第27课 - 二阶构造模式
第27课 - 二阶构造模式
1. 关于构造函数
(1)类的构造函数用于对象的初始化
(2)构造函数与类同名并且没有返回值
(3)构造函数在对象定义时自动被调用
2. 关于构造函数的一些疑问?
(1)如何判断构造函数的执行结果? ==> 在类中添加一个标志(bool),放在构造函数的末尾(判断函数体是否全部执行),通过功能成员函数判断标志状态。这种方式能够完成功能,但是设计不够优美,需要手工进行判断,应该有更好的方法!!!
(2)在构造函数中执行 return 语句会发生什么? ==> 构造函数虽然没有返回值,但是遇到 return 会结束构造函数
(3)构造函数执行结束是否意味着对象构造成功? ==> 构造函数执行结束,对象不一定构造成功

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 class Test 4 { 5 int mi; 6 int mj; 7 bool mStatus; // 判断构造函数是否执行成功 bool型变量 8 public: 9 Test(int i, int j) : mStatus(false) 10 { 11 mi = i; 12 13 return; 14 15 mj = j; 16 17 mStatus = true; 18 } 19 20 int getI() 21 { 22 return mi; 23 } 24 25 int getJ() 26 { 27 return mj; 28 } 29 30 int status() // 功能函数,获取mStatus的值 31 { 32 return mStatus; 33 } 34 }; 35 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 Test t1(1, 2); 40 41 if( t1.status() ) 42 { 43 printf("t1.mi = %d\n", t1.getI()); 44 printf("t1.mj = %d\n", t1.getJ()); 45 } 46 47 return 0; 48 }
3. 构造函数的真相
(1)构造函数只提供自动初始化成员变量的机会,但不能保证初始化逻辑一定成功
(2)执行 return 语句后构造函数立即结束
❉ 构造函数能决定的只是对象的初识状态,而不能决定对象是否诞生!!
4. 半成品对象的概念
(1)初始化操作不能按照预期完成而得到的对象(构造函数没有正确执行)
(2)半成品对象是合法的C++ 对象,也是 Bug 的重要来源
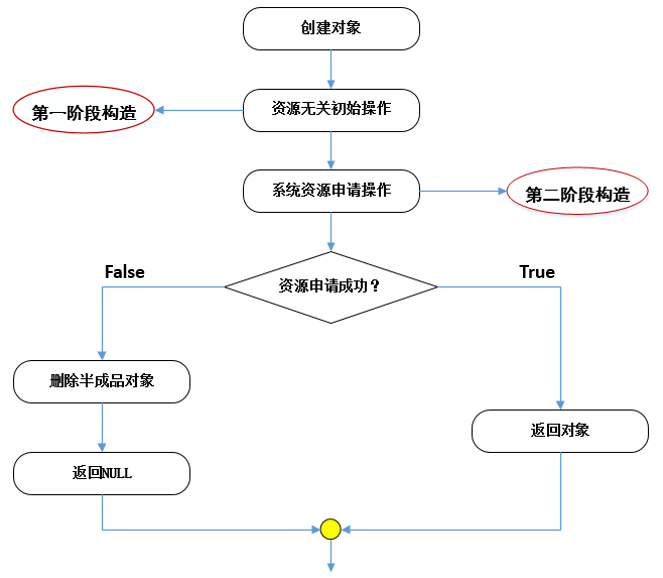
5. 二阶构造
5.1 工程开发中的构造过程
- 资源无关的初始化操作:不可能出现异常情况的操作
- 需要使用系统资源的操作:可能出现异常情况,如:内存申请、访问文件
5.2 二阶构造示例
二阶构造过程如下:



1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 class TwoPhaseCons 4 { 5 private: 6 TwoPhaseCons() // 第一阶段构造函数 7 { 8 } 9 bool construct() // 第二阶段构造函数 10 { 11 return true; 12 } 13 public: 14 static TwoPhaseCons* NewInstance(); // 对象创建函数 15 }; 16 17 TwoPhaseCons* TwoPhaseCons::NewInstance() 18 { 19 TwoPhaseCons* ret = new TwoPhaseCons(); 20 21 // 若第二阶段构造失败,返回 NULL 22 if( !(ret && ret->construct()) ) 23 { 24 delete ret; 25 ret = NULL; 26 } 27 28 return ret; 29 } 30 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 TwoPhaseCons* obj = TwoPhaseCons::NewInstance(); 35 36 printf("obj = %p\n", obj); 37 38 delete obj; 39 40 return 0; 41 }
// 数组类的加强

1 #ifndef _INTARRAY_H_ 2 #define _INTARRAY_H_ 3 4 class IntArray 5 { 6 private: 7 int m_length; 8 int* m_pointer; 9 10 //将构造函数变为私有的 11 IntArray(int len); 12 bool construct(); //第2阶构造函数 13 14 public: 15 static IntArray* NewInstance(int length);//提供创建对象的函数 16 int length(); 17 bool get(int index, int& value); 18 bool set(int index, int value); 19 ~IntArray(); 20 }; 21 22 #endif

1 #include "IntArray.h" 2 3 IntArray::IntArray(int len) 4 { 5 m_length = len; 6 } 7 8 bool IntArray::construct() 9 { 10 bool ret = true; 11 12 m_pointer = new int[m_length]; 13 14 if (m_pointer) 15 { 16 for(int i = 0; i<m_length; i++) 17 { 18 m_pointer[i] = 0; 19 } 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 ret = false; 24 } 25 26 return ret; 27 } 28 29 IntArray* IntArray::NewInstance(int length) 30 { 31 IntArray* ret = new IntArray(length); 32 33 if(!(ret && ret->construct())) 34 { 35 delete ret; 36 ret = 0; 37 } 38 39 return ret; 40 } 41 42 IntArray::~IntArray() 43 { 44 if(m_pointer) 45 { 46 delete[] m_pointer; 47 } 48 } 49 50 int IntArray::length() 51 { 52 return m_length; 53 } 54 55 bool IntArray::get(int index, int& value) 56 { 57 bool bRet = (0 <= index) && (index <m_length); 58 59 if(bRet) 60 { 61 value = m_pointer[index]; 62 } 63 64 return bRet; 65 } 66 67 bool IntArray::set(int index, int value) 68 { 69 70 bool bRet = (0 <= index) && (index <m_length); 71 72 if(bRet) 73 { 74 m_pointer[index] = value; 75 } 76 77 return bRet; 78 }

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include "IntArray.h" 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 IntArray* a = IntArray::NewInstance(5); 7 8 printf("a.length = %d\n", a->length()); 9 10 a->set(0, 1); 11 12 for(int i = 0; i< a->length(); i++) 13 { 14 int v = 0; 15 16 a->get(i, v); 17 18 printf("a[%d] = %d\n", i, v); 19 } 20 21 delete a; 22 23 return 0; 24 }
6. 小结
(1)构造函数只能决定对象的初始化状态
(2)构造函数中初始化操作的失败不影响对象的诞生
(3)初始化不完全的半成品对象是Bug的重要来源
(4)二阶构造人为的将初始化过程分为两部分
(5)二阶构造能够确保创建的对象都是完整初始化的