temp=p; while(temp!=root) { if( temp->flag >0 ) se.insert(temp->id); temp=temp->fail; } } if(!se.empty())///输出答案 { num++; printf("web %d:",cnt); for(set<int>::iterator it=se.begin();it!=se.end();it++) printf(" %d",*it); printf("\n"); } } int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { root=new node(); num=0; cnt=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { getchar(); scanf("%s",word); insert(word,i); } get_fail(); scanf("%d",&m); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { getchar(); scanf("%s",s); query(s,i); } printf("total: %d\n",num); } return 0; }
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5231
尝试用数组模拟指针写AC自动机,数组第0行相当于根节点。将模式串构造出AC自动机,再用母串跑,标记母串走过的路径,接下来再用模式串去匹配,看看能匹配母串走过的路径的前缀是多少。

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<math.h> #include<string> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<ctime> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f const double pi=3.1415926; using namespace std; int maxx=10000005; int n,m; char s[10000005]; char a[100005][111]; int ans[100005]; map<char,int>mp; int ac[10000005][5];///用数组模拟字典树和AC自动机 int fail[10000005]; int flag[10000005];///标记主串走过 int cnt; void insert(char *s,int k) { int p=0; int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int c=mp[s[i]]; if( ac[p][c]==0 )///开创节点,即新开一行数组分配 ac[p][c]=++cnt; p=ac[p][c];///跳到这一行 } } void get_fail()///构造失配指针 { queue<int>que; for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) if(ac[0][i]!=0) que.push(ac[0][i]); while(!que.empty()) { int now=que.front(); que.pop(); for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) { if(ac[now][i]!=0) { fail[ ac[now][i] ]=ac[ fail[now] ][i] ; ///now是当前行数,总会有一个下标不为空,表示一个字母是后续。这个后续的失配指针 是 当前行数的失配指针的儿子 ///最开始的失配指针总是指向0,相当于是根节点。 que.push(ac[now][i]); } else ac[now][i]=ac[ fail[now] ][i];///如果匹配不到就 指向失配指针节点的儿子。如果失配指针节点是0,那就是重新开始 } } } void query(char* s) { int p=0;///主串在ac自动机上跑的指针 int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int c=mp[s[i]]; p=ac[p][c]; int j=p;///临时指针 while(j!=0)///如果到了当前节点还有后续,就将当前节点的失配指针节点都标记 { if(flag[j]) break; flag[j]=1;///标记这个点走过 j=fail[j]; } } } int find_ans(char* s) { int p=0,res=0; int len=strlen(s); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { int c=mp[s[i]]; p=ac[p][c]; if(flag[p]) res=i+1; } return res; } int main()///P5231 { mp['E']=1; mp['S']=2; mp['W']=3; mp['N']=4; while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF) { cnt=0; memset(ac,0,sizeof(ac)); memset(fail,0,sizeof(fail)); memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag)); memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); getchar(); scanf("%s",s); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { getchar(); scanf("%s",a[i]); insert(a[i],i); } get_fail(); query(s); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) printf("%d\n",find_ans(a[i])); } return 0; }




